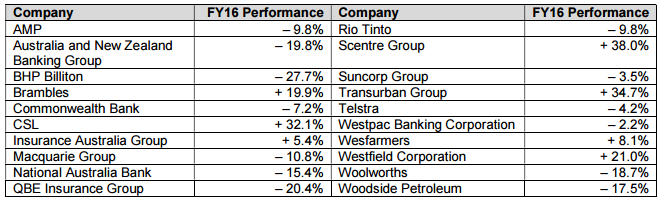
In the 2015/2016 financial year, the average investor performed poorly, despite typically being invested conventionally. The All Ordinaries Accumulation Index masked the significantly worse performance of the top 20 stocks in the market – the S&P/ASX20 Accumulation Index returned negative 7.0% for the year (including dividends). This is noteworthy because of the market capitalisation dominance of those top 20 companies, which at the time of writing constituted over 51% of the All Ordinaries Index. The names are very familiar and dominate most retail investors’ portfolios, but many of the individual stocks did significantly worse than the index.
2015/2016 performance of largest 20 companies on ASX
Investing in large, familiar companies
These companies constitute the most conventional of stock holdings and it begs the question, just because someone is invested conventionally, does that mean that they are being conservative? Most investors who hold large positions in these companies believe that because they are household names they must also be the least risky stocks to hold. But the connection between company size or familiarity and risk is a tenuous one.
The most important determinant of investment risk is the price paid for the asset. A poor asset purchased well under liquidation value can still be a great investment, just as a great asset bought at too high a price can prove a lousy one.
In his book Common Stocks and Uncommon Profits, first published in 1958, famed investor Philip Fisher, said:
“Unfortunately, often there is so much confusion between acting conservatively and acting conventionally that for those truly determined to conserve their assets, this whole subject needs considerable untangling.”
He highlighted what he thought were the four important characteristics of conservative assets:
- Superior operating performance, defined as being a ‘very low cost producer or operator in its field, [with] outstanding marketing and financial ability and a demonstrated above-average skill on the complex managerial problem of attaining worthwhile results from its research or technological organisation’.
- Outstanding, high quality people, employees who are responsive to change and enjoy their workplace, and management who are disciplined in building long-range profits (and not solely focused on short-term results).
- Inherent characteristics that demonstrate above-average profitability – ‘what can the company do that others would not be able to do about as well?’ – typically demonstrated by a superior return on invested assets and/or profit margin on sales.
- The price paid for the investment.
Focus on the price paid
The fourth characteristic is often the most significant factor when determining the expected return on an investment. We focus on finding investments that are priced in a way where we expect an attractive total return with a sufficient margin of safety should business conditions or company circumstances prove to be worse than our initial expectation.
Most of the businesses we are attracted to have the following characteristics that are commonly sought after (as highlighted by the similarity between this list and Philip Fisher’s four dimensions):
- a simple business model selling products and/or services we are familiar with
- a sustainable competitive advantage
- an attractive return on invested capital
- significant cash flow generation
- a strong balance sheet, and
- competent, disciplined management.
Many of the large Australian businesses listed in the table above we would characterise as good businesses. But a good business bought at too high a price will still generally make a poor investment, especially from a risk-adjusted return perspective. Our view a year ago was that many of these businesses were priced well above our estimate of fair value. They may have appeared to be conservative investments, but in reality they were more conventional investments, and somewhat expensive conventional investments at that.
We are reminded of the Warren Buffett adage, “Price is what you pay, value is what you get.” Investors should ensure they receive more value than they pay for when purchasing securities. If they do so over time, investors should earn an adequate return on their capital.
Tim Carleton is Principal and Portfolio Manager at Auscap Asset Management, a boutique Australian equities-focussed long/short investment manager. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any individual. A person should obtain the Product Disclosure Statement before deciding whether to acquire, or to continue to hold, units in any Auscap fund.