With the Australian Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) industry just shy of $30 billion in assets and ETFs more actively traded than stocks in the US, investors are increasingly adopting ETFs as core building blocks of their portfolios. This trend is set to continue as exchange traded products have evolved from being only index-tracking strategies, and they now also provide a simple way to add exposure to particular asset classes such as gold. They can be used as a tool in a specific strategy, such as taking sharemarket exposure but with reduced market volatility. ETFs are low-cost, offer instant diversification and investment transparency.
The below five tips may help beginner ETF investors.
1. Understand the basic structure and liquidity
Unlike shares, the size of the ETF in terms of assets under management, the daily volume traded and the volume of units quoted ‘on screen’ is not indicative of an ETF’s liquidity.
An ETF’s open-ended structure means units of an ETF can be created or redeemed by market makers, in contrast to company shares which have a fixed amount of stock outstanding on any given day. The supply on offer for an ETF can be adjusted to cater to the demand. Therefore, the ETF fund size, daily volume traded and ‘on screen’ liquidity are not meaningful when assessing the liquidity of an ETF. An ETF’s liquidity is mainly determined by the liquidity of the underlying holdings of the fund. This is demonstrated in the example below, in which the daily liquidity is reflected by the daily average volume of the underlying holdings for BetaShares FTSE RAFI Australia 200 ETF (QOZ). Note onscreen liquidity is in millions while the underlying market is in billions:
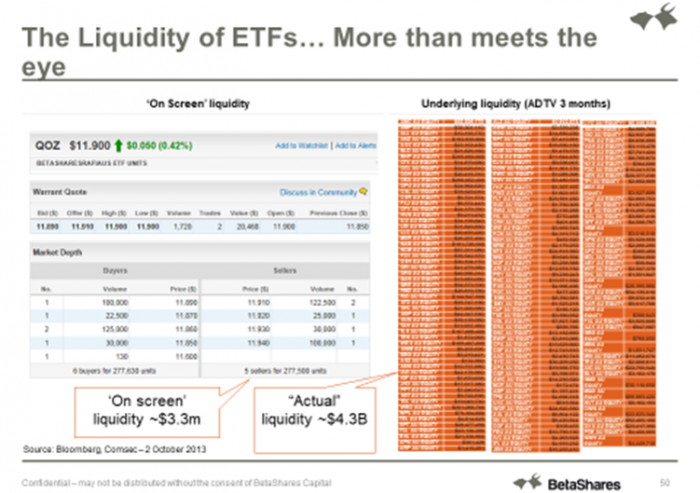
ETF investors and liquidity
2. Use the indicative Net Asset Value (iNAV) to determine the price to trade
To help determine a fair price to buy or sell an ETF, investors should refer to its indicative net asset value or ‘iNAV’ (if available). The iNAV is the estimated intra-day ‘fair value’ of the ETF (which is the price per unit of the basket of underlying securities held by that particular ETF less any liabilities such as management fees), which updates regularly. INAVs bring intra-day pricing transparency to ETFs in contrast to unlisted managed funds, for which net asset values are determined daily (or sometimes less frequently) once the trading day ends.
INAVs can be found on the website or on the respective product page of the issuer.
3. Understanding bid and offer spreads
All exchange traded and unlisted investment funds are subject to bid and offer spreads (known as buy/sell spreads for unlisted funds). In the case of ETFs, a bid/offer spread is the difference between the NAV of the ETF and the price at which the ETF can be bought or sold on the ASX. A ‘spread’ is a market maker’s compensation for the time and financial risk they bear to make markets and enhance liquidity i.e. acting as a buyer and seller of ETF units on the exchange and creating and redeeming units based on investor demand.
Spreads for each ETF vary as they are largely dependent on liquidity of the underlying securities. In general, the more liquid the security, the tighter the spread. Market makers also seek to maintain tight spreads to ensure they do not give their competition the potential to arbitrage profits.
4. Know the difference between ‘market orders’ and ‘limit orders’
When placing an order through a broker, whether it is for a share or an ETF, there is the choice to place the trade as a ‘market order’, agreeing to buy or sell at whatever price the market demands, or a ‘limit order’ at a specific price.
The risk with the market order is that there may be many orders placed at the same time relative to the demand on offer. For example, a previous investor may have placed a large order which momentarily depletes the volume offered at the current market price. The trade runs the risk of being filled with the next best market bid and this may be worse than the best price possible. A volatile market may also cause the iNAV of the ETF to fluctuate and spreads to widen, which also may lead to bids being filled at undesirable prices.
Placing a ‘limit order’ will avoid this risk. Although the order may not be filled immediately, there is no risk of getting worse than your desired price for the ETF.
5. Time when you buy or sell
ETF investors may also wish to avoid trading near the market open and close. This is because market makers can experience higher risk at these times, which may result in wider than normal spreads. At the market open, market makers look to determine the accurate pricing of the ETF’s underlying securities, taking into account the fact that only some, but not all, of the securities, have commenced trading and therefore have current prices available. This occurs as companies commence trading on the exchange in tranches on a staggered basis, as shown in the diagram below:

Source: MarketIndex.com.au – how to buy shares
Market makers experience higher risk when markets open and near market closing time, as prices of securities tend to fluctuate more. This volatility occurs especially around the market close as the ‘matching period’ approaches. That is, all trades that take place on the close transact at a price determined by the market. The higher risk in pricing at this point may lead to wider than normal spreads.
Buying and selling ETFs on market is straightforward and an application form is not required. ETFs can be simply bought and sold through a broker as with any share on the ASX.
Aditi Grover is a Business Development Associate at BetaShares, a sponsor of Cuffelinks. This article is general information and does not address the needs of any individual.