Well, that was unexpected. The election delivered a revolt against Labor's franking credit policy. Prior to the election, we thought there would be little influence on the hybrid market because there was sufficient demand outside the affected investors to soak up the next few years of supply. If and when SMSFs did react to the policy, their biggest issue was their franked equity portfolio. Equity allocations are much larger in most SMSF portfolios.
At time of writing, the bank component of the Elstree Hybrid Index is up around 0.5% compared to the 9% increase in the S&P/ASX200 Bank Index. The hybrid return is only just in the top 5% of two-day returns over the last 10 years. Given that the election outcome was clearly unexpected, it indicates there are not yet a lot of pension SMSF investors returning to the market.
Ignore us and think long term
When it comes to hybrids, investors should consider our short-term guesses as next to useless for the simple reason that we believe hybrids should be a component of most income portfolio. Investors should be insensitive to 1%-2% price movements because of the favourable characteristics hybrids bring to portfolios:
- Cash rates are going to 1% and term deposit rates will be around 1.5% in a few months.
- The hybrid return of cash rates +3% or so is close to equity market returns over the long term and equivalent to income returns from high yield bonds or loan funds.
- Hybrids are not volatile except in big equity market drawdowns. Since the GFC, we’ve seen 20% decreases in equity markets and a maximum 3% drawdown in hybrids.
- Hybrid return weakness is short term.
- The risk factors and pattern of returns are uncorrelated to both equities and other income categories. High yield bonds and loan funds are more highly correlated to equities in a statistical and fundamental sense and if (and when) we do get a recession, they are more likely to fall by more than 10%.
- Hybrids are liquid, with a few exceptions. Other higher-yielding income categories have unproven liquidity and are probably lobster pots (easy to get into, impossible to get out of). In stress, they will trade below their doubtful NAVs.
It's worth understanding Sharpe ratios
We’ll get a bit techie here, but the concept of risk-adjusted return is easy to understand. You want to earn more for investing in risky investments, if only because lots of volatility upsets investors and they sell at the wrong time. The Sharpe ratio measures the extra return for extra risk and is expressed as a ratio. If it is positive, it means that you have received extra return for the extra risk and the more positive the better. In the chart below, we show the Sharpe ratios for the Elstree Enhanced Income Fund (including franking credits but excluding fees) and the All Ords Accumulation Index over the past 10 years. We use the rolling 3-year ratio as a good timeframe over which to judge investments.
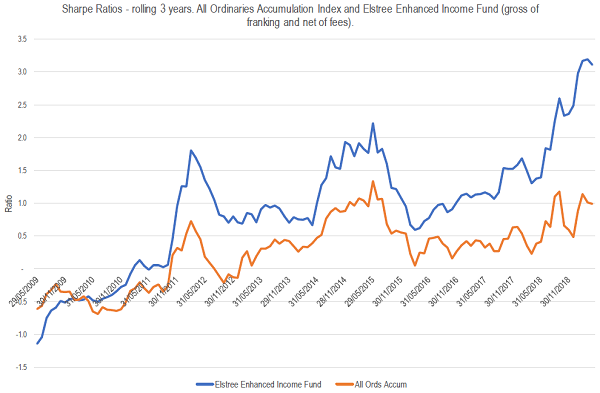
So, what does that tell us?
Since the GFC (when hybrid margins rose from the 1% pre GFC to average about 3.5% since), equities have returned 7.7% per annum compared to the Elstree Enhanced Income Fund (EEIF) return of 6.8% p.a. But because hybrids don’t have the annual 10% ups and downs that equities experience, the Fund has a Sharpe ratio of 1, which is twice as good as Australian equities.
Investors considering hybrids should take comfort from the following features:
- Sustainable returns that aren’t much below prospective equity returns and well above cash.
- Structurally lower risk than equities, and reasonable prospective risk (although lower than senior debt and subordinated debt in the capital structure).
- Structurally different risk factors than other non-cash and bond asset classes.
Hydrids can be complex in structure and investors should consider the features of any instrument or fund before committing capital, but at least the threat of a removal of franking credit refunds from SMSFs has been removed.
Campbell Dawson and Norman Derham are Executive Directors of Elstree Investment Management, a boutique fixed income fund manager. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any individual investor.