Cash returns from 'traditional' cash investments such as cash management trusts and term deposits are extremely low with little prospect of climbing higher soon. Investors are reluctantly leaving funds in equities or property markets, but alternatives exist in the professional or 'wholesale' securities market where investors can improve their returns.
The wholesale debt market alternative
The wholesale market gives investors access to a multitude of securities, allowing tailoring of portfolios to enhance cash returns. However, investors must satisfy a minimum $2.5 million net asset test and/or minimum $250,000 annual income test, and there is a minimum transaction size of $500,000. This high barrier for retail investors can be overcome by accessing this market via ‘cash funds’ and ‘cash enhanced funds’ which have a much lower minimum investment and often also offer quick redemptions.
It is important that investors review how each fund operates and what each fund means by ‘cash’ as this can vary widely. Investors should pay attention to the liquidity and credit characteristics of the fund’s portfolio as poor liquidity or creditworthiness can compromise redemption requests. Some cash funds offer franking credits which may further enhance returns.
The wholesale market, at approximately $2 trillion, is larger than the market capitalisation of the ASX ($1.6 trillion) and has existed for decades. It is where most bonds and capital instruments are issued (primary market) and bought and sold (secondary market).
The table below outlines securities available in the wholesale market:
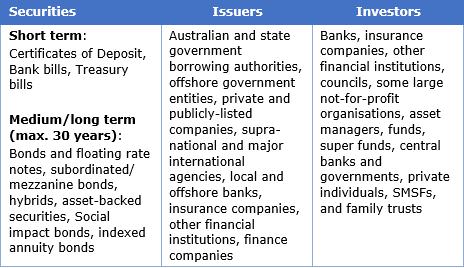
Securities are typically rated by Standard & Poor’s, although unrated bonds are increasing.
A comparison with bank retail products
The table below shows the returns offered on securities issued by a major bank in the wholesale market against the traditional term deposits offered by the same bank on the same day.
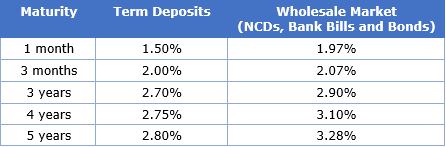
Sources: Bank website, Thomson Reuters, Broker rate sheets, Prime Value sources as at 5 June 2018
The predominant risk on wholesale securities is ‘counterparty’ risk, meaning the risk the issuer will not meet its obligations to pay coupons and then principal at maturity. The holder of a term deposit also has this risk, however, the Australian Government guarantees deposit accounts up to $250,000 per entity (or individual) per ADI (bank). An investor can place multiple such deposits with different ADIs. Hence, a strict comparison of rates between deposit accounts may require an adjustment for the guarantee, given the Australian Government’s credit rating (AAA/Aaa) is higher than any bank (the major four banks have a rating of AA-/Aa3).
Wholesale securities are traded instruments hence their price varies with interest rates and credit risk although eventually converging to par at maturity. With term deposits, being non-traded, their redemption value does not vary directly with the market but if the money is required before maturity, the redemption proceeds will depend on the bank’s policy. Generally, there will be penalties for early withdrawal possibly including the foregoing of interest, and redemption proceeds may vary with how rates have moved since the deposit commenced.
Enhanced cash yields
There are several ways cash yields can be enhanced in the wholesale market:
- Security selection: investors can add 0.10%-0.40% to NCD rates via Floating Rate Notes (FRNs) or bonds that may be coming into maturity.
- Credit risk: 0.10%-0.30% can be added by investing in the NCDs of a non-major bank or ADI.
- Tenor: Extending maturity will add yield, but instruments beyond a 12-month tenor are not considered ‘cash products'.
Other strategies to enhance cash yield and reduce portfolio risk are listed below, but they each involve additional risk:
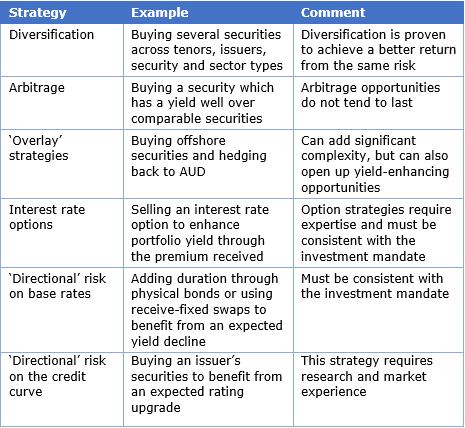
Investor decisions
Security selection must take into account many factors, such as:
- Credit risk
- Term
- Ranking (senior unsecured, senior secured, subordinated, etc.)
- Issuer type (local, offshore, company, government entity, etc.)
- Security type (bond, certificate of deposit, bank bill, hybrid, etc.)
- Fixed or floating rate
- Franking credits
- Liquidity risk (can the security be readily sold and what bid/offer spreads apply)
- Inflation protection
Investors must also choose between trying for a ‘real’ (inflation protected) return or a ‘nominal’ return. Investors can map their ‘risk/return paradigm’, i.e. how much return above the ‘risk-free’ return is desired and what risks the investor is willing to bear to achieve this return. They must consider risk/return ‘tradeoffs’, such as:
- earning a higher return for taking term (maturity) risk
- earning a higher return for holding subordinated risk
- earning a lower return as the cash is needed in the near future
- earning a higher return even though liquidity in the security is poor.
Finally, the investor must set out any other strategies they are prepared to employ to add yield, such as using options. The kaleidoscope of securities available in the wholesale market allows investors to tailor their portfolio to their desired risk/return paradigm. Bank deposits are limited in this regard.
Hybrids and franking
Franking benefits can significantly enhance cash yields but can only be accessed on dividend-paying securities, such as shares or hybrids, which are riskier and rank lower in the capital structure of the issuer. Shares and hybrids are not ‘cash products’, they are ‘yield products’.
Retail investors using managed funds
Retail investors will struggle to access these opportunities directly as they are often available only to large institutions and funds, but the benefits can be accessed through a range of managed funds in various structures available to most investors.
Matthew Lemke is the Fund Manager of the Prime Value Cash Plus Fund, an enhanced cash fund which was established in 2014. See www.primevalue.com.au. This article is meant for educational purposes and is not a substitute for tailored financial advice.