One of the reasons I generally don’t buy into company floats (initial public offerings or IPOs) is a little thing called information asymmetry. This term was popularised after George Akerlof (US Federal Reserve chair Janet Yellen’s husband) wrote a paper in 1970 about the used car market entitled 'The market for lemons'. It earned him a Nobel Prize in 2001.
Why sell a good company?
It’s a fancy term for a simple idea. If the seller of an item is singing its praises, why would they want to sell it? They are the ultimate insiders so they must be selling it for more than what they know it is really worth. The owner knows much more about it than I do? Before I buy anything, I stop and ask myself: What does the seller know that I don’t? If it’s such a good company, why don’t they want to keep it or buy more?
Company floats are an example of how this can often lead to bad outcomes for unwitting buyers, especially where the owners are taking cash out of the float. In some floats, the vendors are the founders, and at other times they are private equity firms seeking to offload their stake for a profit. Dick Smith and Myer are prime examples.
When a company floats, the founders are the ultimate insiders. They have spent years learning everything they possibly could about the company, the market, competitors, profitability, cash flows, assets, liabilities, the outlooks for supply and demand - much more than I could possibly ever know. If they know all of this and they come to the conclusion that they want to sell it, why would I want to buy it?
There are several cases of good floats where the vendors cashed out, notably when governments sell for strategic reasons or because they can’t afford to keeping injecting the capital required for growth. Commonwealth Bank and Cochlear were outstanding successes for investors in their floats. But not all government sell-offs are good. Telstra is a prime example of the government taking advantage of a crazy bubble market to sell out at ridiculous boom-time prices that never made any fundamental sense.
IPOs of private companies can tell us a lot about how the founders/vendors view its prospects. Look at what they do rather than what they say. In the case of the float of mortgage lender RAMS in 2007, nobody knew more about the mortgage market, the bad debt cycle, and the internal books of RAMS than founder John Kinghorn. In the float, he pocketed $650 million cash at the top of the mortgage market just before the sub-prime crash. Within weeks, RAMS issued profit downgrades and corrections to its accounts. Within three months, the share price fell 90%. The New York Times called it the ‘worst IPO of the decade’.
Kerr Neilson floated his funds management company Platinum at the top of the boom in 2007 right before the GFC crash. It was a stroke of market-timing genius. The $5 IPO price was hyped up to $8.80 on the first day of trading, but the very next day it started an almost straight line 70% decline to $2.75. It is still below its high more than 10 years later.
What about the Sydney housing market?
Not many people know more about residential property than John McGrath. He picked the perfect time to pocket $37 million in cash when he floated his McGrath real estate agency in December 2015. If he was bullish about housing, he would have kept his company. The share price peaked at $1.88 the day after it listed and the very next day it started its almost straight line 70% slide to where it is now. The market cooled, regulators introduced new controls to slow lending and clamp down on foreign purchases, and banks raised rates.
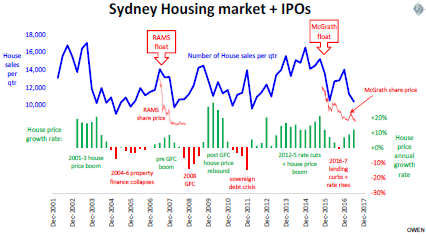
I have missed out on a few of good IPOs over the years, but I have avoided hundreds of duds by watching what people do rather than what they say. Successful investing is mostly about not blowing up your money in the duds.
Ashley Owen is Chief Investment Officer at advisory firm Stanford Brown and The Lunar Group. He is also a Director of Third Link Investment Managers, a fund that supports Australian charities. This article is general information that does not consider the circumstances of any individual.