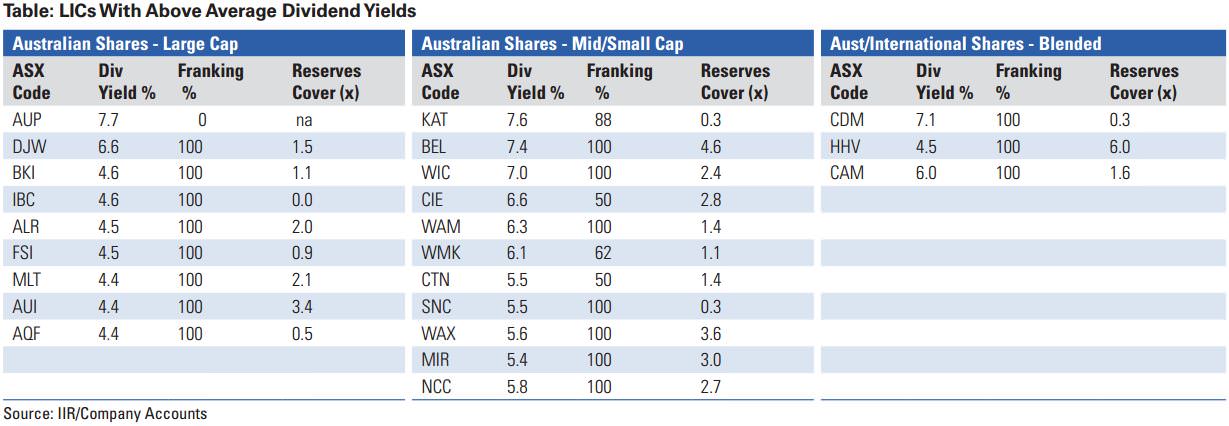
One of the reasons investors have embraced the listed investment company (LIC) sector is the fact that many LICs offer a reliable source of franked dividend income. We have calculated that LICs with an Australian large cap shares focus currently offer an average dividend yield of 4.4%, with most dividends fully franked. For LICs with an Australian mid to small cap shares focus the average yield is 4.6%, although not all dividends are fully franked. Twenty-three LICs on our data base with an Australian shares focus and those with a blended portfolio of Australian and international shares with a dividend yield of 4.4% or higher are shown in the table below.
While dividends are a key consideration, investors should not buy LIC shares purely on the basis of dividend yield. It is also important to look at valuation metrics such as premiums and discounts to NTA as well as performance of the underlying portfolios. To this point, our data tables provide analysis that can help investors choose LICs to suit their own specific investing strategies.
Dividend sustainability
Dividend sustainability is a critical issue when choosing LICs. To understand whether dividends are sustainable, we first need to look at how LICs earn their profits. Most of the older, internally managed LICs, such as AFIC (AFI), Argo (ARG) and Milton (MLT) are long-term investors and do not actively trade shares. This means their earnings are largely dividend based. On the other hand, the earnings of the LICs with more actively traded portfolios and those with a focus on small or emerging companies, tend to have a greater reliance on capital appreciation. In times of a prolonged market downturn, when overall market returns are negative, LICs that have a greater reliance on capital appreciation are likely to experience greater pressure on earnings and could in fact report losses in the P&L account.
LICs that rely largely on dividend income for earnings are less likely to report losses during periods of market downturns, and therefore the dividends they pay to their own shareholders are likely to be more sustainable. However, if the companies they invest in are forced to lower dividends due to reduced earnings, then, depending on their own payout ratios, the LICs may also be forced to reduce dividends, or at best hold them at current levels. This happened following the global financial crisis when banks and a number of companies were forced to cut dividends to preserve capital. MLT dropped its dividend in both 2009 and then again in 2010, with a total reduction of 26% before resuming the upward trend in 2011. ARG’s dividend was down 17% from 2008 to 2010 before resuming its upward trend. AFI was able to hold its dividend flat post GFC, but it did not start increasing again until 2013.
LICs with a greater reliance on capital appreciation were forced to take more dramatic action in relation to dividend payments following the GFC. The WAM Capital (WAM) dividend halved from 16 cents per share in 2007 to 8 cps in 2008 and then fell to 4 cents per share in 2009. With better markets, the dividend has rebounded rapidly with WAM paying 14.5 cents per share in 2016. After paying a dividend of 8 cents per share in 2008, Contango MicroCap (CTN) did not pay a dividend in 2009, with dividends resuming again in 2010. In more recent times, Westoz Investment Company (WIC) dropped its dividend from 9 cents per share to 6 cents per share in 2016. The dividend was maintained in 2015 despite the LIC reporting a large loss due to poor performance of its West Australian dominated portfolio, but this ate into profit reserves. With the company reporting a small profit in 2016 the dividend was cut to prevent further erosion of profit reserves.
In order to be able to pay dividends, LICs need to generate profits. However, it is possible for LICs to pay out more than they generate in profits in a given year by dipping into retained profit or dividend reserves from prior years, as WIC has done. So it is possible for LICs to smooth dividend payments to their shareholders by retaining profits rather than simply paying out 100% of earnings each year. The table above shows our estimates (based on published accounts) of the number of years each LIC could retain its current dividend payments without generating any additional profits. This is a good indicator of dividend sustainability when markets turn down. Coverage of one means that a LIC could maintain its current dividend payout for one year without generating any profit in the current year.
There are a number of LICs in the above table with dividend coverage of more than two years which means they are reasonably well placed in the event of a sustained market downturn. Of the LICs in the table, Hunter Hall Global Value (HHV), WAM Research (WAX), Australian United Investment Company (AUI) and Mirrabooka Investments (MIR), all stand out as having particularly strong dividend coverage.
Over the next year, we expect some LIC dividends may come under pressure as the income from their own portfolios declines due to lower dividends from resources and energy stocks and perhaps also the banking sectors. We note that Djerriwarrh Investments (DJW), one the highest yielding LICs currently, has already said it expects to cut its dividend from 24 cents per share to 20 cents per share in 2017. Based on the current share price this would lower the dividend yield to 5.5%, still an attractive, fully franked yield. This highlights the importance of watching management commentary for indications of potential changes to dividend payouts.
Conclusion
The LIC sector offers investors attractive dividend yields, but in periods of market downturns all LIC dividends are likely to come under pressure. While LICs that rely largely on dividend income from their underlying portfolios will suffer from reductions in dividends from their own investments, those with a higher reliance on capital appreciation are likely to come under greater pressure to reduce dividends. LICs with high levels of profit reserves are best placed to maintain dividends during periods of market weakness.
Peter Rae is a Supervisory Analyst, LIC Research at Independent Investment Research (IIR), an independent investment research house based in Australia and the United States. This article is general information and does not consider individual circumstances.