Property real estate income funds can be an attractive investment for those people seeking a reliable source of regular income. Most of this income comes from rent earned on the fund’s underlying properties and, as rent is usually paid monthly, a property fund is able to pay distributions monthly or quarterly, which is an advantage for an investor’s personal cash flow. At times, some of the income from property funds may include a component of ‘tax-deferred distributions’.
Though due to their complexity, tax-deferred distributions are rarely understood by anyone outside professional investor or tax specialist circles.
Tax-deferred distributions occur when a fund’s cash distributable income is higher than its net taxable income. This difference arises due to the trust’s ability to claim tax deductions for certain items – such as tax decline in value on plant and equipment; capital allowances on the building structure; interest and costs during construction or refurbishment periods; and the tax amortisation of the costs of raising equity.
In tax technical terms, tax-deferred amounts can give rise to distributions from property trusts of ‘other non-attributable amounts’ for trusts that have elected to be Attribution Managed Investment Trusts (AMITs) and ‘tax deferred’ components in non-AMITs – all referred to as tax-deferred distributions in this article.
Tax-deferred distributions are generally non-taxable when received by investors. Instead, these amounts are applied as a reduction to the tax cost base of the investor’s investment in the property fund, which is relevant when calculating any Capital Gains Tax (CGT) liability upon disposal of the investment units or once the tax cost base has been reduced to nil. Therefore, any tax liability in relation to these amounts is ‘deferred’, typically until the sale or redemption of an investor’s units in the fund when CGT may arise.
At its simplest, tax deferral works as follows: suppose a trust earns rental income of $100 and has building allowance deductions of $20. Then the net taxable income is $80, which is distributed to unitholders to be included in their taxable income. The remaining $20 of cash is distributed to the unitholders too, but for tax purposes it is regarded as a reduction in cost base of the units invested in the fund by the unitholder.
So long as the accumulated tax-deferred income is less than the investor’s acquisition cost, the tax is generally able to be deferred. If tax-deferred amounts have reduced the cost base to zero – that is, if the investor has received total tax-deferred distributions at least equal to the original cost of the investment – then any excess must be declared as a capital gain in the year it is received.
Capital gains are distributed by a trust only when the trust sells capital assets at a tax profit. These gains are then subject to tax in the investor's hands, the same as other gains. Alternatively, investors are taxed on any capital gains, including any accumulated tax-deferred distributions, when they dispose of their units in a trust or the trust is wound up.
Benefits
An incidental benefit of tax-deferred distributions for investors is the ‘deferral’ of tax until a CGT event, such as when the sale of your units or the wind-up of the trust, triggers a CGT liability.
Tax-deferred distributions reduce the investor’s cost base for CGT purposes, thereby increasing the CGT gain upon realisation. If the investor holds the units for more than twelve months, they may be able to significantly reduce the tax payable by applying the 50% discount for individuals, or by the one-third discount for superannuation funds.
Tax-deferred distributions may also be reinvested until such time as a CGT event occurs. The compounding benefit from reinvesting these distributions can be significant over time.
Case Study
The case study below shows the effect of tax-deferred distributions for an investor on the top marginal tax rate (assumed to be 45%). The case study compares a hypothetical $100,000 investment into an interest-paying investment earning 5% per annum with a property investment paying 5% distributions.
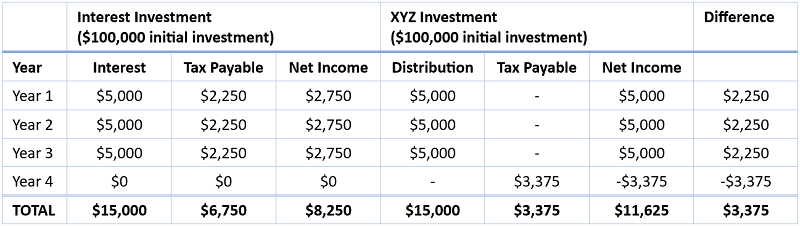
As you can see, an investor on a marginal tax rate of 45% and entitled to a 50% CGT discount makes a tax saving of $3,375.
Capital gain = $100,000 capital redemption, less reduced cost base of $85,000 ($100,000 initial investment less $15,000 tax-deferred distributions = $85,000) = $15,000 capital gain. Tax payable = $15,000 x 45% x 50% = $3,375. The tax payable does not take into consideration any Medicare Levy surcharge.
Assumptions used in the case study:
- An individual investor invests $100,000 into XYZ Investment (for example, an unlisted property trust) in Year 1 at a cost of $1.00 per unit (XYZ Investment).
- The XYZ Investment is redeemed in Year 4 (i.e., after three years) at a unit price of $1.00.
No allowance has been made for any potential capital gain or loss from unit price increases or decreases during the period the investment is held. This would also have CGT implications.
- Distributions from XYZ Investment are 100% tax-deferred for the full period of the investment (in order to illustrate the potential savings).
- XYZ Investment distributes 5.0 cents per unit, per annum.
- The investor does not have any capital losses available to offset gains.
Michael McLaughlin is Head of Tax at Cromwell Property Group. Cromwell Funds Management is a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is not intended to provide investment or financial advice or to act as any sort of offer or disclosure document. It has been prepared without taking into account any investor’s objectives, financial situation or needs. Any potential investor should make their own independent enquiries, and talk to their professional advisers, before making investment decisions.
For more articles and papers from Cromwell, please click here.
From the team at Firstlinks: Congratulations to Cromwell on its Cromwell Phoenix Property Securities Fund being awarded ‘Australian Property Securities Fund of the Year ’ at the Money Management 35th Annual Fund Manager of the Year Awards 2023.