Indexing has become an undeniable force in the investment world. Consider that US$1.4 trillion in net new cash and reinvested dividends flowed into US equity index funds and ETFs in the decade through year-end 2016, which is astonishing compared with the US$1.1 trillion in net outflows from active funds in the same period.
Indexing’s rise did not happen by accident. At Vanguard, the improvement in index fund management included refining index sampling techniques, better approximating the fundamental characteristics of benchmarks, working closely with benchmark providers and strengthening index methodologies.
But the push to improve indexing does not stop there. In my new role as Vanguard’s Chief Investment Officer, my global team and I are dedicated to staying abreast of new themes in the investment world, especially exploring the details of what makes indexing tick. Our mission is to optimise the investment outcomes for our clients and investors overall at a low cost.
I am a firm believer in the value indexing delivers to both the investor and the market as a whole. But over the last few months, indexing has received criticism from a few commentators alleging indexing hurts price discovery, stifles competition via common ownership, and leads to higher volatility. I believe those claims are inherently false, so let’s walk through these arguments and set the record straight.
1. Does indexing hurt price discovery?
The concern about indexing hurting price discovery is naive. Price discovery is driven by active managers, Vanguard included. I know from my years as a bond guy the vital role that active managers play in keeping security prices aligned with their value. The thought that indexing could somehow get in the way of that is troubling for me. But the truth is that even though indexing has grown in popularity, it’s still a small part of overall trading volumes (i.e. portfolio managers’ trading of index funds’ underlying securities). Since indexing represents about 5% or less of US equity daily volumes, as shown in the chart below, there is still considerable price discovery and liquidity provided by active managers.
Breakdown of overall individual stocks’ trading volume
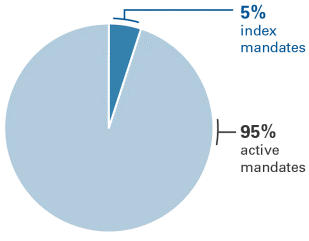
Sources: Vanguard and Bloomberg, 2017.
2. Does indexing cause a lack of competition?
Critics claim that managers of corporations whose stocks are in some of the leading indexes become complacent participants, rather than competitors, because stock prices are propped up by the steady drumbeat of index investments. There is no evidence to support these anticompetitive practices or that there is a cause-and-effect relationship between common ownership and product price competition. All the corporate executives that I know are diehard competitors and are doing everything in their power to expand market share, increase revenues, and boost profits.
In addition, as owners of just about every company in every industry, index funds have no incentive to favour one industry over another as higher product prices in any one industry would cut against fund investors’ interests in other sectors.
We believe fierce industry competition produces greater shareholder return and a healthier industry as a whole, since competition forces companies to constantly innovate and find new ways to deliver value to both consumers and shareholders. We firmly believe the best performers should be rewarded, which is why we advocate for executive compensation plans to be tied to performance, not stock price, and have explicitly promoted competition among firms in their respective peer groups.
3. Does indexing drive volatility?
I do not see any substance to the concern that equity index funds contribute to market volatility. Regardless of size, indexing is not a monolithic investment strategy. Index investments are spread through many market caps and investment styles, and the majority of index assets are held by long-term investors in broad-based, market-cap-weighted funds. There is no convincing evidence that the growth of index funds has had an impact on market volatility or the dispersion of stock returns. Even as index funds’ share of mutual fund assets has consistently grown, market standard deviation has risen and fallen in a seemingly random pattern. Dispersion among the stock market’s securities has remained somewhat constant, except for the tech bubble and the global financial crisis.
The real truth: indexing has earned its accolades
Indexing has transformed the investment experience for millions of investors. We take pride in the fact that we have helped investors enjoy the many benefits of indexing, including:
- Low cost
- Broad diversification
- Relative predictability
- The potential for long-term outperformance compared with the performance of many high-cost active fund managers.
Indexing offers a firm foundation for investors seeking to achieve their investment goals, and as Vanguard’s CIO, it’s my job to make sure that indexing and active management continue their symbiotic relationship in the investment landscape.
Greg Davis is the Vanguard Group’s Global Chief Investment Officer. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.