A decade ago, over 40,000 SMSFs a year were being established. It’s now closer to 20,000, but that looks more like a maturity than a sector decline. The 2019 Vanguard/Investment Trends SMSF Reports show funds are being established when trustees are at a younger age, and one in five institutional super fund members is considering setting up an SMSF in the near future.
Superannuation remains a contestable and growing space, despite the banks withdrawing from wealth management and many fund managers struggling to retain money.
The Reports show responses from 5,000 SMSF trustees and 300 financial planners who advise SMSFs. This sector holds $750 billion compared with $1.8 trillion in all the large funds. There are now 600,000 SMSFs with average assets of $1.2 million, although the more meaningful median measure is $693,000, usually between two members. At $350,000 each to last for decades of retirement, SMSFs are not only used by wealthy people.
More defensive and diversified
Despite low interest rate, SMSFs remain heavily invested in cash and cash products, rising to 25% of assets in 2019 at the expense of a small drop in unlisted managed funds. Over the last eight years, the amount in listed investments such as ETFs, LIC and REITs has doubled, with much of it now going into fixed interest and global equities.
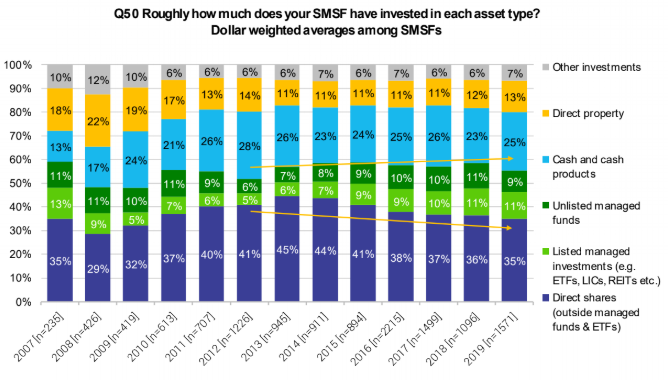
Source: Investment Trends 2019
SMSF trustees intend investing further in blue chip shares, with 54% nominating this investment choice for the next 12 months. While SMSFs are seeking overseas exposure, 52% of respondents still cite lack of knowledge about overseas markets and currency risk as a barrier.
Explaining the defensive mood, 31% say building a sustainable income stream is the main investment goal, while a rapidly-rising proportion now at 15% say protecting their assets against market falls is the main goal.
Unmet need for advice
SMSF trustees want advice on estate planning, tax and income strategies, post-retirement planning, portfolio strategies and investment selection. About 15% of trustees say managing their SMSF takes more time than expected, with investment selection the clear leader among the hardest aspects of running a fund.
The number of SMSF trustees who use a financial planner remains unchanged but overall satisfaction among clients is at a seven-year low. With multiple responses allowed, SMSF trustees say lack of confidence in adviser expertise (32%), the level of fees (29%) and difficulty finding a skilled adviser (22%) are the three main reasons for unmet advice needs. About a third (36%) of advisers expect their SMSF business to increase over the next three years.
Movements between types of funds
The Reports show 20% of large super fund members are considering setting up an SMSF, including 5% already doing it and 5% planning the move in the next 12 months. However, most of these are stated intentions and far fewer people actually take the step.
On the other hand, between 2013 and 2019, there is a massive increase in the number of trustees who have considered closing their SMSF and moving to a large fund, from only 4% to 20% (17% industry fund, 3% retail fund). The Royal Commission was a major factor, as well as the franking debate.
However, Investment Trends CEO, Michael Blomfield, said many factors favour retention of SMSFs:
“Number one is that people think their fund is performing okay. They also want greater access to certain asset classes, including property, infrastructure, small cap funds and responsible investment options, and to be able to give them greater weighting. It is also the flexibility to choose which managers they use, whether they use listed solutions or unlisted solutions, or they opt to buy Australian firms directly to access specific sectors.”
The Investment Trends/Vanguard Reports also show the thoughts of potential new SMSF trustees. While reasons such as ‘more control’ and ‘to achieve better returns’ are high, it’s a little disconcerting that ‘advice from a friend’ is the main factor, while accountants and financial planners remain highly influential. It begs the question whether an SMSF is in the best interests of so many people, especially when 17% say they ‘can make better investments than super funds’.
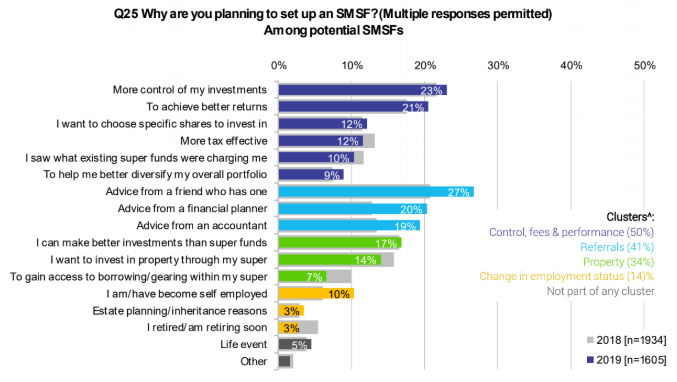
Source: Investment Trends 2019.
It is also becoming more common to hold an institutional super fund as well as an SMSF, with half of new SMSF trustees also retaining their former super fund, perhaps for access to favourable insurance rates. This was only 29% as recently as 2017.
Graham Hand is Managing Editor of Cuffelinks. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.