It’s understandable if investors are a bit shell-shocked.
Central banks around the world are hiking rates in an attempt to slow spending and lower stubbornly persistent inflation. The turmoil's impact on asset valuations has been stomach churning for investors. Nothing has been spared – from equity markets, bonds, property, FX, to crypto.
Investors are probably wondering when the turbulence will end.
Some perspective may provide solace
Given that, we take a step back and look at five key charts that help provide some perspective and context on the current environment for investors.
The good news is the charts provide some hope that we could be reaching some form of an inflection point in the outlook for the economy (particularly surging inflation) and for listed company valuations.
1. Inflation growth may start to moderate from October 2022
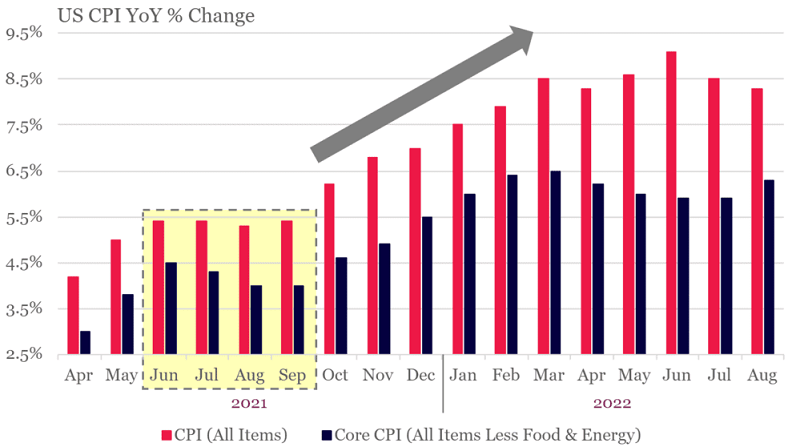
Source: Bloomberg, Montaka Global
As mentioned, the root cause of the current market dislocation is the relentless march toward higher inflation.
When might we see inflation moderate and a subsequent ‘pause’ by central banks in their aggressive interest rate increases? Interestingly, this moment may be mere months away.
If we look at the Consumer Price Index (CPI) this time last year in the chart above, we see a relatively flat path of inflation through September, then a sharp acceleration in the following months starting October.
Since inflation is typically viewed as the rate of change over a 12-month period, this substantial uptick starting in October 2021 means that the year-on-year growth of inflation in October 2022 is going to become increasingly challenged.
Said another way, this simple mathematical reality may lead to a more benign CPI print when the October number is reported on November 10, and potentially for several months subsequently.
This date is certainly worth marking in the calendar. It may be a turning point in how aggressive central banks, particularly the US Federal Reserve, will be in raising interest rates and could pave a path to more rational price discovery in markets.
2. US mortgage rates have more than doubled in 2022
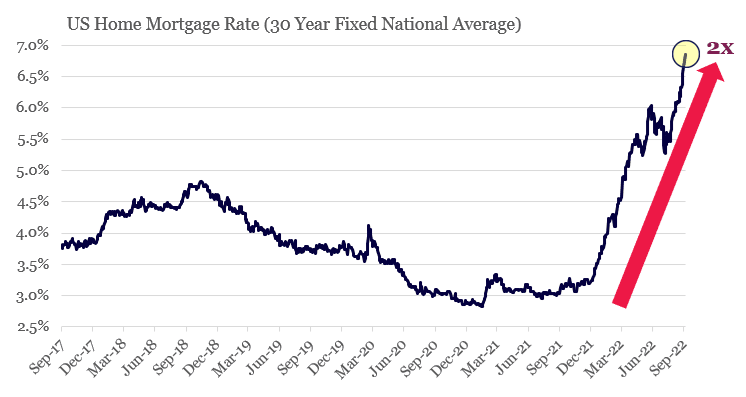
Source: Bankrate.com, Montaka Global
The strength of the consumer is often sighted as a key driver of inflation. Indeed, despite sharp interest rate hikes by central banks, they don’t seem to be putting a dent in consumers’ voracious spending habits.
However, laying beneath the surface of a ‘strong consumer’, is the potential for sharp belt tightening around household budgets. This year alone, mortgage costs have doubled, which means a family that was considering a $500,000 home last year, can only afford a $250,000 home today.
On average, mortgage payments – usually the largest single expense for a family – are around 30% of household income. If a family was required to refinance their home today, it would cost them double what it would have cost just 12 months ago. A family that was previously paying 30% of their household income towards their mortgage could see it rise to as much as 60% as mortgage rates have doubled. A family making $100,000 per year would see their post-mortgage cash flow drop from $70,000 to $40,000.
They very likely will cut back on discretionary expenditures, like travel, holidays eating out; and potentially also cut back on some non-discretionary items, like doctors’ visits and school fees. All of this is highly contractionary and would cause inflation to fall as consumers lower the amount of spending in the economy.
3. Cost of funds for the US Government has tripled in 2022
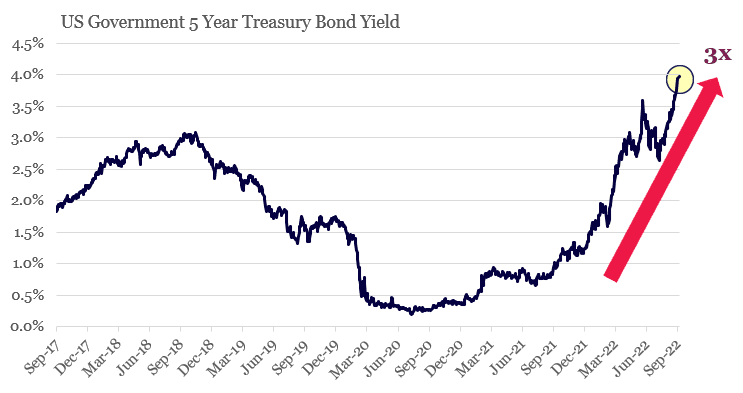
Source: Bloomberg, Montaka Global
Obviously not every household is going to have the misfortune of being in the situation described above, at least not in the immediate term.
However, one of the largest agents in the economy, the US government, is not so fortunate. Over the coming 12 months, the US government will need to refinance US$4 trillion of its US$31 trillion outstanding debt. That will result in an incremental increase in interest expense each year of around US$150 billion above what was budgeted for last year.
Over time, the entire US debt would need to be refinanced at higher interest rates which would present the US economy with a crippling US$1 trillion incremental annual headwind if rates remain where they are today.
These funds may come out of public services, infrastructure spending, schools, social programs or increased taxation. All of which would send a major deflationary force through the economy, offsetting inflation, but likely resulting in a recession as well.
4. Earnings streams temporarily depressed
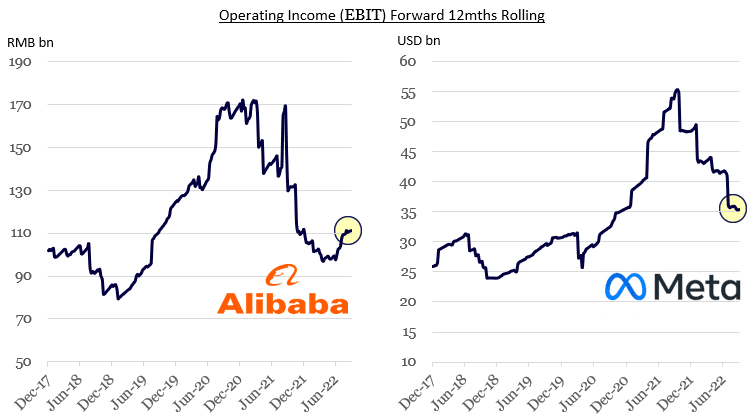
Source: Bloomberg, Montaka Global
Some of the most exceptional companies in the world are experiencing cyclical headwinds tied to macroeconomic conditions and changing business environments. They may also be embarking on major investment cycles that are depressing earnings.
These factors are expected to be temporary.
Examples include Alibaba, which is affected by the hard COVID lock-down policies in China, and Meta, which is investing heavily in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and navigating an evolving digital advertising landscape (Apple’s iOS changes).
It seems the market has dismissed the new opportunities these companies are building for the future. What are headwinds today will become tailwinds tomorrow. The price for substantial incremental cash flow generation has actually never been cheaper.
5. Depressed earnings attracting depressed multiples
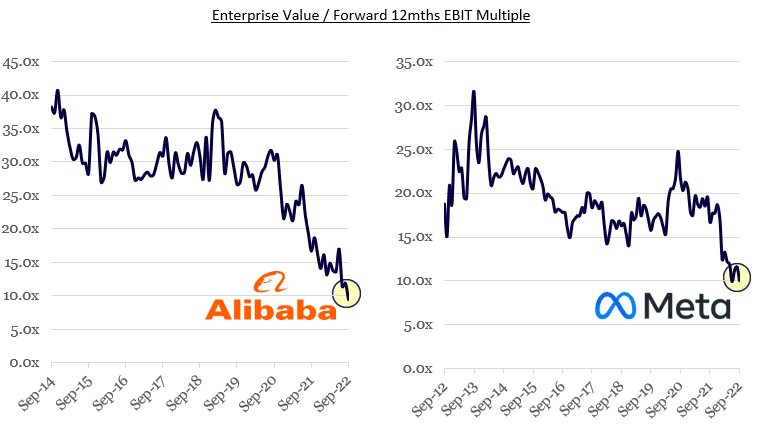
Source: Bloomberg, Montaka Global
Higher interest rates have compressed valuation multiples. But in the case of both Alibaba and Meta, the current environment is creating an outsized impact on them. Their valuation multiples are at post-IPO lows for both companies and imply the market believes the temporary depression in earnings is a permanent situation.
This has created a double whammy for these wonderful businesses: they are being priced on a depressed valuation multiple and depressed earnings expectations.
As multiples normalize and earnings decompress, valuations will likely hit an inflection point followed by a sharp re-rating in stock prices. This creates an extremely rare opportunity for an investor in today’s market.
Looking for opportunities
We believe the inflation-focused environment is creating some phenomenal opportunities in markets. As this major headwind recedes, as we believe it will, valuation multiples are likely to re-rate and reward the patient investor. In fact, Montaka Global has been using this opportunity to increase several portfolio holdings that appear to be significantly oversold.
Amit Nath is a Senior Research Analyst at Montaka Global Investments, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is general information and is based on an understanding of current legislation. Montaka owns shares in Alibaba and Meta Platforms.
For more articles and papers from Montaka, click here.