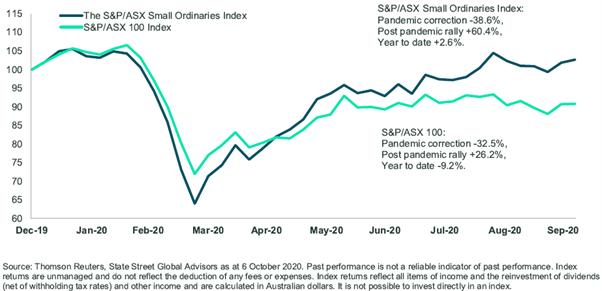
Small capitalised companies have had a great run since the market bottomed in late March. The S&P/ASX Small Ordinaries Index is up 60% since 24 March 2020, but by contrast, the larger capitalised companies as represented by the S&P/ASX100 index are only up 26.2% (as at 6 October 2020).
The significant outperformance of smaller companies has ignited renewed interest in this sector of the market. Figure 1 shows the two indexes since December 2019.
Figure 1. A wild ride in equities and even wilder ride in smaller companies
Greater returns but with more volatility
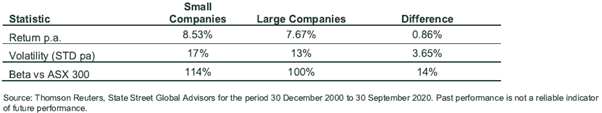
Over the last 20 years, smaller companies have outperformed larger companies by almost 0.86% per annum but this outperformance has not been without risk. On average, the volatility associated with small companies is 17% compared to larger companies with 13%.
This is also evident in the beta (a measure of volatility in terms of the overall market, which has a beta of 1 or 100%) of the small company index averaging 114%, as shown below.
Figure 2. Longer term return and risk characteristics from Australian small and large companies
Smaller companies have had a great run in the last six months but a look at the long term puts that outperformance into some context.
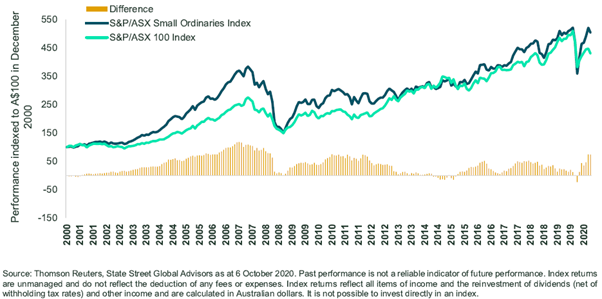
Figure 3 illustrates the journey for the last 20 years. Smaller companies have had periods of significant outperformance, which are historically followed by periods of underperformance. Depending on when you invest, your experience could be quite varied.
Figure 3. Periods of outperformance have historically been followed by periods of underperformance
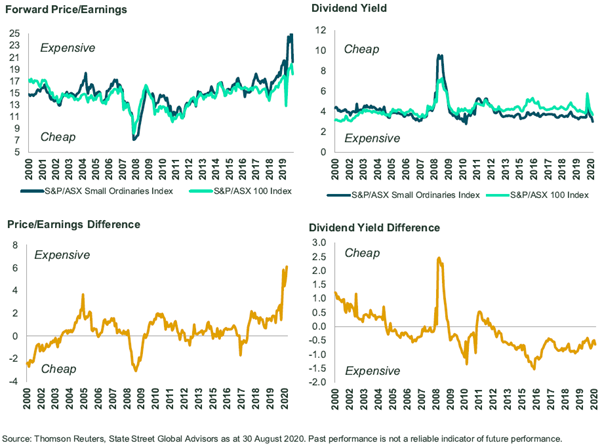
Valuations are rich in absolute and relative terms
On average, over a longer period of time, we find the smaller capitalised companies tend to trade at a slightly higher price to earnings (P/E) multiple and generate slightly lower yields. But this tends to be volatile, as during risk-on periods they can trade at much higher multiples, whereas during risk-off periods, they can trade at below average multiples.
It is entirely possible that the economy will recover and many company earnings will return to pre-pandemic levels, but if they don't, then the small company sector of the market is more at risk of disappointment. From a relative yield perspective, the smaller companies are not as expensive as is implied by earnings multiples.
Figure 4. Smaller company valuations
Watch out for overly optimistic earnings
For smaller companies compared with larger companies, the investment community is usually overly optimistic on earnings. In the last 20 years expected growth for the next 12 months has averaged +21.1% and yet on average this group of companies has only delivered +13.2%. By contrast, the expected growth for larger companies is expected to be lower at only +9.4% and has only delivered +6.8%. It's a much smaller earnings disappointment compared to smaller companies. In both cases, analysts’ expectations have been overly optimistic but in the case of smaller companies, this optimism is exaggerated.
As investment managers that focus on quality, value, improving outlook and lower volatility, we tend to invest in less volatile companies that have not been priced for excessive growth. That does not mean we will not invest in smaller companies if they are expected to provide the right mix of return for risk.
Indeed, as Figure 5 below highlights, we currently own many companies outside the top 50 but within the top 200, but our active weight in these companies changes.
Figure 5. State Street Australian Equity Fund – Active weight to different sized companies since inception^
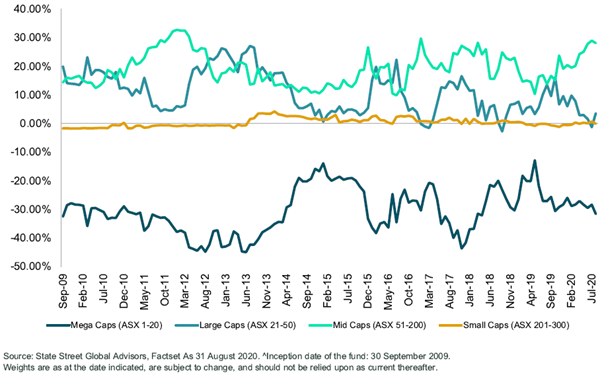
Currently, valuations are stretched for the market and are especially stretched to the smaller end of the index. Most of this has happened in the last six months as investors have been willing to price a strong recovery in earnings.
Bruce Apted is the Head of Portfolio Management – Australia Active Quantitative Equities, at State Street Global Advisors. This general information has been prepared without taking into account your individual objectives, financial situation or needs and you should consider whether it is appropriate for you.