It has been an extraordinarily good period for retirees in recent years, with the stock market recording one of the longest bull markets in history. But bull markets typically end with a bear market, and while no-one knows for sure when that may occur, retirees should be preparing for a change in sentiment.
October 2018 was a bruising month for equity markets, and we think volatile markets are here to stay. While all investors understand that market volatility can affect the value of their retirement savings, many do not realise there is another type of risk lurking in the shadows that could be of greater concern for those nearing retirement. It is called sequencing risk.
The sequence, or order in which your investment returns occur, can have a dramatic impact on the health of your retirement savings. Retirees therefore need to look at strategies that can help them during this vulnerable period.
What is sequencing risk?
A portfolio is exposed to sequencing risk if there are contributions coming into a portfolio, or if withdrawals are coming out of the portfolio to fund retirement. A portfolio with no contributions or withdrawals has no sequencing risk because with multiplication, changing the order of numbers has no impact on the result.
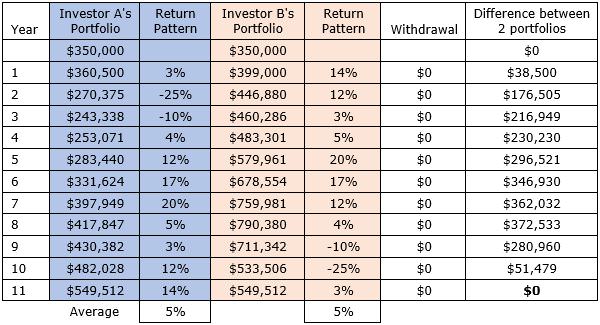
The example below shows two investors, A and B, who both start out with an investment of $350,000. Both investors achieve an average rate of return of 5% per annum over the 11-year period.
Investor A’s portfolio experiences negative returns in the early years of his retirement. Investor B’s portfolio experiences the negative returns later on, exactly reversing the annual timing of the same returns. As neither investor is making withdrawals from their portfolio, at the end of the final year both investors have an identical balance of $549,512.
No sequencing risk
This example is for illustrative purposes only.
A tale of two investors
The concept of sequencing risk could kick in during that phase when an investor moves from the accumulation stage (saving for retirement) to the decumulation stage (living off retirement savings).
Negative investment returns early in retirement can be problematic for retirees. If an investor experiences a higher proportion of negative returns in the early years of their retirement, it will have a long-lasting negative effect on their retirement savings. This will reduce the amount of income they can withdraw over their retirement years.
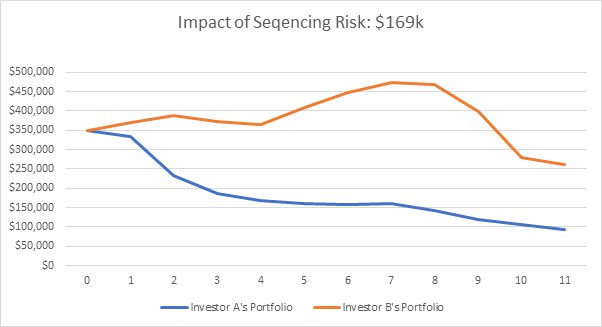
Here we apply the same example above, but this time, Investor A and Investor B are withdrawing $25,000 per year to fund their retirement. They both have identical starting super balances of $350,000. They both have an average return of 5% p.a. over the 11-year period. However, in this case, Investor A’s retirement balance is $169,475 lower than Investor B’s retirement balance. This is the impact of sequencing risk.
The impact of sequencing risk
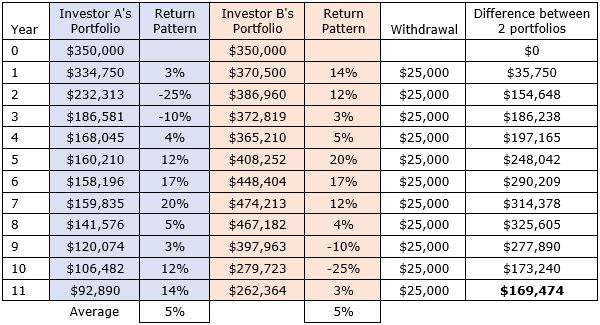
The impact of sequencing risk
This example is for illustrative purposes only.
While Investor B’s portfolio balance grows in the early years of her retirement, for Investor A, negative returns just after retirement have a devastating effect. This is because he is withdrawing funds as his portfolio is losing value and is therefore holding fewer shares that could benefit from positive returns down the track.
How to reduce sequencing risk when it matters most
The timing of share market falls can dramatically impact the length of time a retiree's capital will last. The good news is that there are ways to structure an SMSF or retirees’ assets to manage the risk. These include diversification into uncorrelated asset classes and holding cash to reduce withdrawals from an equity allocation during heavy market falls.
Another strategy is to set aside a portion of retirement savings in an investment that is not as impacted by market or index returns, such as a defensive equity solution. It may reduce vulnerability to an early retirement stock market decline that causes the most harm to retirees. However, if a retiree is at a point where their retirement savings meet their needs and objectives, they should consider dialing down the risk of their investments.
Investors who are exposed to sequencing risk in early retirement may need to work longer or reduce their living standards, so having an effective plan to manage this risk is essential.
Aaron Binsted is a Portfolio Manager at Lazard Asset Management. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.