Is the Australian dollar set to lose its shine for a prolonged period? Australian investors are concerned that the currency will come under downward pressure due to an eroding interest rate differential between US and Australian rates.
When investing in foreign assets, Australian investors are exposed to losses when the AUD appreciates against other global currencies, and make gains when the AUD depreciates. This currency exposure, or risk, can be neutralised through hedging. However, it is common for investors to retain some unhedged foreign currency exposure, particularly for more volatile assets such as global equities. Investors typically fully hedge their currency risk on more defensive assets, such as fixed income, to prevent currency volatility dominating returns.
The temptation now is to reduce this type of currency hedging, but we urge caution as this strategy also increases portfolio risk.
Traditional interest rate differential gone
The AUD has long been a preferred ‘carry trade’ (that is, borrow in one currency and invest in another) due to the higher interest rates in Australia compared with the record low rates in other developed countries. However, the US Federal Reserve (Fed) hiked rates to a target of 1.5-1.75% in March 2018, which is the sixth increase since the near-zero levels in December 2015. The Reserve Bank of Australia meanwhile has kept rates unchanged at a record low of 1.5% since 2016.
Traditionally, investors and analysts believe that the interest rate carry trade is an important driver of AUD performance. This current negative differential is therefore raising concerns that the AUD is set for a sustained period of weakness.
The AUD/USD carry impact is a complex story
Investors generally believe that AUD rates above USD rates deliver better returns from buying AUD/USD. An analysis of the monthly AUD/USD returns, conditional on the difference between Australian and US interest rates, suggests a more complex story, as shown below.
Historical AUD/USD monthly performance statistics (Jan 1995 to Dec 2017)
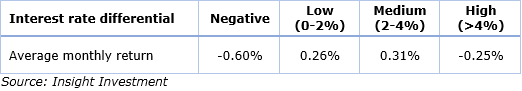
For low and medium interest rate differentials, the average historical monthly returns are 0.26% and 0.31% respectively. When there has been a negative interest rate differential, the average monthly return falls to -0.60%. Surprisingly, for high interest rate differentials the average historical monthly return is also negative at -0.25%.
A deeper dive into the statistics also reveals that as interest rate differentials have reduced historically, so has the volatility of monthly returns. In addition, under medium and high carry levels, the AUD tends to experience more large-negative moves, known as negative skew. This analysis leads to a reasonable hypothesis that the AUD/USD is a lower risk currency when carry is lower.
Correlation and diversification
If both AUD/USD returns and volatility are lower when carry is low or negative, then reducing the level of currency hedging for foreign-currency-denominated assets, in our view, could make sense in the current environment. However, it is important for investors to also consider the correlation between Australian dollar returns and the foreign assets they are hedging.
Our analysis of the data suggests investors need to proceed with caution.
The underlying assumption is that the unhedged currency exposure will provide a diversification effect at the total portfolio level. For this diversification effect to be present, there needs to be a high positive correlation between the returns on the Australian dollar and global equities.
By way of illustration, when equity markets have suffered periods of negative returns, these have tended to coincide with a weaker AUD. For example, the AUD/USD spot rate fell 19.7% in 2008, while the S&P 500 Index also lost 38.5%. If the investor was unhedged in terms of currency exposure, the S&P 500 Index loss in AUD terms was much lower, at 18.8%. In this case, the weaker AUD has added value to the portfolio, partly offsetting the losses suffered on foreign equity investments. Investors were better off unhedged.
This relationship depends on the correlation between the investor’s domestic currency and equity market performance. The chart below shows the rolling 12-month correlation between the monthly returns on the AUD and the MSCI World Equity Index in local currency terms. While the correlation is generally positive, it is not stable and was negative for most of 2017.
12-month rolling correlation between the Global Equities and AUD/USD exchange rate
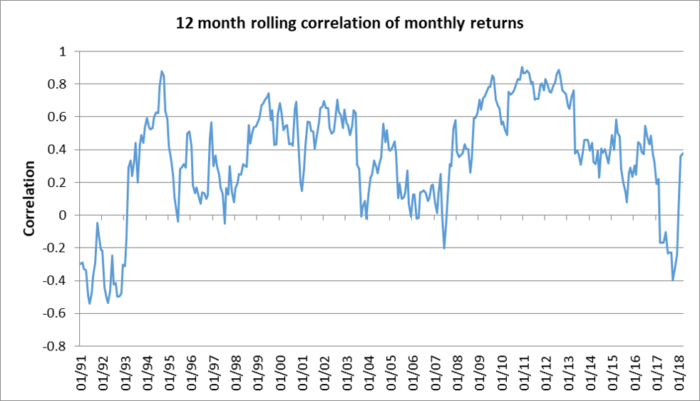
Source: Bloomberg and Insight Investment as at 30 March 2018. *Global Equities = MSCI World Local Currency Index.
As interest rate differentials increase, the correlation between the performance of AUD/USD and global equities has also increased. By contrast, with low interest rate differentials correlation falls, while at negative levels, the correlation is close to zero. Investors may need to reassess their assumptions regarding correlation and the diversification effect in the current environment.
Conclusion on the merits of hedging
We believe, based on the above analysis, that low or negative interest rate differentials have two key implications for AUD investors with global equity exposures:
- The impact of carry on the AUD’s performance is more complex than analysts suggest. Our study shows that the AUD is a more risky currency during periods of high carry. As carry levels fall, monthly returns also fall and the temptation for investors is to lower their currency hedging.
- If the objective of lowering hedges is to improve returns on foreign equities, we suggest investors proceed with caution. Lower correlation could mean the worst-case scenario occurs where the AUD appreciates when global equity prices are falling. In this case, the investor will face losses both on the underlying assets and their currency translation.
Adam Kibble is a Product Specialist at Insight Investment. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.