Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) have been a boon globally for self-directed investors, offering access to a basket of underlying investments, conveniently rolled-up into one security that trades like a stock. They’re listed on public exchanges and require small minimum investments. Launched in 1993, their popularity has soared with total assets globally scraping the US$3.5 trillion mark at the end of 2017.
Australian growth has been rapid
In fact, in 2018, 21% of investors tracking their SMSFs on Sharesight bought or sold an ETF*. This is a significant increase on just 3% in 2008.
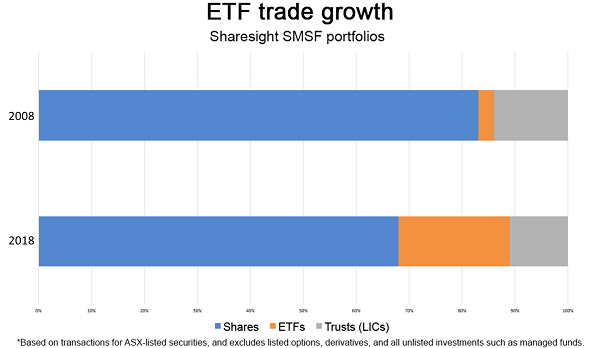
Nowadays there’s an ETF for everything: emerging markets, water scarcity, specific sectors and even cryptocurrencies. A colleague owns a cybersecurity ETF (ASX:HACK) that returned 39% in one year. I’ve personally owned ETFs that track commodity futures and one that shorted the real estate market.
But with this expanded investment menu of ready-access ETFs, Australian self-directed investors face complex realities. Despite all the positive aspects of ETFs, they can be a tax nightmare for Australian investors who’ve chosen to go off-platform or not rely on a managed service.
ETF tax in Australia
For Australian investors, ETFs create tax complications because instead of classifying them as ordinary company shares, the ATO classifies ETFs as trusts. To make things more convoluted, in 2016 the ATO changed the rules around investment trusts by creating the Attribution Managed Investment Trust (AMIT) regime.
Since the vast majority of ETFs make distributions (even those that are growth focused), investors face complex annual taxation statements. If you own an ETF and you don't know what I’m talking about, chances are your accountant or administrator is sorting it out for you.
An example of the ETF tax treatment
In our research, one purchase of Vanguard Australian Shares (ASX:VAS), which paid just four dividends throughout the year, morphed into 17 distribution and two capital gains components on the annual taxation statement. In turn these correspond to 10 items on an individual tax return, giving much complexity for just one buy.
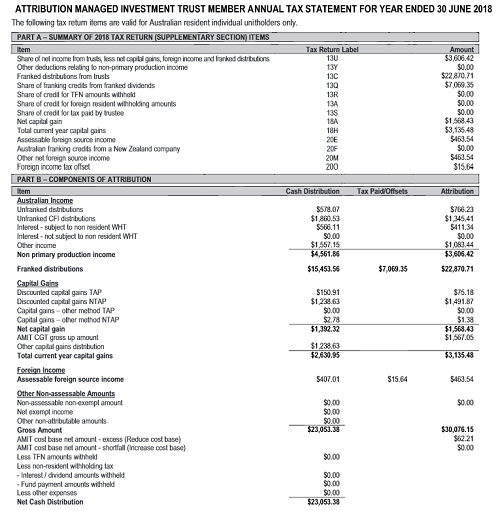
Source: VAS annual tax statement. Click to enlarge.
Why does this happen? VAS invests mostly in ASX shares, whose companies in turn pay dividends, are subject to franking credits and undergo corporate actions. This creates different tax implications. VAS also invests in unlisted securities, derivatives and overseas companies each with their own tax nuances.
When a fund manager runs a large portfolio, they leave room at the margins for inflows, outflows, rebalancing and hedging. It’s impossible for a portfolio manager to be 100% exposed to their core mandate at all times. Portfolios change daily, which means the underlying components of each distribution will be different quarter to quarter as corporate actions occur, or the portfolio turns over. This activity affects your annual tax situation.
As time goes by, you receive VAS distributions in cash (usually quarterly or half yearly), along with a simple statement from the registry showing the net payment. At the end of the year, the registry will send you a final statement.
These final statements contain all of the component and subcomponent information and are far more detailed than what you received during the year. This information can retroactively modify your cost base and taxable dividend income, making your tax lodgement difficult. It runs the risk that investors will pay more tax than they need to.
How Fintech is easing the ETF tax problem
Fintechs like Sharesight have created the expectation for real-time investment information. Once-per-year investment statements are no longer good enough for investors seeking accurate performance data about their hard-earned investment portfolios.
Case in point: in order to provide accurate performance and tax reporting for our clients, we sought to improve the depth and accuracy of ETFs’ distribution data for our self-directed clients and partners.
We knew this would be a big undertaking, but it proved more difficult than anticipated. After beginning our journey, we realised there was a lack of information and no clear rules available to investors. No one at the ASX, the ETF providers, professional firms, or even the share registries held the answer — but all recognised the problem.
Ideally, we thought we’d license the detailed distribution data from the registries or ETF managers on an ongoing basis. This proved impossible because they don’t calculate the data as the tax year progresses. It’s just one opaque process at year-end.
Fortunately, Computershare came to the party and agreed to provide us with the detailed information for some of the most popular ETFs as soon as the financial year ended. We use this data as a basis for calculating the distribution components for the 2017 and 2018 Australian financial years.
Unfortunately, not all the registries were able to provide data for their ETFs. We have no idea how it can be that a registry can send personalised taxation statements out to millions of Australians but not be able to provide even notional data to software companies like Sharesight. In some cases, we did receive sample data, but not always in a useable format.
After months of hard work, tracking down the right people at Computershare, and even buying ETFs ourselves in a Sharesight company account just to get the statements, we managed to build a solution that simplifies ETF tax administration for self-directed investors. After months of research we could not find clear answers from the industry, so we believe our feature hits the mark in terms of both accuracy and usability. Hopefully, it will push the industry towards better reporting standards.
ETFs remain terrific investment options
ETFs have helped democratise investing. I use them myself for long- and short-term investing and we support other fintechs who use them as building blocks for their clients’ portfolios. However, it seems that the zest to market new ‘easy’ ETF investment products wasn’t matched by an ease in tax administration.
The reality is that all investments have a tax implication of some kind. For example, ASX-listed stocks are vulnerable to future franking credit decisions. Tax complexity is just a new piece of the puzzle investors must keep in mind when building and administering their portfolios.
Doug Morris is the CEO of Sharesight, an investment portfolio tracker that provides reliable tax and performance reporting to self-directed investors and financial professionals. Sharesight is an alliance partner of Cuffelinks.
Important Disclaimer. We do not provide tax or investment advice. The buying of shares can be complex and varies per individual. You should seek tax and investment advice specific to your situation before acting on any of the information in this article.