What’s the relationship between hybrids and equities when equity markets are weak? Probably the best comparison are the couples that appear on the Bachelor/Bachelorette: it’s ‘complicated’. There’s almost no correlation between the two assets most of the time, but sometimes there is and sometimes it can be material.
Price markdowns on bank hybrids and bank shares
The chart below details the drawdowns (markdowns in prices) for the Elstree Hybrid Index (Banks Series – yellow line) with the S&P/ASX200 Banks Accumulation Index (source IRESS – blue line).
Banks are actually a bit more volatile than the All Ordinaries Index but the bank index is a better like-for-like comparison. At the time of writing, bank shares are around 10% off their highs and hybrids are weaker by around 0.60%. If you are into statistics, that’s a 1 standard deviation move for both markets. You get worse than that most years.
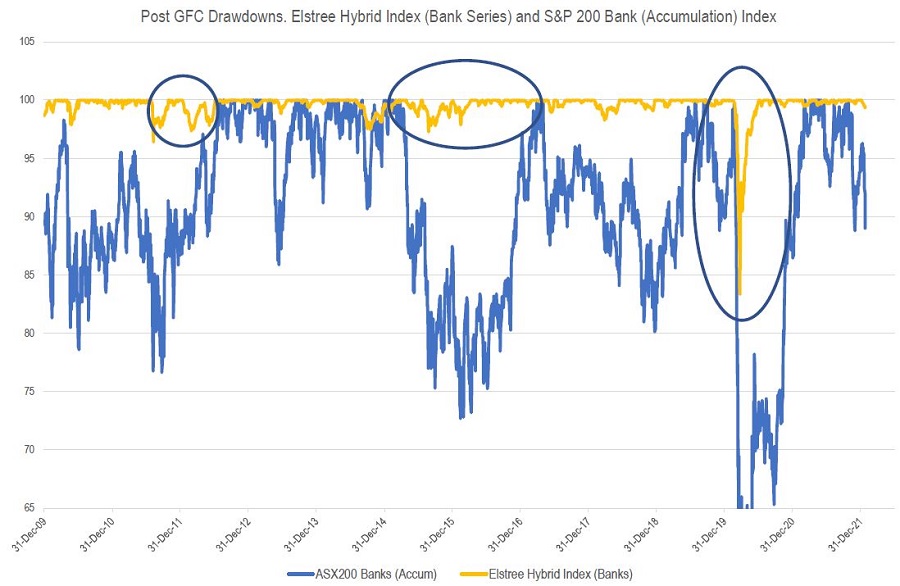
The three circled areas are the periods of material weakness since the GFC and there are some common factors for each of those periods which aren’t present to date in the current sell off:
- Fears of material economic slowdown/economic chaos (China slowdowns, Euro bank problems, Greece, Covid, etc)
- Protracted equity market weakness
- Big drawdowns. Bank equities had to have sold off by more than 15%.
This sell off is not echoing the previous three. It’s an inflation/too fast growth/interest rate led sell off and so far, it’s only around 10%. At this stage, it looks like normal noise for hybrids. We might see another 0.5% - 1% weakness before we get a full recovery, or this might be the bottom if equity markets stabilise.
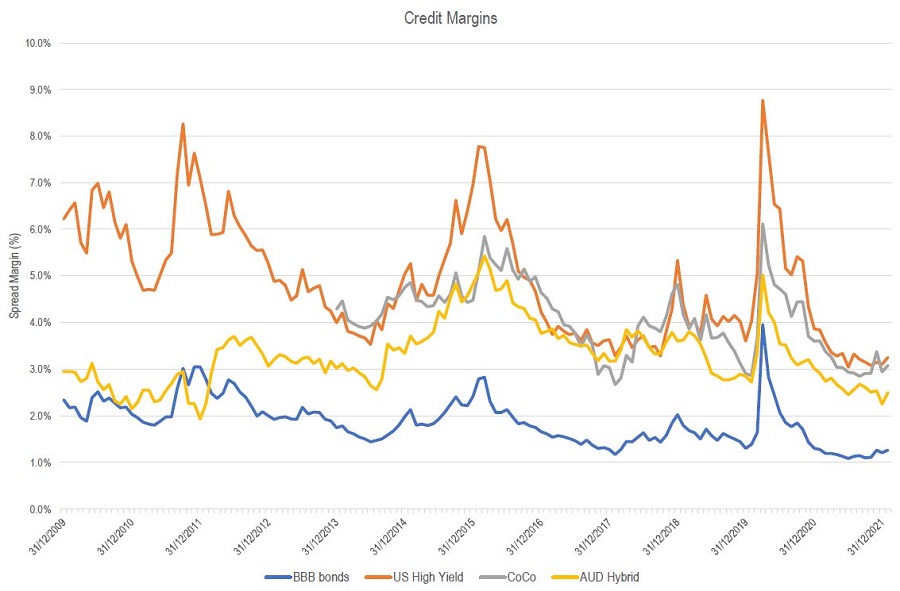
Nothing to see on credit margins yet
The chart below gives a longer-term perspective of credit margins (source BofA/ICE, Elstree) for four types of credit investments: ‘BBB’ rated bonds, High Yield bonds, CoCo (non AUD AT1/hybrids) and Australian AT1/hybrids. The last data point is 26 January 2022.
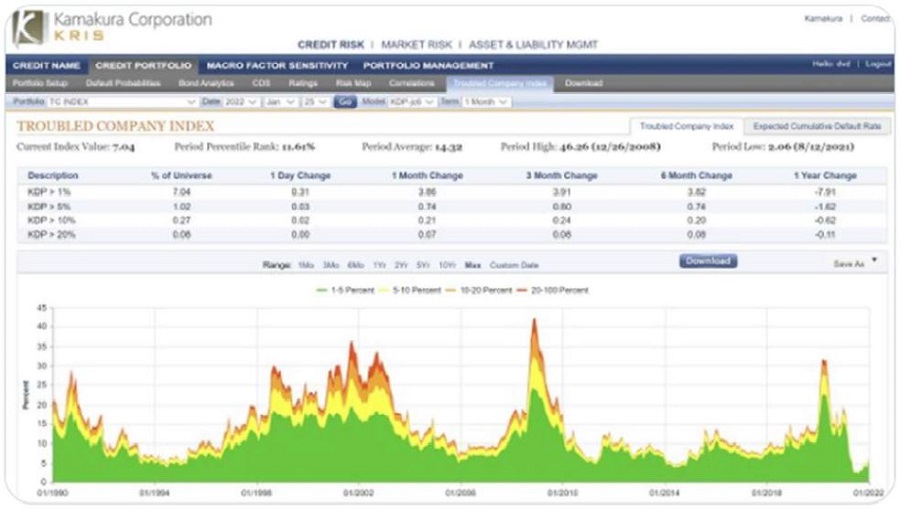
Will the last month lead to a surge in defaults down the track?
That would be nasty. We would be adjusting hybrid portfolios if we thought defaults were coming.
But at this stage it’s a non-event. Our favourite indicator is the Kamakura Troubled Company Index (source Kamakura). The index details the proportion of companies globally in various degrees of difficulty. While it’s a black box model, with its major inputs being equity markets and volatility, it has been extremely accurate predictor of default activity with a 12 month lead time. Credit conditions are still in the 11% of best periods since 1990, despite the month of market falls and its 1/3 as scary as what happened during Covid. There’s no default threat yet. The chart below is the 26 January 2022 update.
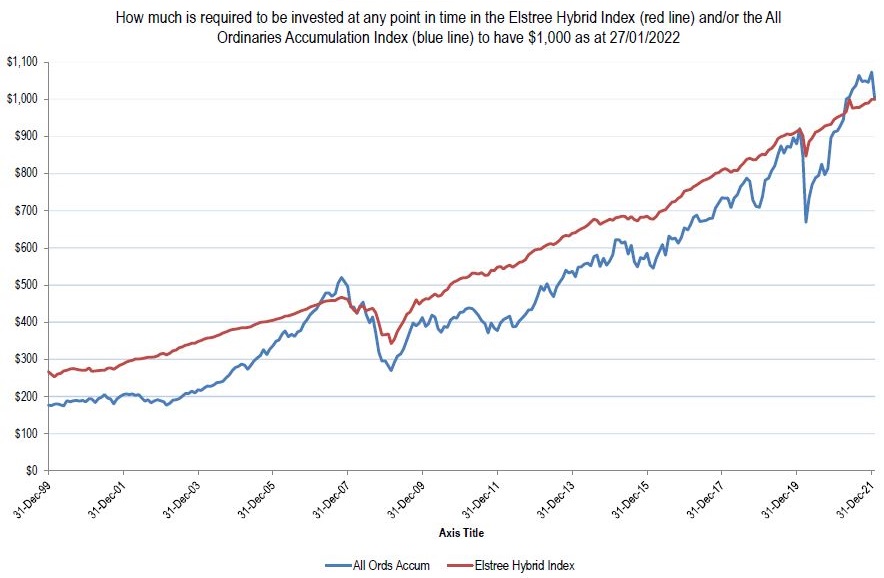
Why you own hybrids
Here's our favourite chart that gives a rationale for investing in hybrids. It shows the amount (in dollars) you need to invest in the hybrid (red line) or equity market (blue line) at any one time over the past 21 years to have $1,000 today. Clearly, a lesser amount is better.
If you invested in our funds, the amount invested to have $1,000 today is even lower than that of the benchmark hybrid index.
The key takeaway is the delivery of similar return outcomes with lower risk. If you wanted to cherry pick data points, hybrids have outperformed equities since 2007 and also since just pre Covid. If you bought equities at the bottom of the Covid drawdown, you would have outperformed, but in general, hybrids have been great for much of the past 14 years. We think that is still a valid reason to invest in the asset class.
Norman Derham is Executive Director of Elstree Investment Management, a boutique fixed income fund manager. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any individual investor. Elstree's listed hybrid fund trades on ticker EHF1.