Watching the Chinese investment markets from a distance is a little like watching a young child learning to ride a bike. Rapid progress is being made but at any time it can all come crashing down. Whilst urbanisation briskly increased from 1982 it is only in the last few years that capital restrictions have begun to ease. Restrictions on lending and deposit rates are being loosened, property ownership restrictions are being dropped and access to the share markets has been freed up for retail investors. As a result, non-bank lending has grown exponentially, property has boomed and stock prices have gone up like a skyrocket. There’s a real sense that in the last few years the training wheels have been removed and investors are being left to discover how capital markets work on their own. Whilst markets are going up everyone is happy but are investors even considering it is possible they can go down? Below are two case studies which might provide some insight on how much due diligence Chinese investors are undertaking.
Hanergy Thin Film Power Group
From the perspective of Chinese investors, Hanergy Thin Film was a one way trip to wealth with its Chairman, on paper, briefly reaching the top spot on China’s rich list. The problem is that there is apparently little or no actual business and its ‘revolutionary’ technology is far from proven or profitable. The Bloomberg graph below shows that a year ago shares could be bought for little over one Hong Kong dollar, they peaked at 7.88, then crashed by 47% in a day and have since been suspended from trading.
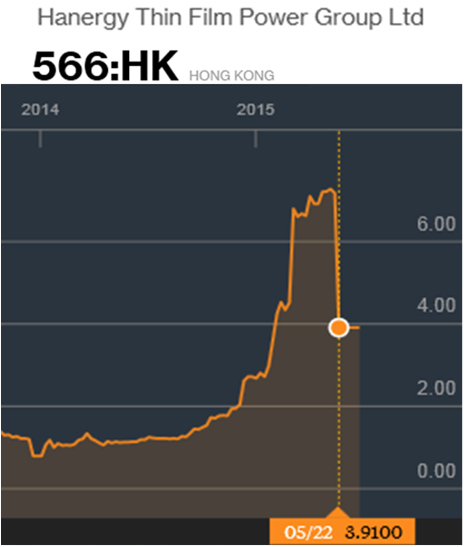
Most shocking is that this is not a two dollar company. It grew to a market capitalisation of over US$40 billion with few questions asked. Barron’s and Bronte Capital did some digging in the months before the share price collapse and concluded something was badly wrong. A simple wander around one site showed few employees and little activity, certainly nothing like what would have been expected by such a supposedly booming company. Information pointing to shorting by the Chairman and margin loans has emerged in the aftermath of the share price collapse, but the opaque related-party transactions and concerns about manipulation of the share price were well known before the collapse. One article asks whether Hanergy is China’s equivalent to Enron. The Hong Kong securities regulator is undertaking an investigation and the shares remain suspended.
Zhuhai Zhongfu Enterprise Co.
Zhuhai Zhongfu has a real business selling plastic bottles to the likes of Coca-Cola and Pepsi in China. Business has been tough in recent years as some of its customers seek to bring their bottle manufacturing in-house. Revenues have been falling, there were big losses in 2012 and 2013 and only a small profit in 2014. Cash levels were declining and were far too small to meet a large portion of debt classified as a current liability. One line of its debt had last traded at a 19.3% yield in June 2014 before the bonds were delisted. A Chinese broker had named it as one of the four riskiest borrowers in China in April 2015. All of this is familiar territory for a company close to default and so there should have been no surprise when on 29 May 2015, Zhuhai Zhongfu couldn’t repay all of the principal due that day.
What is unusual is that the share price rose by 211% in the year before the default on a fairly consistent upward trajectory with a market capitalisation of US$1.4 billion on the day of the default. The credit rating was at A+ until seven days before the default when it was cut to BB. Investors and the Chinese credit rating agency appear to have paid no attention whatsoever to the company financials which pointed to imminent issues.
Conclusion
As an outsider it is very difficult to know whether these companies are representative of listed equities in China. With a median P/E ratio of 75, an explosion in margin loans and a rapid increase in retail investors, suspicions are high that there is a bubble. What can be said with confidence is that in these two cases, Chinese investors didn’t do basic due diligence such as visiting the company and reading the financials. If these two examples are representative of the Chinese share markets then a collapse that rivals the dot com bust or Japan in the 1990’s could be on the cards.
Jonathan Rochford is Portfolio Manager at Narrow Road Capital. This article was prepared for educational purposes and is not a substitute for professional and tailored financial advice. Narrow Road Capital advises on and invests in a wide range of securities, including securities linked to the performance of various companies and financial institutions.