With the S&P 500 Index delivering its worst December performance since 1931 and credit spreads widening back to their long-term averages, fears of a recession in 2019 have increased.
But are those fears justified?
Some market-based metrics have been quietly signaling an increase in the risk of recession, with one of the more popular being the flattening US yield curve. While not perfect — and market watchers need to be cautious about false positive signals, such as in the late 1960s (see illustration below) — the predictive powers of the yield curve historically have been quite high. So how should investors think about this?
I think about it in two ways.
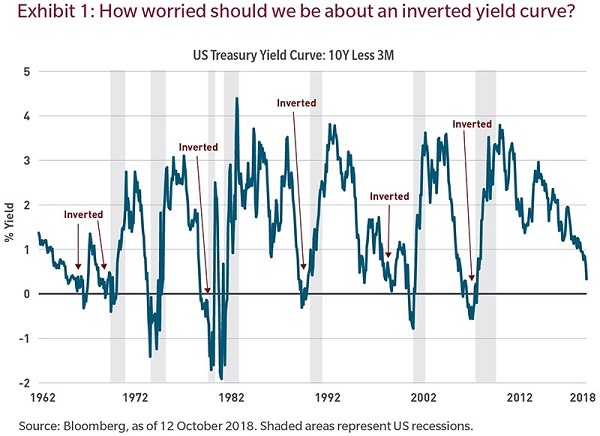
1. Would a recession matter to financial markets?
Market falls and recessions have coincided more often than not, as we observed in 1982, 2001 and 2008. So the answer is yes. However, that has not always been the case.
Economic health — or the lack thereof — and investor sentiment are two different things. While the economy is made up of many varying elements, financial markets reflect investors’ expectations regarding profits and cash flows. While each can heavily influence or lead the other, we have observed periods in which capital market declines and recessions have been mutually exclusive, like in 1990 (a recessionary non-bear market) or in 1987 (a non-recessionary bear market).
2. This economic cycle has been different from others in many ways.
As MFS chief economist Erik Weisman recently said to me, “In terms of the traditional drivers of recession, most aren’t evident today. We haven’t just ended a war; there is no negative supply shock (as with oil in 1973 and 1979); and the US Federal Reserve isn’t aggressively trying to contain overly high inflation (like the Volker Fed in the early 1980s). Outside of corporate leverage, macro excesses in the US economy are hard to identify.”
Something else that makes this cycle different has been the rise of internet platforms. They have provided a new way for enterprise and consumers to optimize business operations and everyday life. They have fostered “de-materialization.” In other words, the world is doing more with less capital, and that has been disinflationary.
For example, cloud computing allows enterprises to better engage with customers in a more cost-effective and productive manner. Internet infrastructure technology has allowed enterprises to better manage inventories and deploy capital more efficiently. Similarly, consumers have de-materialized. Internet platforms have allowed people to rent what they once owned, avoiding large, upfront costs in categories such as shelter and transportation.
Not only in the United States, but also in Germany and the United Kingdom, consumers allocate more than half of their discretionary spending to experiences or intangibles rather than physical goods. We are seeing similar trends in emerging markets such as India and Colombia.
The result has been a decline in the volatility of real demand, which partially explains why this business cycle has been low in growth, long in duration and with fewer excesses compared with history.
In conclusion, we are generally not concerned about a recession in 2019. To me, the Treasury market, which has rallied in recent months, is signaling greater concern about a potential Fed policy error than about an overheating economy. However, we have grown concerned about market complacency surrounding margin sustainability and financial leverage. So while we are less concerned with recession risks, we believe investors should be more thoughtful about how portfolio risk is allocated today as compared to how it was in the past decade.
Robert M. Almeida is a Global Investment Strategist at MFS Investment Management. The comments, opinions and analysis are for general information purposes only and are not investment advice or a complete analysis of every material fact regarding any investment. Comments, opinions and analysis are rendered as of the date given and may change without notice due to market conditions and other factors. This article is issued in Australia by MFS International Australia Pty Ltd (ABN 68 607 579 537, AFSL 485343), a sponsor of Cuffelinks.
For more articles and papers from MFS, please click here.