Another strong response to our survey, with some surprising results.
Before we go too far analysing the numbers, we should acknowledge that opt-in polls are not as independent as using a statistical method to pick respondents. It’s important how people are chosen, and where the respondents choose themselves, pollsters argue the sample does not reflect the general sentiment.
With this qualification, it was surprising that 60% of respondents believe negative gearing should not be retained in its current form, given that most readers are investors and market professionals.
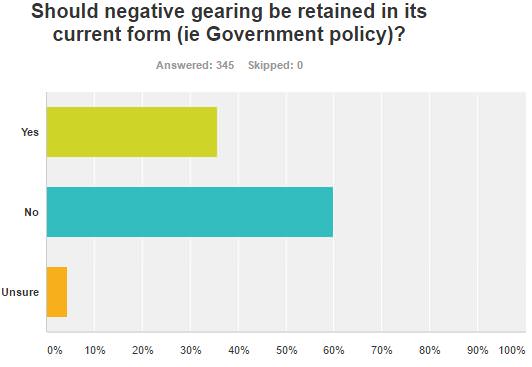
The comments reveal the rationale for this result, with responses dominated by two groups:
- those against negative gearing argue property investment has become speculative and is contributing to making housing unaffordable for first-home buyers. There are equity and intergenerational issues and it is a subsidy from the taxpayer.
- Those in favour of negative gearing argue it is a basic principle of investing and business that an expense is a tax deduction, and negative gearing is used by medium-income earners to build security, not only the wealthy.
There was a lot of support for capping the loss in some way, either by the number of properties or the type of income the loss can be claimed against.
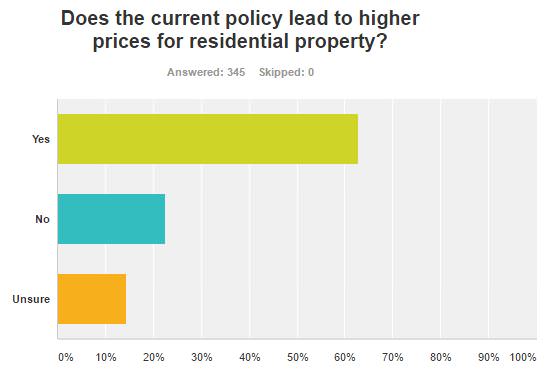
Respondents strongly believe that the current policy leads to higher house prices, with only 22% saying it does not. Main reason is that the tax benefits encourage demand for investment property.
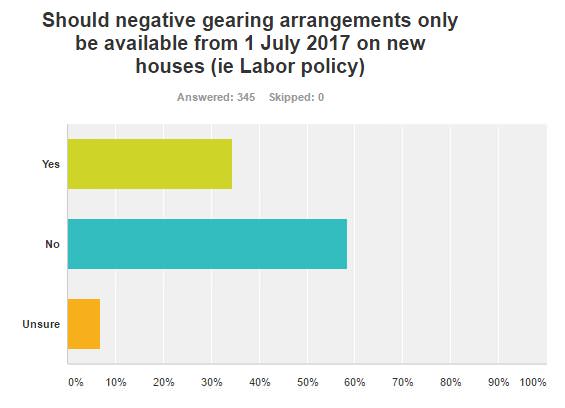
On the proposed Labor Party policy of restricting negative gearing to new properties from 1 July 2017 (and retaining existing arrangements), 59% disagreed, mainly because it would create distortions and lift the price of new homes.
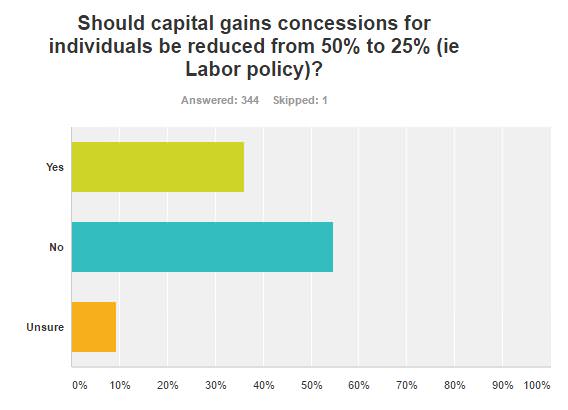
On Labor’s proposal to cut capital gains concessions, although a strong 55% were against, there was decent number arguing the current 50% is too high, with 36% in favour of the change.
There are many good comments in the final section of the survey, too numerous to reproduce here.
A few observations on the policies:
- Labor will retain negative gearing on new property, in a policy designed to encourage a supply of new housing, but there's a potential downside. Already, many new apartment developments are over-hyped in elaborate marketing campaigns, glossy brochures and photographs taken from the top floor. With obvious exceptions like Barangaroo, early resales are often disappointing when the building is actually finished. The negative gearing on new property and the easier access to these apartments for foreign investors may lead to an even more expensive primary market and a disappointing secondary market. Plus there will be a rush by investors to buy existing property before the 1 July 2017 deadline, exacerbating the affordability problem.
- For the majority of Australians, owning their own home is an important part of life’s journey. The dream goes like this (warning: sweeping generalisation coming) – have a good education, find the right job, meet a partner, buy a home, start a family, pay off the mortgage, buy an investment property, move onto other investments …). Unlike other countries where it is acceptable for even senior executive to rent homes on 10- and 20-year leases, in Australia, home ownership is a right of passage. With average household income about $80,000 a year and median capital city house price about $723,000 (and over $1 million in Sydney), the nine-times house-to-income ratio is destroying dreams, or creating massive debt burdens, notwithstanding lower interest rates.
- Many property investors over-extend themselves believing prices can only rise. There’s a naivety about piling into debt to buy property rarely seen in other asset classes. Investors are willing to accept property expenses exceeding income in the hope of future gains. The latest CoreLogic rental data for combined capital shows average gross rental yields of 3.3%, which would net to around 1% after costs (council rates, strata fees, repairs, etc). Subtract mortgage costs of at least 4% and there’s the negative gearing. Rental yields are at record lows. Fuelling the fire, the expected capital growth has certainly played out in the last five years, as shown below for total returns from residential property (including capital gains):
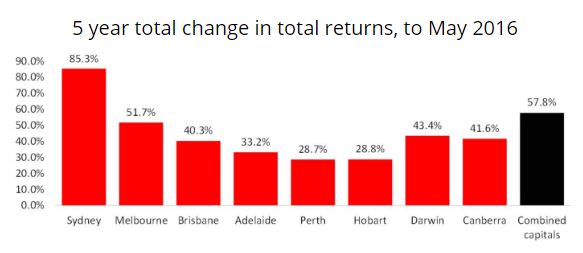
Source: CoreLogic RP Data Accumulation Index
Little wonder housing investment remains popular. There’s not enough space to outline what can go wrong in future with this plan, but suffice to say that the thousands of inexperienced property investors borrowing five to ten times their annual gross salary to buy an off-the-plan apartment in an over-supplied market will end in a lot of tears.
It’s a complex policy area of intergenerational equity, rich versus poor, renters versus landlords and massive personal debts and leverage. So far, the people who own the properties are mostly the big winners.
Graham Hand is Editor of Cuffelinks.