February’s ‘reporting season’ took place whilst global equity markets were in free fall. As at the end of February 2016, the Australian All Ordinaries Accumulation Index had posted a negative return year-to-date of -6.78%. We are not alone in our pain however, with similar sentiment across many other international (developed) equity markets. The two major US indices, the Dow Jones Industrial Average and S&P 500 kick-started the year with the worst opening week performance in history, and the story was much the same across most European exchanges.
Whilst volatility in equity markets was driven by continued oil price weakness and fears surrounding the extent of China’s ‘hard landing’, according to those responsible for setting Australia’s monetary policy, the picture doesn’t look that bad. Economic growth continues to track within an acceptable range and there are no unanticipated signs of structural decline in any areas of the economy. In this seemingly contradictory environment, it is worth delving into the challenges and tailwinds facing businesses as reported by them during February’s reporting season.
What do we like to see?
The stock market is likely to reward companies that could:
- grow revenue in a sustainable manner and
- increase earnings through a combination of revenue and margin growth, rather than only cost-cutting.
Indeed, in an environment where earnings remain elusive and growth even more scarce (as evidenced by the high multiples paid for stocks that provide even a hint of this, such as Blackmores, Bellamy’s, Burson, IPH Limited), many analysts feared the worst in the reporting window. What resulted, however, surprised many, with Goldman Sachs stating, ‘Relative to expectations, this earnings season is on track to be one of the stronger post GFC period.’
According to Goldman Sachs’ research, at the close of the second week of reporting season (22 February), of the 54% of all companies that reported (the remaining falling into the final week of the month), 46% of these beat expectations by greater than 2%. Whilst this may not seem such a stunning result, the same research claimed that only twice in the past 15 earnings seasons have more than 40% of firms beaten expectations.
Those that performed the best, in line with the broader economic picture, operated in the consumer discretionary sector and relied on growth in domestic demand to increase revenue and earnings. While the consensus trade in February was from growth/momentum stocks to those in the resources sector (which also didn’t disappoint but mainly as a result of cost-cutting initiatives being delivered on time), it was momentum stocks that also produced some of the strongest ‘consensus beating’ results as at the time the research was undertaken.
In terms of underperformers, importers were hit especially hard by falls in the Australian dollar, particularly those whose currency hedging positions rolled off. The key challenge for these businesses is how best to pass on price increases to highly sensitive consumers without damaging demand - a fine balance to find.
Where is growth in earnings per share coming from?
In terms of overarching trends, perhaps one of the most interesting has been Earnings Per Share (EPS) overtaking Dividend Per Share (DPS) in certain sectors such as Industrials and Banks. EPS, simply speaking, is the proportion of a company’s profits allocated to issued capital (common shares). Growth in EPS is positively viewed by investors as it shows how much money the company is making for its shareholders, not only due to changes in profit, but also after all the effects of issuance of new shares.
As the picture for earnings remains elusive, where is the growth in EPS coming from? Previously, we had seen the delivery of cost-cutting initiatives and low interest cover charges to boost profit margins. Looking at the EBITDA operating margins, we can see that profit margins have now stopped increasing suggesting that benefits from these inputs have diminished and any future growth in earnings will need to come solely through revenue growth, particularly for those companies in the Industrials sector. The chart below shows the operating margins of the ASX-100 Industrials since 2010.
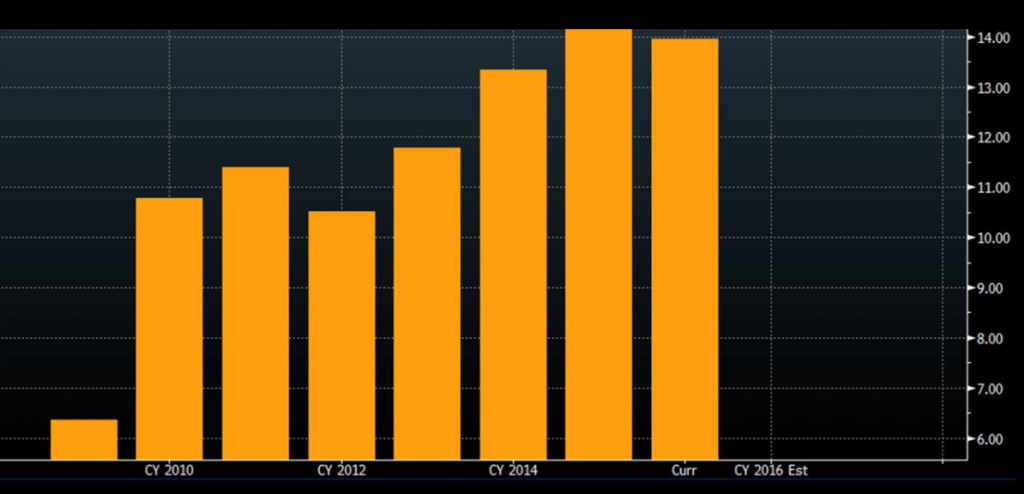
Source: Bloomberg
Volatility is disguising economic health
Tying together company performance and key indicators of Australia’s economic health, we conclude that the picture is not as bleak as the recent volatility in equity markets suggests. Looking at the underlying reasons for the recent market fall (before the March 2016 rally):
- Oil price weakness: Positive for net importers of this commodity as it represents, as per Howard Marks of Oaktree, a “multi-hundred-billion-dollar tax cut, adding to consumers’ disposable income. It can also increase an importer nation’s cost competiveness”, and
- Growth headwinds in China: Whilst growth levels have fallen, they still remain attractive relative to other global economies. Further, areas within China are experiencing strong growth, such as consumer spending, particularly in retail sales and travel. Retail sales in China are up almost 11.5% versus this time last year and the latest statistics relating to inbound tourism from China to Australia show growth of almost 11% from this time last year. Further, in relation to China’s impact on US growth, according to US national income accounts, only 0.7% of US profits are generated in China. Goldman Sachs’ research estimates that a 1% drop in China’s GDP growth will have a 0.1% impact on US GDP from direct and indirect exposure. If you compare that to the GFC, the banking system in the US had a 39% exposure to US mortgages, hence why the shock was so great. Yes, there is always a risk of financial contagion from China to other countries, but we think this risk is being overplayed.
What is the key criteria for successful investing through this period of equity market volatility?
As a value-driven investor, we look for companies that have the ability to leverage the ‘quality’ aspects of their business, such as strong brands, people, balance sheets and the ability to move quickly and efficiently to implement changes to position them as leaders. Whilst profitability is, of course, important to assess, it presents the market with a value to ascribe to a company’s stock ‘at a given point in time’. As such, inefficiencies can be created and therefore opportunity can present for those with a longer-term horizon.
Sebastian Evans is Chief Investment Officer and Managing Director of NAOS Asset Management. This information is general only and does not take into consideration the investment objectives, financial situation or particular needs of any reader. Readers should consider consulting a financial adviser before making any investment decision.