Talk to most investment professionals about their investing style, and they will speak about macroeconomics, interest rates and sector valuations as their primary drivers of decision making. But will this really create investment performance and returns? We believe the macro picture is not the secret to success.
Rather, it is the ability to benefit from structural changes that underpin the earnings growth of companies. It is these companies that will deliver the strongest returns over the long term, regardless of the economic backdrop or point in the cycle.
Market evolution and the few companies that do really well
The key is to recognise what the stock market really is. It is a market of companies, and it is continually changing and evolving. For instance, oil and gas used to be the biggest sectors in the S&P 500 index but today it is technology. General Electric Company (GE) was once the biggest company in the world, but it is now at risk of falling out of the S&P 500, while Amazon – which did not exist 25 years ago – has taken its place, with a market cap of over $800 billion.
It is only a handful of companies that truly create and deliver wealth for investors over the long term. A study in the Journal of Financial Economics by Hendrick Bessembinder (Do Stocks Outperform Treasury Bills, updated 2018) looked at every company that has listed in the US over the past 90 years, and what happened if an investor bought and held every stock.
He found that most companies out of 14,000 in total destroyed value versus Treasury bills, with the vast majority going to zero. A further 8,000 companies made enough to offset what the other 14,000 had lost. And 1,100 companies or only 5% of the total delivered all the return in the US market (above Treasury bills). Of these 1,100, there were actually 50 companies that made up 40% of the entire wealth created in the US stockmarket over that 90-year period.
The trick for investors, therefore, is to identify these 50 companies early on, and buy and hold them.
Sounds simple? Of course, it isn’t.
The S-curve helps identify the wealth creators
This is where the idea of the S-curve comes in. In business terms, the S-curve tracks how a company or industry grows over its lifecycle. There comes a point in the lifecycle when growth inflects, driven by a structural change. It is the tailwind created by the structural change that allows a company to deliver and create wealth.
We argue that the S-curve always beats the macro when it comes to investing.
Companies like Facebook, Amazon and Apple have ridden the wave of demand for technology products and services that did not exist 15 or 20 years ago, but which are now considered indispensable in our daily lives. As investors, we seek to identify the next round of structural changes, and then invest in the companies that will benefit from them, at the start of the S-curve and not at the end.
Apple is a good example here. From 2008 to 2017, while the growth in the overall mobile handset market was relatively flat, smartphone penetration went from less than 10% to roughly 70% over the same period. In 2008, there were 10 mobile phone stocks to choose from but only two really worked out – Apple and Samsung. Once household names like Blackberry, Motorola, Eriksson and Nokia failed to seize the structural growth opportunity in smartphones.
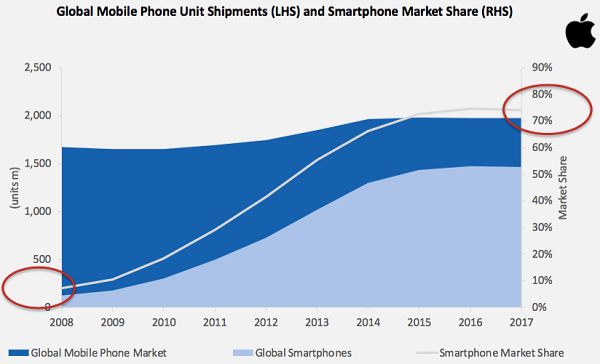
Source: Bloomberg. Click to enlarge.
The smartphone market has now stopped growing and Apple is relying on price hikes and its services revenue for growth. The smartphone industry is now at the end of its S-curve.
Video Streaming and Netflix, on the other hand, is still growing. Yes, Netflix’s earnings multiples are high, and it is not yet making material profits, but what’s important is how much earnings it makes 10 years from now, not what it makes in 2019 or 2020. And on this basis, Netflix is poised for immense growth. It is currently in just 10% of broadband homes around the world, and its monthly pricing is low relative to the value of content it offers, so its potential for earnings growth is huge. Video Streaming is still toward the beginning of its S-curve.
Successful company characteristics
Once we identify industries at the beginning of their S-curve, we then need to find the companies that can fully benefit from the structural change. To do this, we consider five company characteristics that we believe are essential for success:
- Potential for growth: exhibit faster earnings, EBITDA or revenue growth versus peers and growing Total Addressable Market (TAM).
- Economic leverage: exhibit pricing power or economic leverage to improve margins.
- Sustainability: exhibit ability to sustain growth due to scale, position, intellectual property or locational advantages.
- Control: exhibit strong management ownership and incentives.
- Customer perception: Exhibit strong customer reviews and rapid adoption.
Companies that display all these characteristics are best placed to capitalise on their structural tailwind. Examples we would highlight today would be Amazon in eCommerce, Danaher in Innovative Health and ServiceNow in Digital Enterprise.
Nick Griffin is a Founding Partner and Chief Investment Officer of Munro Partners. This article is for information purposes only and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.