There are few free lunches in investing, so any reward from reducing a tax burden is worth the effort. Financial advisers are increasingly presenting a more tax-effective investment solution to clients as part of their value proposition. The challenge is making sure everyone understands the opportunity.
In this article, we examine how tax optimisation can work using Separately Managed Accounts (SMAs).
1. Avoid tax inheritance
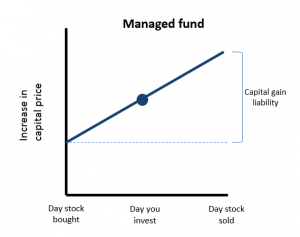
Investors should avoid the inheritance of a capital gains liability. The chart above shows a hypothetical increase in a managed fund’s unit price over a period that begins when a fund manager buys a stock into that fund, and when it sells that same stock. In the middle of that period, the investor buys units in that fund. The price of that unit has inflated since the stock was originally bought, because it includes the accrued capital gain.
The investor has no choice but to buy into that gain if they want to invest in the fund, even though they were not invested during that initial period. Investors have inherited a capital gain liability. Of course, for the sake of simplicity we have made very simple assumptions, but the concept remains.
For completeness, it should also be noted the opposite is true. If a fund is carrying a capital loss, then the investor can inherit those losses and potentially reduce taxable income, although that is not typically the objective of investing.
The following chart shows what happens with an SMA.
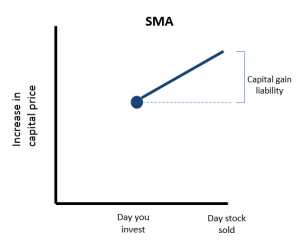
With an SMA, the investor has beneficial ownership of the shares in a portfolio, and that makes all the difference in terms of the tax burden for an individual investor.
If we assume an investment on the same day through the period as in the previous example, the capital gain begins from the day of investment, and not the start of the period. The managed account structure means investors are buying shares in their own name, rather than units in a fund carrying capital gains. They will avoid inheriting a capital gains liability. All other things equal, the tax burden should be lower.
2. In specie transfers
Another way to optimise tax is to transfer stock holdings into the SMA via an in specie transfer, which saves selling down assets and avoids a capital gains liability even before the new investing takes place.
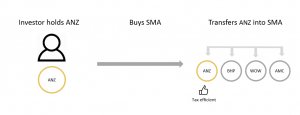
In the example above, an investor holding ANZ moves their investment into an SMA which also holds ANZ alongside other stocks. The key point here is through a transfer, the amount of selling is minimised through the transition into the SMA.
The opposite also works. An investor moving out of an SMA may decide to keep ANZ and sell out of the rest. That may reduce the tax burden on the way out.
Logistically, the ‘in specie’ stock transfer is typically nominated during the platform application process. The adviser (on behalf of the client) will nominate where in specie transfers apply, saving the investor any avoidable capital gains.
And by avoiding the trade, the investor also saves on brokerage costs.
This is the advantage of having beneficial ownership of shares. The same outcome is generally not possible with managed funds.
3. Manage individual holdings
As a beneficial owner of stocks, SMAs also allow investors to manage their holdings in a way that optimises their personal tax position. An investor can elect to hold or sell parcels of stock depending on their overall tax position. For example, a gain on one parcel may be used to offset a loss on another, and so on. This technique of splicing individual parcels is generally not available in a managed fund arrangement.
Managed funds have their benefits too
While the examples above highlight some examples of tax advantages of SMA over a managed fund, there are still plenty of reasons a managed fund arrangement may be suitable for other investors.
For example, there are more investment options available in the managed fund space, especially if the investor has a specific portfolio need such as in an illiquid investment or a low-risk equity income strategy. Many of these are not offered in an SMA.
Andrew Stanley is Head of Australian Equities at Ralton Asset Management. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor, and SMAs are usually available only through a financial adviser.