[Editor's introduction: Nathan Zaia is an equity analyst, covering the banking and insurance sectors at Morningstar Australasia. Given the importance of bank stocks in many portfolios, this article reproduces Nathan's latest research on Australian banks. With bank share prices moving around rapidly, these opinions are based on circumstances last week and may change at any time.]
Uncertainty is elevated and unprecedented events are unfolding. But with Australian bank share prices down about 40% since late February, those risks are in the price and bank shares are cheap in our view. The Reserve Bank of Australia says the pending economic contraction is a once-in-a-century event, and with earnings tied to the health of the economy, investors worry how the banks will fare. Our confidence in estimating loan losses and asset growth in the short term has reduced, which has major implications for earnings, dividends, and capital adequacy. However, after revisiting our forecasts to incorporate a wider range of outcomes, and more near-term downside, we maintain our positive view.
Key takeaways
- We reduce our major bank valuations by up to 7% after factoring in higher loan losses and small equity raisings via dividend reinvestment plans. On price/book values of 0.7-0.8 times, the banks trade at substantial discounts to the five-year historical averages of about 1.5 times, and to our fair value estimates. We believe the market is overly focused on near-term earnings. We expect major bank loan losses to normalise and for return on equity to average 10.5% by fiscal 2023.
- After enjoying impairment charges as low as 0.1% of loans over the last three years, we expect a meaningful increase to 0.50% over fiscal 2020 and fiscal 2021, before returning to midcycle levels around 0.20% by fiscal 2023. On average, our short-term earnings forecasts fall around 20%.
- We expect all banks need to materially reduce dividends with payout ratios expected to average 50%–65% over the next three years. Our base case assumes ANZ, National Australia Bank, and Westpac each raise AUD 3.5 to AUD 4.0 billion of new equity in the next two years. We expect partially underwritten dividend reinvestment plans, but a traditional placement and share purchase plan is possible.
- In our bear-case scenario, loan impairment expenses peak at 1% of loans in fiscal 2021 with cumulative impairments of 2.2% over fiscal 2020-2023. While the banks remain profitable in this scenario, we estimate three of the majors would need an additional AUD 5.5 billion in capital to offset likely growth in risk-weighted assets. Payout ratios will also contribute to the actual amount banks could end up raising.
- Given the increasing uncertainty around the economic outlook, and the broader range of potential outcomes, our uncertainty ratings increase to high from medium for all four traditional Australian banks.
Australian bank shares cheap, pricing for more pain than our bear-case scenario
We expect earnings and dividends to be under pressure in the near term with compressed net interest margins and rising loan losses, a view shared by the market. Our long-term view differs though. Based on grossed-up share prices, the Australian major banks trade on P/E multiples of around 7.5 times our fiscal 2024 forecasts, with the exception of Commonwealth Bank (ASX:CBA), which is at about 11 times. Seeing through the current high forward P/E ratios and low dividend yields, due to the trough in earnings, should reward long-term shareholders if the economic recovery plays out as we expect.
Exhibit 1: Share prices imply long-term pain for the banks
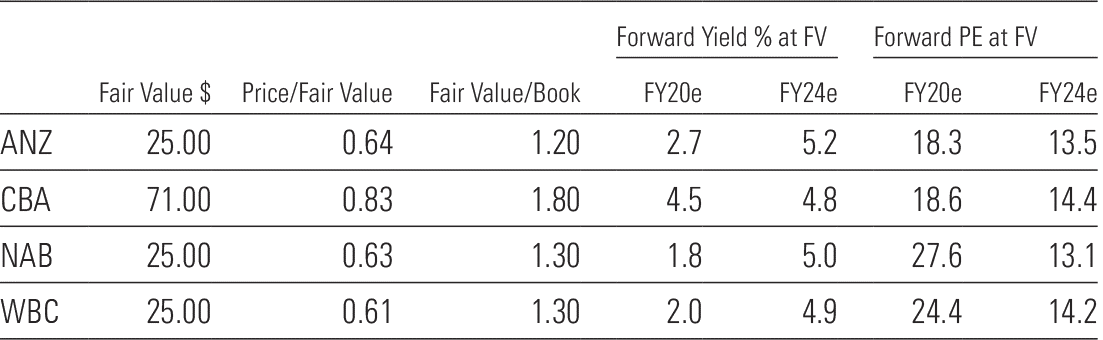
Source: Morningstar Estimates/Morningstar Direct: Prices as at 23 April 2020
Our overarching thesis for the banks is earnings by fiscal 2024 will be around 24% higher than fiscal 2019 levels, with earnings bottoming over fiscal 2020 and 2021. We assume low-single-digit loan growth of 3.5% over the next five years, with NIMs falling on average by 15 basis points from fiscal 2019 to fiscal 2021. After reaching a low of 1.83% we expect a modest recovery to 1.95% by 2024 as cash rates begin to lift. The current environment has the potential to prolong ultra-low cash rates, however, such an environment could see loan losses fall back to levels banks recorded pre-coronavirus.
We also expect customer remediation and regulatory penalties to be materially lower in the future. Coupled with lower loan losses and additional operating cost savings, we project cost/income ratios for the majors will trend towards 40% to 45% versus a peak of 50% in fiscal 2020. This is a return to fiscal 2019 ranges when accounting for the significant one-off items which have been incurred. Our loan impairment expense assumptions of 0.5% of loans in the short term fall back to midcycle levels of 0.2% by fiscal 2023.
While the pandemic means our confidence in projecting earnings and dividends in the short term is low, we remain comfortable with midcycle earnings forecasts. If our bear case for loan losses was to play out in the short term (cumulative loan impairments of 2.2% of loans over three years), but loan losses normalise back to our forecast midcycle levels, with all other base case assumptions held, we estimate our fair value estimates for the Australian major banks would fall around 5%. In this scenario, our fair value estimates would still be around 30% above current share prices.
Higher near-term economic uncertainty, especially with regard to the potential downside risk captured in our bear cases, means we increase our uncertainty ratings to high from medium for all of the Australian banks. Our bear case fair value estimates are around 0.65 times our base case, versus 0.75 times previously.
Exhibit 2: Price/book value of major banks
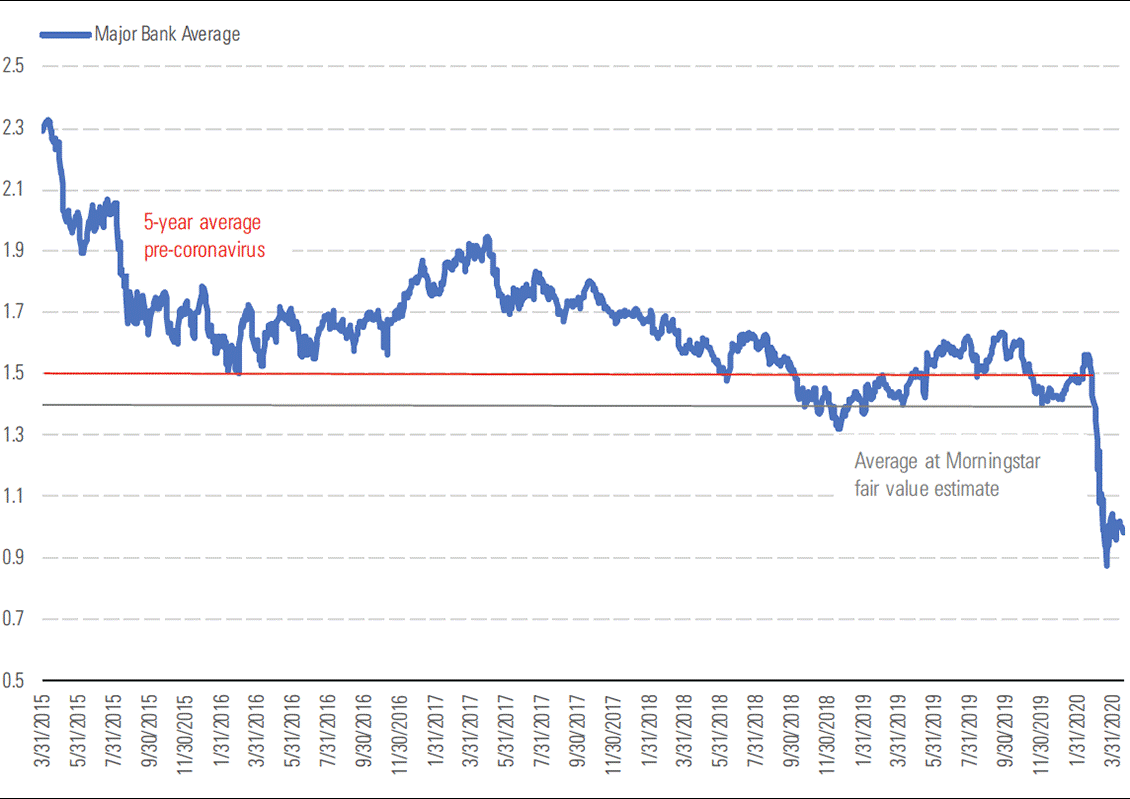
Source: Reuters/Morningstar Estimates
Prepare for large loan losses, but don’t rule out a recovery
Heading into this recession, fiscal and monetary stimulus, including specific industry measures to help ease the pain, is unprecedented. We expect it will ease the economic pain somewhat. While pain is likely across business and consumer lending, we expect availability of credit, low-cash rates, and stimulus to prevent GFC (0.75% of gross loans) or early 1990s loan loss levels (2%) from reoccurring. The ability to defer payments such as mortgages, rent, insurance, electricity, private health, switch to interest only, and draw on emergency superannuation funds buys all those affected by the lockdown some time. Measures rolled out by the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority, or APRA, to curb high loan/value ratio loans and interest-only loans, which have slowed loan growth among the majors in recent years, should also reduce the pain experienced in this downturn. We do not believe the government will pull the economic lifelines immediately as social distancing restrictions are eased, with government recognising it will not be a return to normal policy settings once economies reopen.
Our bear-case fair value estimate for the majors are AUD 17.00 for ANZ Banking Group (ASX:ANZ), National Australia Bank (ASX:NAB), and Westpac (ASX:WBC) and AUD 46 per share for Commonwealth Bank. While Commonwealth Bank trades at 1.25 times our bear-case fair value, the remaining banks trade at 0.9 to 0.95 times. Given heightened uncertainty around loan losses, and potential growth in risk weighted assets (via growth in loan balances and potential changes to risk loss assumptions), the downside now appears worse than we previously imagined.
In our bear case, we assume loan impairment expenses of 0.75% of loans in fiscal 2020, rising to 1% in fiscal 2021 as stimulatory measures only soften but not stop rising unemployment and business closures. Due to the severe contraction we expect, loan impairment expenses now remain above 0.3% of loans for the forecast period in our bear case. In this scenario, we also assume additional pressure on interest margins. We expect banks to refrain from repricing loans, despite higher near-term credit risk, as it would push more businesses and consumers into default, creating a vicious cycle. Government pressure on the banks not to reprice could also see the banks refrain from exercising pricing power. Nonbank lenders also remain a hinderance to bank earnings. They continue to access cheap funding and keep competitive pressure on rates, and ultimately margins. The Australian government announced in March 2020 it would make available AUD 15 billion for small bank and non-bank lenders, helping negate short-term risks they have no access to competitively priced funding.
Despite revenue being under attack on all fronts in our bear case, we assume cost-saving initiatives are fruitless with increased risk and compliance spend on tougher regulatory scrutiny and investment to maintain and upgrade technology leading to higher operating costs.
[For the full research paper, see the link below, and for more views from Nathan, see the following short video].
Video: Banks will see out corona crisis
Nathan Zaia and Glenn Freeman

Nathan Zaia is an equity analyst, covering the banking and insurance sectors at Morningstar Australasia. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor. Please consult a financial adviser before taking investment decisions. To continue reading Nathan’s views on this topic, premium members can access the full article here.
Morningstar Premium gives investors access to analyst ratings on hundreds of Australian and overseas companies, as well as a broad range of research material.