Once upon a time, a transformative new technology enthralled the marketplace. Silicon Valley venture capitalists opened their wallets, as did retail shareholders. Veteran portfolio managers were bemused. No doubt the industry would prosper, but given its sky-high valuations, and the fact that many of these first-stage businesses would fall by the wayside, were those stocks worth owning?
The past has returned. As with 1999's internet companies, today’s artificial intelligence startups face directly forward. Rarely is upcoming change so apparent. Without question, AI technology will dramatically reshape the economic future.
Individual stock returns
This leads to the logical investment question: How would those early internet buyers have fared had they purchased a basket of shares and stashed it away for the next 25 years? Mutual fund history tells us nothing. Of the 12 funds that had the word ‘internet’ in their names when the millennium began, only one still exists, and that fund invests more than half its equity assets in energy stocks, including a 17% position in Texas Pacific Land Corporation TPL.
So, fuhgeddaboudit. For the purposes of this article, fund records are useless. So, too, are the track records of internet stock indexes. They show the return for portfolios that are monitored and updated. Of the 10 largest companies in today’s Dow Jones Internet Index, only two were publicly traded 25 years ago. Most of the industry’s current giants, such as Alphabet GOOGL and Meta Platforms META, were founded during the following decade.
To assess the startups’ fates, I found a January 2001 version of the Dow Jones Internet Index. Many of its holdings have long since been forgotten. (If you know what happened to Covad Communications, Excite@Home, or Tibco Software, or indeed that they ever existed, you are ahead of me.) I located the fate of 38 of that index’s 40 positions, sorting the outcomes into three groups: 1) Still Existing, 2) Purchased, and 3) Bankruptcy.
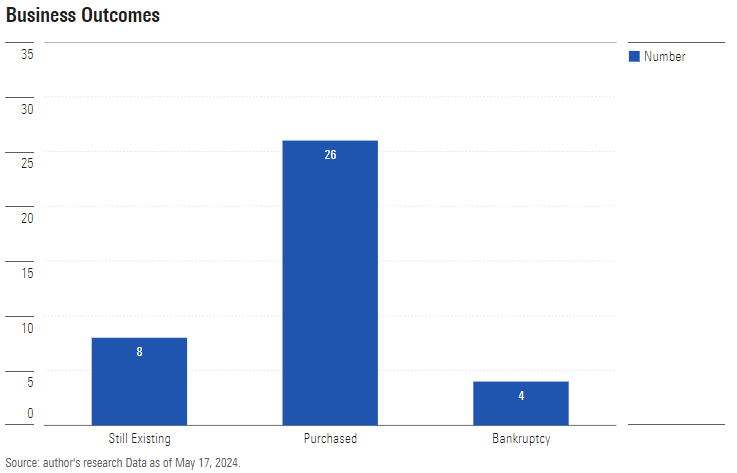
Better than I had expected! Most of the list’s businesses had persisted (in some form) rather than liquidating into a puddle. But had they retained significant value? It’s one thing for a company to be so coveted that it is purchased before its second birthday—as with YouTube, for which Google paid $1.65 billion. It’s quite another to drift for a decade, attempting to right the ship, before selling the business for pennies on the dollar.
The total returns
I could not find the performance records for three of the 38 companies, but I was able to compute returns for the rest. When possible, I began the calculations in March 1999, when the Dow Jones Internet Index went live. However, as my reference article of holdings was published two years later, it included several firms that were not in the index’s initial version. In those cases, I used the stock’s inception date.
I concluded the study this February, which marked the index’s 25-year anniversary. The next chart shows the cumulative total returns for those 35 stocks. This time, I created five groups, ranging from 1,000%-plus grand slams to money-losing strikeouts.
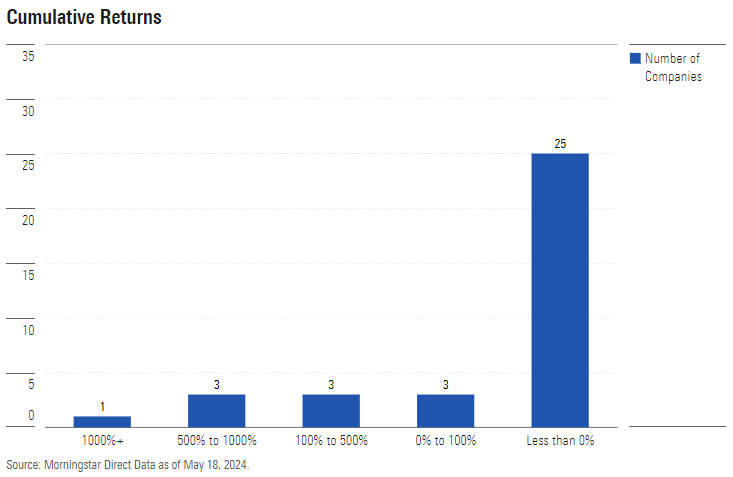
Make that ‘grand slam’, singular. The only 10-bagger on the list, to use Peter Lynch’s term for a spectacularly successful investment, was an online retailer with the peculiar name of Amazon.com AMZN. Three companies gained between 5 and 10 times their original outlay, and three more at least doubled their money. That was it for the triumphs. No other stock kept pace with inflation over the period. Nearly all finished in the red.
That most stocks stink is no secret. Long-term equity performance is asymmetrical, with a few winners carrying almost all the baggage. But internet startups seem to have carried that principle too far. Over stock market history, found professor Hendrik Bessembinder, 51% of all stocks have suffered negative lifetime total returns. Among the 35 internet stocks, though, the failure rate was 71%, or 25 of the 35 entrants. That is a tough hurdle to clear.
The portfolio
I then measured how the entire portfolio would have performed. For that exercise, I used only the 23 stocks that existed in March 1999, because the proper comparison for AI stocks is when the sector is booming, as with AI today and internet companies in spring 1999, rather than after a downturn has already occurred. I split a $10,000 one-time investment among those 23 companies and let the portfolio ride—no trades, not even rebalancing.
One question remained: How to treat stocks that were acquired? After some deliberation, I decided to invest the proceeds into the Morningstar US Market Index. Ignoring that money would understate the portfolio’s return. On the other hand, employing other assumptions—such as dividing the proceeds among the portfolio’s remaining companies—would add complexity without meaningfully altering the conclusions. So, the simpler approach it was.
The illustration below contains four comparisons: 1) The entire internet portfolio, 2) the internet portfolio without Amazon, 3) the previously mentioned Morningstar US Market Index, and 4) inflation.
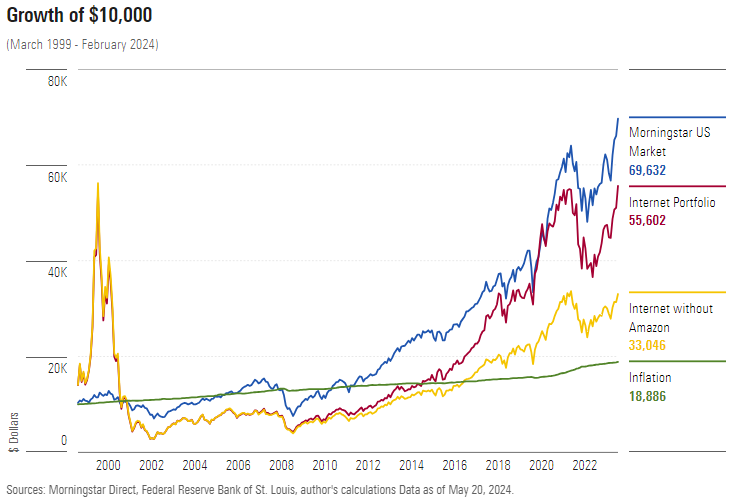
The good news for the internet portfolio was that, albeit with spirit-breaking volatility—the reason the internet funds vanished—it eventually surpassed inflation. What’s more, if the portfolio had contained another company that became as successful as Amazon, it would also have outgained the US stock market. The bad news, of course, is that investment ‘ifs’ don’t pay the bills.
Conclusion
This result surprised me. When beginning the project, I already had Amazon in mind and figured that a few champions such as eBay EBAY would have propelled the internet portfolio to relative victory. But the winners were too few and their gains insufficient. Only VeriSign VRSN, eBay, and Priceline (now Booking Holdings BKNG) beat the overall stock market, and not by a very wide margin.
This test is a sample size of one, but it strikes a cautionary note. At least with internet stocks, most of the industry’s future leaders arrived not with the first wave of technology, but the second. In effect, the companies in the first wave threw ideas against the wall hoping to find one that would stick. The firms that succeeded them learned from their predecessors’ mistakes. They benefited rather than suffered from arriving later.
For those with the patience to own an investment as volatile as the AI sector, buying and holding a stock basket might make sense. However, based on internet stocks’ history, one need not rush to do so.
John Rekenthaler has been researching the fund industry since 1988. He is a columnist for Morningstar.com and a member of Morningstar's Investment Research Department. The views of the Rekenthaler Report are his own. The author does not own shares in any securities mentioned in this article. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor. Originally published by Morningstar and edited slightly to suit an Australian audience.
Try Morningstar Premium for free