The RBA cut the target cash rate to 2.25% in an effort to boost consumer and business confidence and arrest growth in the unemployment rate. Whilst this move was positive for equity investors and saw the ASX hit multi year highs, it was a negative for savers, especially retirees living off the income generated by their term deposits. ANZ cut its one year TD rate to 2.6% and with the inflation rate for 2014 running at 2.5%, savers are receiving close to a zero percent real return (after inflation) on their term deposits.
The result of this rate cut will be that investors who rely on the income produced by their portfolio will be forced to move up into riskier investments just to maintain their standard of living.
Millionaires eating baked beans on toast!
Earlier this week I met with a well-respected fund manager who raised an interesting point. He said that historically a retiree would feel secure in funding their retirement if they had, through a lifetime of careful saving and judicious investing, amassed $1 million dollars in their superannuation account. Indeed in 2008 this investor would have received a risk free income of over $80,000 from investing their portfolio in term deposits, enough to cover a comfortable existence without risking their nest egg.
Currently that same strategy would deliver just $26,000 for the retiree with $1 million dollars, effectively the ‘poverty line’ in 2014 of $25,896 calculated by the Melbourne Institute for a couple with no dependants that own their own home. I found this observation interesting as in the funds management world, the vast majority of our focus is on growing the capital, rather than thinking about the ongoing income that this capital is often required to deliver.
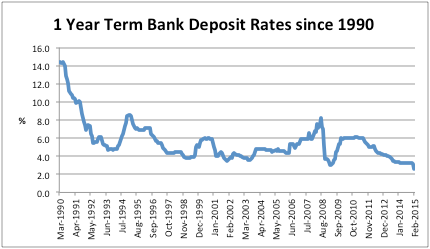
Source: RBA
The Australian banks have been significant beneficiaries of falling term deposit rates, not only through the declining cost of capital, but also due to the increase in retail appetite for bank hybrids. This retail interest has allowed the banks to build their capital bases in the lead up to Basel III, without issuing equity that would dilute earnings (and compromise bank CEO’s earnings per share growth targets). In the last three years Australian banks have raised $20.4 billion in hybrids and subordinated debt from mostly retail investors at attractive margins for the banks. These issues have been sold to yield-hungry investors primarily based on the headline rate and the name recognition of the big bank issuing them, often with little regard to the actual terms and conditions of the issue.
For example in January, ANZ ‘s Capital Notes 3 raised over $750 million at a margin of +3.6% or a current coupon rate of 5.85%. Not only was this margin too low given the ten-year term of the issue, but also in a ‘worst case scenario’ investors are no better off than ordinary shareholders, despite owning these ‘preference shares’. ANZPF holders will receive a pre-tax distribution of 5.85%, whereas ANZ common stock holders are looking at a grossed up dividend of 8.3% (which can grow) for facing similar risks.
A more extreme variation on this theme of investors not getting compensated for the risks they are taking is the continuing success of finance companies raising money from investors. Companies like Fincorp and Westpoint offered investors interest rates of 9.25% and 12% respectively, which sounded very attractive and almost double the prevailing interest rate. Unfortunately these funds were used to make mezzanine finance loans to property developers, so investors really should have been demanding double this interest rate!
Look behind the yield on high-yielding equities
Over the last few years among the most common questions that I have received from investors are around the theme of ‘juicing up’ distributions by picking higher yielding stocks. Typically this comes in the form of a list of the highest yielding ASX200 that the investor has obtained from a website and questions as to why these stocks are not in the portfolio.
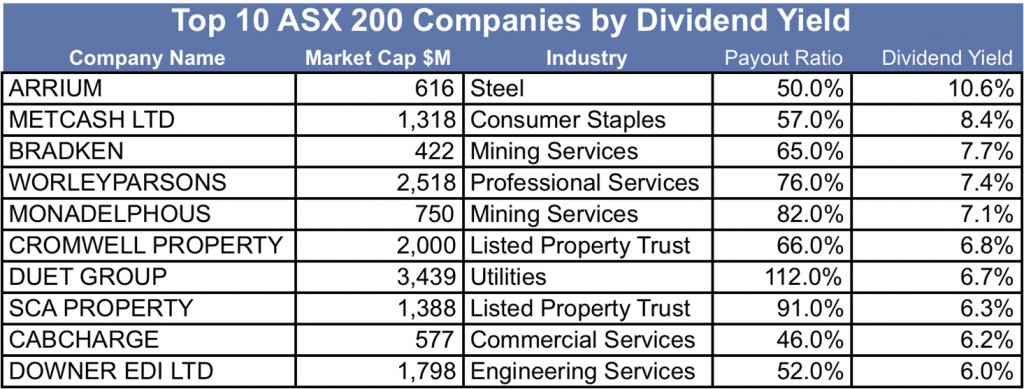
Source: Bloomberg, Philo Capital
Basic high yield strategies tend to underperform and have done so on the ASX over the past 20 years. We see that this is due to the characteristics of companies that tend to pay high dividends:
a) mature companies in decline
b) companies in industries with low growth
c) companies where there is material risk that the dividend will be maintained.
Looking at the above table of the large listed companies ranked by dividend yield, a number of them have all three dividend risk characteristics. Arrium’s steel and Metcash’s supermarket businesses could be characterised as being in decline and the market has concerns about both companies’ ability to pay dividends in the future. Duet’s energy utility business is low growth and faces upcoming regulatory risk, which could impact distributions especially in light of the very high payout ratio (Duet pays out more in distributions that it currently receives in profit). The future of Cabcharge’s payments business is opaque with their monopoly on taxicab payments processing being undermined by technological developments such as Uber.
Whilst investors may be able to temporarily generate a high yield from owning a basket of these stocks, there is not a great chance that these companies can maintain their dividends, let alone grow them ahead of inflation.
Hugh Dive is Head of Listed Securities at Philo Capital Advisers. This article is for general investment education purposes. It does not take into account individual objectives, financial situation or needs.