The recent release of the ‘Panama Papers’ shone a spotlight on offshore financial centres, but unfortunately, most of the reporting painted an incomplete picture of the industry. Many articles confused the concept of an offshore financial centre with that of a tax haven, but these are two separate concepts. The important differentiating feature of a tax haven is not that is has low or no taxes, but rather that it tends not to share data with the tax or regulatory authorities of other countries. In other words, not all offshore financial centres are the same.
This article explains the differences and why setting up a fund offshore can be attractive.
The Cayman Islands, for instance, is a popular domicile for hedge funds and has no corporate taxes, although it does have a well-developed reporting framework that automatically shares important tax data on locally-domiciled entities with the relevant tax authorities in the US and UK. For this reason, it is not regarded as a tax haven despite having zero tax rates.
A few articles took matters a step further, suggesting that all offshore hedge funds were secretive and opaque investment vehicles used by wealthy individuals to avoid paying taxes. This fiction was enhanced when the hedge fund is incorporated in a jurisdiction which was incorrectly portrayed as a tax haven.
Although this makes a great story, the press frequently confuses a tax neutral jurisdiction with a tax haven. The reality is that the largest investors in hedge funds are institutions including pension funds, sovereign wealth funds and insurance companies in developed countries and regions like the US, UK and Europe. These investors require the benefits that come from investing in a tax neutral, offshore jurisdiction.
No imposition of an additional layer of taxes
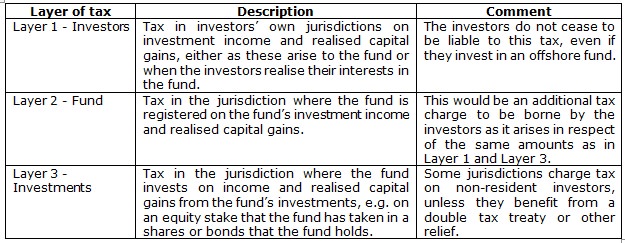
Tax neutrality essentially means that the country where the fund is domiciled (or registered) does not impose its own additional layer of taxes on the investors in the fund. But this does not mean that investors in tax neutral funds do not pay taxes. Tax neutral status is not unique to offshore funds and there are tax-neutral investment fund categories in the UK and the USA, for example. What sets offshore funds apart is the combination of tax neutrality and investment flexibility allowed by the fund structure.
Investment through a fund adds a potential layer of tax as opposed to the investors owning the underlying investments directly. Funds are given tax-neutral status to prevent the layer 2 tax being applied in addition to the taxes incurred at layers 1 and 3, so that an investor would be indifferent to holding the assets directly or through a fund, as illustrated Table 1 below.
Table 1: Different layers of potential tax in any fund
Investment flexibility
Another key benefit of investing in an offshore fund is that it can have more investment flexibility than a domestically domiciled fund. Although we have a flexible investment regime for domestically-incorporated hedge funds in Australia, other countries are not so fortunate. For those managers the ability to leverage investments with borrowed money, or to undertake short selling, is an important part of being able to manage their client’s capital effectively.
Regulation is continually evolving, and as it has the scope of ‘know your client’ rules have been expanded. As such, investors in certain offshore fund jurisdictions are fully and automatically reported to international tax authorities such as the US IRS and the UK HMRC. With the implementation of FATCA, the hedge fund must register and provide this data and if it does not, it will face penalties and will be unlikely to be able to trade with market counterparties (who are required to confirm the FATCA compliance of firms or funds they deal with). Funds will likely expel investors who refuse to disclose sufficient information about their identity rather than risk running foul of the tax authorities.
This is what makes offshore funds so attractive to investors. Investors seeking to invest in stocks or bonds have a choice. They can either buy these instruments directly themselves or via collective investment vehicles such as funds, which pool monies from a number of investors and then manage the pool on their behalf. The use of collective investment schemes gives investors, including pension funds and other sophisticated investors, the ability to diversify their portfolios across a broad range of investment strategies such as those pursued by hedge funds.
The investment fund management industry is global in terms of the location of investors, the fund management team and the portfolio investments. Consequently, the challenge for fund managers is how and where to create investment fund structures which are able to accommodate in a cost- efficient way investors from all over the world. They must operate within the complexities of existing tax and securities laws that apply to those investors, the management team and the business or investment activities, in their multiple home jurisdictions.
Craig Stanford is Chair of the Alternative Investment Management Association (AIMA)’s Investor Education Committee in Australia and Head of Alternative Investments at Morningstar Investment Management Australia. This article is adapted from the AIMA paper, ‘Transparent, Sophisticated, Tax Neutral: The Truth About Offshore Funds.’ For further information, contact AIMA. The information provided is for general use only and does not constitute personal financial advice. Views expressed are those of the Alternative Investment Management Association and do not necessarily represent those of Morningstar Investment Management Australia or Morningstar, Inc.