Diversified income funds which invest in a range of debt, bonds and hybrids have been extremely popular and have performed well recently. With cash and term deposit rates falling, this popularity will continue, but most investors in diversified income have little knowledge of what their fund buys and where its exposures lie. Many investors incorrectly assume that because of the focus on ‘income’ and ‘fixed interest’, the returns should be relatively stable and similar to term deposits and even cash.
Our conclusions are that most of the asset sub classes that make up global diversified income funds are not ‘income’ at all. Returns are volatile and dependent on changes in the capital value derived from equity markets, changes in high yield margins or movements in long duration bonds. We calculate that a typical diversified income fund is actually around 30% equity and 10% long bond exposed.
Diversified income funds – what’s in the recipe?
Although every portfolio is different, most of the diversified income portfolios offer a combination of the following assets or sub sectors:
- global investment grade bonds (fixed rate, investment grade)
- global high yield bonds (fixed rate, sub investment grade)
- convertible bonds (fixed rate, sub investment grade on average)
- high yield bank loans (floating rate, sub investment grade on average)
- hybrids (floating rate, low investment grade on average).
The charts used in this paper are rather busy, but each coloured bar represents a type of security, as listed above, included in a typical diversified income fund.
Returns
We gathered benchmark and fund data to evaluate the drivers of returns and risks of these assets. We used four return periods; 2012, 2011, the post GFC period (September 2009 as the starting point to avoid the immediate post GFC bounce), and the GFC period (defined as March 2007 - March 2009). In addition, because most bonds are fixed rate, we isolated the credit spread on BBB and BB bonds to calculate the ‘credit effect’. The non AUD component is generally hedged into AUD.
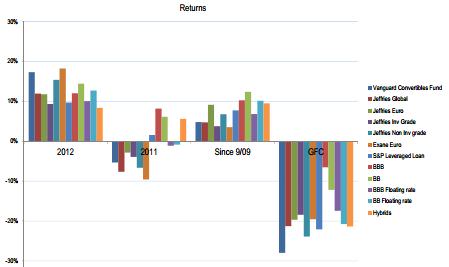
The return results on the graph below can be summarised as:
2012 returns: all sectors performed well, including investment grade and non-investment grade credits, aided by a contraction in margins and small falls in interest rates.
2011 returns: any sub sector with equity exposure did badly (markets sold off heavily), while anything with duration did well (US bond yields fell) and Australian hybrids did okay.
Post GFC returns: equity-related income produced reasonable returns while duration-related assets performed well, and Australian hybrids did better than high yield bank paper.
GFC returns: convertibles obviously produced poor returns given the implicit equity exposure, fixed rate BBB bonds performed relatively well given the fall in fixed rates and Australian hybrids did poorly.
Risk
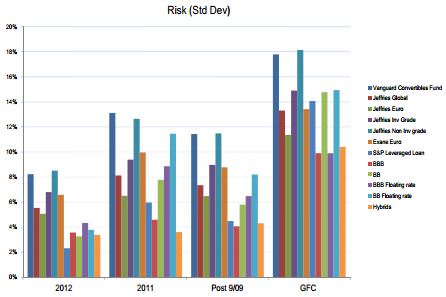
The chart below shows the risk (annualised standard deviation) over the same time periods of the same types of security. The pattern is consistent over all periods:
- convertible bonds display risk that is around half that of the equity market
- all the ‘credit’-type subsectors have lower risk by up to half that of equities
- hybrids are the least risky of the subsectors.
Surprising correlations
The following chart displaying the correlations to equity and government bond markets was the one that surprised us the most.
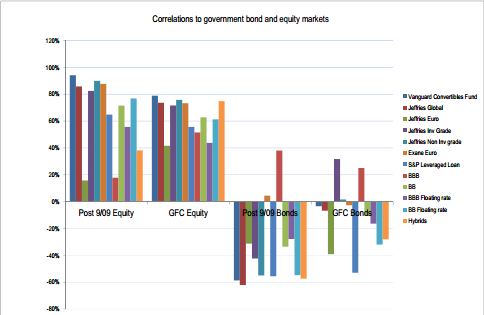
Our conclusions include:
- convertible bonds have a high correlation to equity markets and negative correlation to bond markets. Investors in convertible bonds have about a 40% equity beta on their investment. It’s not income at all.
- high yield bank loans display a high correlation to equity markets and given their floating rate nature, a high negative correlation to government bonds.
- BBB fixed rate bonds have a low correlation to equities since the GFC (but not during the GFC) and a high correlation to government bonds. An investment in US BBB bonds will be dominated by changes in fixed rate bond yields. It is not alternative income.
- other credit-type investments show the ‘expected’ correlations. That is, a relatively high correlation to equities during the GFC and less so afterwards, and low correlations to government bonds (except for BBB fixed rate credit).
- Australian hybrids have displayed a relatively low correlation to equities since the GFC.
Hedging – the interest rate differential bonus
The factor that has made diversified income funds really work for investors since the GFC has been the hedging interest rate differential. When investors buy non AUD assets and hedge them, they receive the interest rate differential. Since the GFC the interest rate differential has been in the order of 2% to 3% p.a. Most of the return of the diversified asset classes has been capital in nature, so the interest rate differential has been an added bonus. Note, however:
- the process of hedging is complex and it is difficult to remove all exposures. For example, if you had hedge a $100 investment in US high yield pre GFC and its price fell to $80, you are exposed to the currency effect on the unhedged amount. The AUD fell around 30% after the GFC which would have resulted in a 6% currency loss to add to the asset loss. In addition, legal agreements often allow counterparties to require collateralisation or a cessation of the hedge.
- interest rate differences are narrowing and therefore, the hedging benefit is unlikely to deliver the same level of ‘income’ in future.
Value of an allocation to hybrids
Hybrids are valuable in a diversified income portfolio for the following reasons:
- the listed hybrid market is now predominantly an investment grade, floating rate market, and while there is more event and maturity risk, there is no interest rate duration risk
- there is less equity risk than alternative sectors, and therefore correlation benefits
- they have been, and are more likely to be, less volatile than other alternative sectors
- yields on hybrids are currently higher than other alternative income sectors, although there are varying views about risk-adjusted returns
- for an Australian investor, there are benefits in not having to hedge currency risk.
Portfolio structure and future returns
Our analysis indicates that ‘income’ is often not really income at all. Returns are volatile and dependent on movements in the capital value of equities and fixed rate bonds and changes in credit margins, and investors must decide if they want these exposures in an ‘income’ fund.
Diversified income products should work by combining subsectors with various risks that have a correlation benefit. However, many of the securities used are highly correlated to equities and long duration bonds, and can suffer significant capital losses at times of market stress.
For the past few years, there has been a favourable combination of excellent overseas equity markets, contracting credit margins and falling bond yields which have bolstered returns. In addition, Australian investors have earned the currency hedging benefit. If there is a reversal in some or all of these factors, returns are at risk in these types of income funds.
Campbell Dawson is on the executive at Elstree Investment Management, a boutique fixed income fund manager.