Investors have a strong desire to make money now, to have their investments pay off sooner rather than later.
There are certainly opportunities that can play out successfully over shorter periods, but a short-term strategy is not fool proof because it requires more ‘guess’ work about where multiples will be and how and when sentiment will change, if at all.
The alternative is for investors to be patient, take a long-term approach and focus on earnings, which are more durable and predictable than changes in valuation multiples. Investors may face down years and periods of lacklustre returns along the way, but they will likely be rewarded with a bigger payoff in the end.
Therefore, one of the most important decisions an investor faces is whether to pursue investments over a short or long investment horizon.
Both approaches have benefits and drawbacks and understanding the differences is critical to effectively managing an investment portfolio. Clearly discerning between strategies can help investors improve their research process to identify money-making opportunities while minimizing risk and successfully navigating inevitable bouts of market volatility.
So how do investors decide whether to invest for the short term or long term?
We believe there are five key considerations that investors should evaluate before choosing between investments with shorter (18-month horizon) and longer time horizons (7 years).
1. Source of opportunity (structural versus cyclical)
Long-term investment opportunities are typically underpinned by structural transformations that take place over many years or decades, such as the explosion of artificial intelligence and cloud computing, rising allocations to alternative assets, online shopping increasing, and payments shifting from cash to card.
These transformations can create massive markets with sustainably high growth rates, which the best companies capitalise on. For example, over the last eight years global card payments have more than doubled to over $US20 trillion. Over the same period Visa, the world’s largest card payment networks, has increased revenues 2.3 times and its stock price has risen four-fold.
On the other hand, short-term investment opportunities often arise from differences in market perceptions around economic cycles and near-term idiosyncratic events. Stocks of banks and retailers may sell off heavily in an economic downturn but can rebound quickly when the environment turns and profits jump.
For example, the share price of Foot Locker, an athletic apparel company in the US, halved during the COVID pandemic as reported profits fell by more than half in 2020. Then in the following year profits almost tripled and the stock price rose more than three-fold from trough to peak when the economy rebounded.
2. Driver of return (earnings versus multiples)
Over a longer-term horizon, investment returns are dominated by the change in earnings power, which tends to overwhelm the change in earnings multiple. That’s especially the case for the most successful businesses in structural growth industries.
However, over shorter investment horizons, the opposite is true, and the valuation multiple is a greater driver of investment returns than earnings growth.
To illustrate the point, we projected the earnings growth of three large well-known but different US companies: Bank of America, one of the largest banks in the US; Home Depot, the leading home improvement retailer in the US; and Microsoft, a global leader in cloud computing and AI.
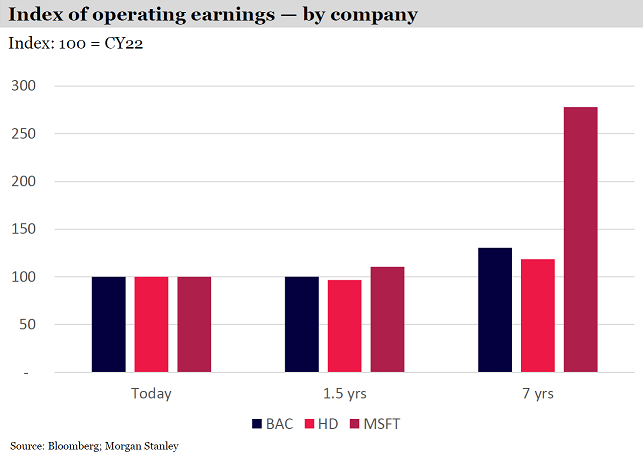
Over an 18-month forecast period, the earnings growth is almost unnoticeable across the three companies, even though they operate in different industries with vastly different prospects. The projection period is just too short for these differences to show up in differentiated financial performance. This means the stock returns over this horizon will be fully determined by the change in trading multiples.
For an investor with a much longer 7-year horizon though, the calculus flips upside down.
Bank of America and Home Depot are forecast to moderately grow their profits … but Microsoft’s earnings are projected to nearly triple as cloud computing revenues expand driven by the rapid uptake of AI services. Even if Microsoft’s multiple halved and the others’ multiples remained unchanged, Microsoft stock would still handily outperform the others.
3. Potential for outsized gains (multi-baggers versus singles)
A natural corollary is that longer-term investments have the power to become proverbial ‘multi-baggers’ with total stock returns that are many times the initial investment outlay.
For example, if Microsoft’s trading multiple held its ground, earnings grew in line with our projections, and excess cash flows were paid out to shareholders in dividends, then Microsoft stock could be a ‘four-bagger’ over the 7-year horizon.
In fact, the potential for upside can be even greater when burgeoning companies go on to achieve ‘outlier’ levels of success over extended periods.
Spotify, the world’s most popular streaming service, could end up being a ‘ten-bagger’ over the next decade as its base expands past one billion listeners worldwide, more services are offered, advertising takes off, and profitability inflects from break-even today.
Unfortunately, the possibility of making multi-bagger gains is considerably diminished by investing over much shorter horizons, because earnings growth does not have time to change exponentially and changes in valuation multiples do not usually themselves multiply so quickly, if at all.
4. Degree of deviation (rougher versus smoother)
While a long-term investment horizon has the power to boost returns exponentially, the path can be highly unpredictable, and returns can deviate significantly – often wildly – from the performance of broadly diversified stock market indexes.
In a 2020 research paper, Professor Hendrik Bessembinder observed that the companies that created the most value over a decade-long horizon did not avoid dramatic share-price retracements along the way. On average, the 100 most successful stocks recorded a maximum price ‘draw down’ of 33% before going on to create trillions of dollars of shareholder value.
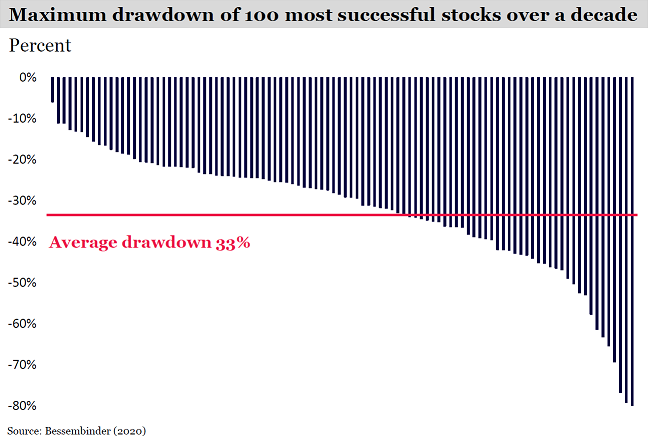
Conversely, investments made over a shorter horizon tend to deliver a smoother journey even if the destination is ultimately less fruitful. Shorter hold periods can lend themselves to less stock price variability, and the associated trimming of positions as they move against investors, or deviate from the market, dampens losses. Of course, trimming positions as they run to take profits can also hold back total returns.
5. Portfolio turnover (low versus high)
The distinctions between long-term and short-term investments reach beyond the nature of returns and risk, to meaningfully influence portfolio management and process.
Investments with longer-time horizons lower portfolio turnover rates, which means that investors have more time to spend researching the companies they will hold for years to come.
Deeper research offers investors the opportunity to discover novel insights about their holdings that can increase their conviction to see through difficult markets or, alternatively, to unearth risks that may be avoided by selling a stock early.
By contrast, shorter-term investments necessarily create higher turnover within a portfolio, which requires investors to find new ideas more frequently and leaves less time to acquire an intimate understanding of each investment.
Choosing a horizon
We believe that a long-term approach to investing will provide a more rewarding experience for investors by delivering superior compound returns, even though the journey will almost certainly be much more uneven and unpredictable.

However, that doesn’t mean that investors need to completely shun shorter-term money-making opportunities when they arise.
We reserve some space in Montaka’s portfolio for investments that may play out over short horizons. We just make sure they complement a large core of long-term compounders rather than replace them.
Chris Demasi is a Portfolio Manager at Montaka Global Investments, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is general information and is based on an understanding of current legislation.
For more articles and papers from Montaka, click here.