Information overload is a modern day problem.
Between smartphones, websites and watches that alert you even when you have ignored the phone, it is hard, if not impossible, to tune out the noise of the world. Trade wars, Brexit, currency slumps and geopolitical tensions are just the headlines that can dominate the news cycle on any given day. Thankfully the Australian cricket team provided some welcome relief – and restored a little national pride – at Edgbaston this week.
A long-term look at markets
Vanguard has been publishing its annual index chart that plots the performance of all the major markets and asset class indices for Australian investors for 18 years. It allows investors to look at how markets have rewarded them for the risk taken through periods of market rises and periodic slumps.
This year’s chart provides the data to 30 June 2019, and naturally there is always a tendency to focus on what has topped the performance table. While interesting, that is not the key message from the chart.
The core message – and the reason for continuing to publish it over such an extended period of time – is to understand the power of markets over the long-term.
Think of a major event that roiled investment markets and look at that point on the chart, say, the last Australian recession in 1992 or the collapse of Lehman Bros in 2008 to understand its impact at the time. Then zoom out to see how it affected returns over the full 30-year time period covered by the chart.
The other message provided by the index chart is when investors lean towards wanting to predict what will be the top performing asset class next year … and the year after that.
You can view the digital version of the chart here (or order a print copy here) but if you are tempted to try and time markets, it’s worth taking a look at the table below from the index chart brochure which shows the total returns across all the major asset classes featured in the chart.
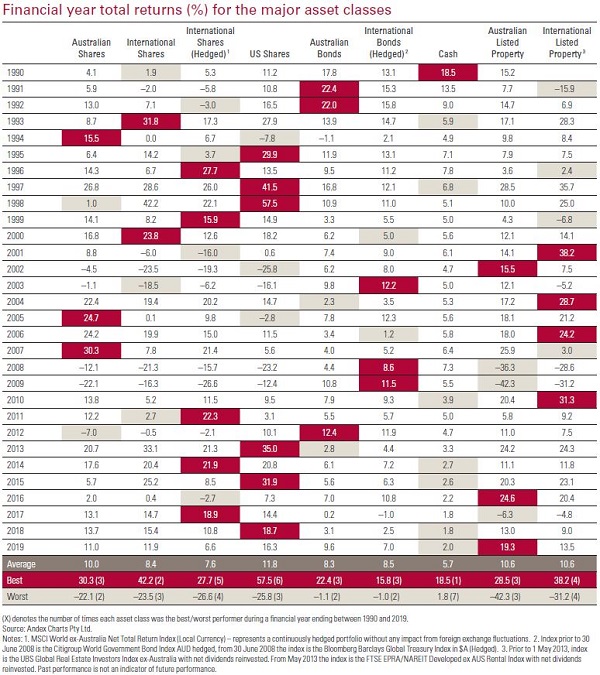
No discernible performance pattern
The best and worst performing asset classes are highlighted across each year, and feel free to let us know if you spot a performance pattern because what we see is what Burton Malkiel captured so elegantly in his investment classic, A Random Walk Down Wall Street.
The index chart shows the performance of markets over the long term, but for individual investors its value is in understanding how you blend all of those markets to create a portfolio with the right asset allocation to achieve your investment goals within a risk level that you are comfortable with.
For investors, a sense of perspective is a critical tool in the armory that can help tune out short-term noise, focus on your long-term goals and, as the legendary founder of Vanguard, Jack Bogle said, help you to “stay the course”.
Robin Bowerman is Principal and Head of Corporate Affairs at Vanguard Australia, a sponsor of Cuffelinks. This article is for general information and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.
For more articles and papers from Vanguard Investments Australia, please click here.