Attractive tax benefits and a hassle-free giving experience means more people are donating their money into philanthropic sub-funds – and they are giving a lot, especially as the end of another financial year approaches.
New research released by Swinburne University shows that sub-funds in public foundations are the 'growing force' in Australian philanthropy with assets held in sub-funds totalling over $1 billion. More than $123 million of donations flowed into these structures last financial year. In fact, there are now more sub-funds in public structures (Public Ancillary Funds or PuAF) than Private Ancillary Funds (PAFs) in Australia, demonstrating that while PAFs and big philanthropy may be more publicised, the accessible and convenient sub-fund is more popular.
How does a public sub-fund work?
A sub-fund is a giving account or fund within a larger public charitable foundation (a PuAF). It is established by making a tax-deductible donation which is set aside into your own named sub-fund. Each year at least 4% of your sub-fund balance is given to charities recommended by you. While you think about who to recommend, the balance is invested and your charitable money is put to work. Returns are tax-free, so good investment management can see the balance grow, increasing the amount you can recommend to charity over time.
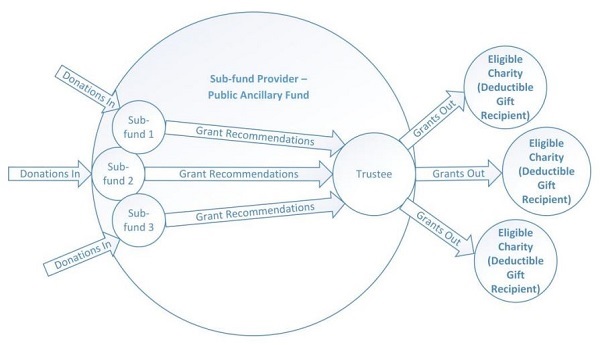
Australian philanthropy; public ancillary fund
Source: Centre for Social Impact, Swinburne University of Technology
Attraction of immediate tax-deductability
Structuring giving in this way is an especially attractive strategy for donors who need a tax deduction now, and the flexibility to distribute the funds to charity over time. For example, pre-retirees in a higher tax bracket than might be expected in the future can bring forward multiple years of charitable giving and make a lump sum contribution to a sub-fund. It gives the donor the tax deduction needed while they are still earning assessable income but allows them to continue a regular flow of charitable giving throughout retirement.
Similarly, a sub-fund alleviates the pressure of a donor having to ‘panic choose’ a charity to support in the final days of the financial year. They can receive both the tax deduction and the liberty of time to take a breath and consider who they want to support. At the same time, the balance is being invested for growth.
The data reflects the experience of sub-fund service providers like Australian Philanthropic Services (APS). When Chris Cuffe AO founded APS as a not-for-profit organisation with the aim of helping people more easily give their money to charity, the focus was initially on a private ancillary fund (PAF) service. The organisation’s offerings quickly broadened to include a PuAF, allowing people to establish a giving account within the APS Foundation.
What was initially a complementary offering for donors who did not want the administrative responsibility of a PAF, or who required a lower entry point to structured giving, has now become Australia’s fastest growing PuAF. The establishment of sub-funds at APS now outstrips PAFs by three to one.
The growing popularity of sub-funds can largely be attributed to their accessibility and simplicity. They can be established painlessly in one day and with entry points from $20,000. You don’t need to be a multi-millionaire to take advantage of the benefits of structured giving.
PAFs remain a good option for donors with at least $1 million to contribute. However, they come with greater administrative responsibility which might not suit donors who don’t want to be concerned with board meetings or managing the investment of the PAF’s assets. A sub-fund allows donors to focus solely on the giving.
A personal experience
Mark Lazberger, former Chief Executive of Colonial First State Global Asset Management, and his wife Anne decided several years ago to go down the sub-fund route.
“Choosing a sub-fund instead of a PAF was initially the best option for us because of its flexibility and there were some scale benefits that it offers.”
The ability to transfer the balance of a sub-fund to a PAF (and vice versa) is a plus for donors who might want to change giving structures in future. For Mark, the investment credentials and acumen behind the public foundation were extremely important. A since-inception return of 11.5% per annum has increased the amount that Mark and Anne can recommend to charities. The fund is bolstered by the support of a number of specialist fund managers who deliver an investment and social return by providing their services pro bono. Instead of the fund manager receiving a management fee, it is rebated to the APS Foundation to be distributed to charities recommended by giving fund holders like Mark.
“If we hadn’t had confidence in Chris Cuffe’s investment acumen and how the APS Foundation goes about making its investment decisions, we would have had to take a different path.”
The role of philanthropy in wealth transfer
As Australia approaches the largest intergenerational wealth transfer in history, baby boomers are looking to philanthropy as a way to nurture relationships through the generations, and to allow children and grandchildren who have been brought up in privilege to see a different view of the world.
For Deborah and Miles Protter, structured philanthropy was a way for them to have conversations with their daughter about their family’s values.
“Having the sub-fund has helped us to cement our long-term commitment to the Hunger Project and provides us with a way to give direction to our giving as a family. Our daughter, now 22, has always valued what we’re doing with the Hunger Project, but never felt part of it. Having this vehicle provided us with a way to have that conversation and talk about what’s important to us as a family.”
The sub-fund market in Australia is yet to realise the boom experienced in the US with their equivalent, the Donor Advised Fund. Assets held in Donor Advised Funds are one hundred times the value of assets held in Australian sub-funds, surpassing US$100 billion in 2017. The requirement in Australia that at least 4% of a sub-fund balance be distributed to charity each year provides comfort to donors in this country who take seriously their philanthropic responsibilities. Last year, $57 million was granted by sub-funds to charities, well above the minimum amount required by law.
Many sub-fund providers, like the APS Foundation, are primed to support the growing number of philanthropists by doing away with chequebook charity and moving towards a more structured way of giving. The ease with which donors can use sub-funds to give and grow money for charity, coupled with appealing tax benefits, means their growing role in Australian philanthropy will continue unabated.
Rachael Rofe is the manager of the APS Foundation, a Public Ancillary Fund offered by Australian Philanthropic Services. The research released March 2019, ‘Snapshot of Sub-funds in Australia’, was undertaken by Krystian Seibert of Swinburne University’s Centre for Social Impact.