Planning for how you would like your retirement years to play out can be an exciting proposition. Amid those holidays and time spent with family, however, it is important to also consider the 'frailty years'. They are the later years of retirement where you might experience physical and cognitive decline. A plan is needed if you want to maintain independence for as long as possible.
The reality is that we are all likely to experience some cognitive decline or lose some of our physical ability as we age. This is a natural process but does not mean we will all develop dementia or lose the ability to live independently.
But at some point, we may need to ask for help with our normal activities of daily living. This might be help we access in our own home, or we might need to move into residential care for a higher level of support.
Funding the increasing costs of care allows greater independence and control, which is key to a happier retirement. Take control while you still have capacity to make these choices yourself.
Rethinking retirement planning
We need to rethink our approach to retirement planning to consider the increasing cost and complexity of aged care.
Recognising and accounting for retirement income needs can reduce the risk of retiring with insufficient savings. This should include the means to deal with the increased cost of care in the later stages of retirement which can influence when we are 'retirement ready'.
Historically, the approach to retirement planning has been to decide what income you need and then calculate how much you need to save to generate this income. Most people assume a flat (or declining) level of income which grows with inflation. However, if you consider the cost of care, the pattern is more likely to follow an upwards curve as shown in the graph below.
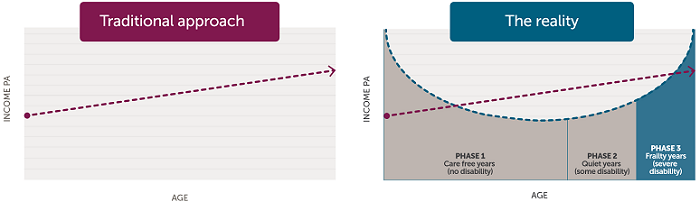
Retirement phases: care-free, quiet, and frailty years
The three phases of retirement
There are three phases of retirement linked to a retiree’s health, including years:
- without disability
- with some disability
- with severe disability.
Retirement planning and projections need to consider the income requirements for each of these phases, including the frailty years when expenditure patterns change.
An average 65-year-old retiree will have a health pattern as shown in the diagram below.
Spending patterns in retirement are likely to vary over the three phases.
Phase 1 is the initial period of retirement with 'care-free' years to focus on travel, spending time with family and friends and basically loving life! Health and wellbeing during this time are good, and the income needs of this phase of retirement are generally well accounted for in the planning process.
Phase 2 includes the 'quiet' years when health starts to decline. As we experience some disability, the level of activity and therefore spending declines.
Phase 3 is when we experience severe disability, and can be described as the 'frailty' years. This can account for 17%-25% of retirement years where help may be needed with daily living activities, and more is likely to be spent on dealing with aged care needs.
Preference for ageing in place
Older Australians strongly prefer to age in place (in their homes) rather than move into residential care. The costs of aged care have been accelerating at a rate higher than inflation. The opportunities for home care (in terms of home adaptations) are also increasing, adding pressure to retiree household budgets.
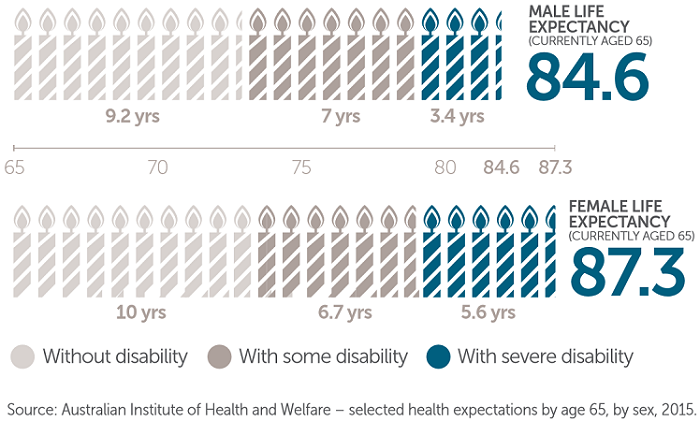
We might need increasing levels of support over the last 10-12 years of our life, with many people experiencing high levels of care dependency in the last 4-5 years. This may require income to cover:
- home care costs
- home adaptions to make the home suitable, such as widening doorways for wheelchairs and ramps.
Aged care costs can be difficult to predict and can vary from $100 - $5,000 a week ($5,200 p.a. - $260,000 p.a.) depending on care needs and family circumstances. Access to government subsidies helps to drastically reduce the cost payable by the user, but having adequate savings expands the options available and the ability to control the level and type of care received.
Did you know: ASFA Retirement Standard
Modest retirement for a single 85-year-old only allows $31.04 per week for care and cleaning. This is less than half the basic daily fee for a home package and that’s before extras!
Fragility is the third pillar of retirement risks
When planning for retirement and calculating the required level of savings, we usually consider two key retirement risks - longevity and sequencing risk. Longevity risk means savings may run out earlier than anticipated.
There is a third pillar of retirement risk – frailty risk - which if ignored, could also cause savings to run out earlier than anticipated, exacerbating the longevity risk. We need to manage the greater spending in the third phase, and in particular, care costs could be significant. Planning for frailty years should consider independence and control and the ability to stay in your home as long as possible, including:
- How you expect to fund aged care costs – recognising that legislation has been shifting towards a greater user-pays basis
- The role of your home in meeting aged care costs – including your willingness to access the equity in your home as against a preference to maintain the equity in your home as an inheritance for your family
- Ability to rely on family and friends to provide care and financial support
- If you choose to move to residential care, what options you have for funding the accommodation deposit and ongoing costs
It is important that you discuss these issues with your financial planner to ensure that you plan for a secure and comfortable retirement throughout all phases of your retirement – including the frailty years.
Assyat David is a Director of Aged Care Steps.