One of the greatest risks facing retirees today is the uncertainty over how long they might live. How do you plan your retirement when you don’t know how long you need your savings to last? Whilst an individual’s lifespan can never be known with complete certainty, the more information retirees have on how long they are likely to live, the easier it will be to make sustainable retirement plans.
The most commonly quoted life expectancy figures are from the Australian Life Tables and are based on the whole population. If we allow for recent trends in improving mortality to continue, these tables show that 65 year-old Australian men have a life expectancy of 87 and women, a life expectancy of 89. However, different cohorts of the population will live longer than others.
Wealth and education lead to longer lives
Research from around the world has shown that wealth and higher levels of education are strongly correlated with longer life expectancy. SMSF trustees are, on average, both wealthier and better educated than the average Australian so they are one such cohort that might be expected to live longer than the average.
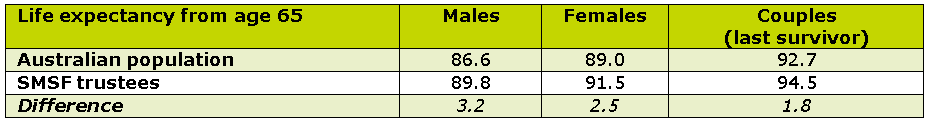
In the first research of its kind in Australia, Accurium’s SMSF Retirement Insights paper, SMSF Trustees - healthier, wealthier and living longer, carried out a mortality investigation on the 65,000 SMSFs in its database to test this hypothesis and calculate how much longer SMSF trustees might live. The results showed that SMSF trustees can expect to live around three years longer in retirement than average.
The table below shows the life expectancies of SMSF trustees in retirement compared to the population as a whole:
Half will live even longer
While life expectancies are helpful for retirement planning, few people will live to their exact life expectancy. Even amongst SMSF trustees, only one in six will live to within a year either side of the life expectancies shown above. Life expectancy is just an average. In fact over half of SMSF trustees will live beyond this.
Many retirees want greater certainty that their savings will last for life so it can be useful to look at the probabilities of living to older ages. Accurium’s research predicts the proportion of trustees who will survive to each age in retirement. These figures can be used as confidence levels for retirees when setting their retirement planning horizons. The table below shows the age trustees retiring at age 65 should plan for with differing levels of confidence:
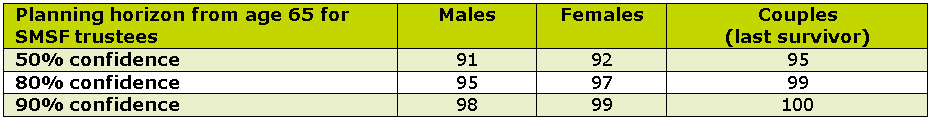
For example, one in five 65 year-old women with an SMSF is expected to live to age 97, therefore those wanting 80% confidence in their retirement plans should be planning for their savings to last around 32 years. A couple wanting 90% certainty should be planning for living for a further 35 years to age 100.
The price of long lifespans is a high cost of retirement and requires trade-offs between how much an SMSF couple spend each year in retirement and how much risk they are willing to accept around outliving their capital.
‘Typical’ couples may need $1.3 million to $2.5 million
Accurium estimates that a 65 year-old couple wanting to spend $70,000 each year and willing to accept an 80% probability of a successful outcome would need $1.3 million as an SMSF starting balance; those wanting to spend $100,000 a year would need a starting balance at 65 of $2.1 million. To achieve 95% certainty that they won’t outlive their capital, that same couple would need $2.5 million if they wished to spend $100,000 per year.
Exactly how long an individual is expected to live has been found to be affected by a number of different factors as well as age and gender. Factors that are known to influence individual life expectancy include smoking, genetics (e.g. family history of certain diseases), current health problems (such as diabetes), occupation and geographic location. SMSF trustees retiring in good health are likely to fall into the higher percentiles for life expectancy and should be planning accordingly.
An important conclusion is that, while fewer SMSF trustees will pass away in the early years of their retirement compared with the population as a whole, a greater proportion will live to their mid-nineties. SMSF trustees can have greater certainty over how long they will live.
Longevity risk for a retiree isn’t the risk that they will live a long time; it is the risk that they will live longer than they have planned for. As long as trustees set their retirement plans using appropriate time horizons, this research shows that SMSF trustees really can have their cake and eat it. Not only will they live longer than the average Australian, but they actually have less longevity risk too.
Doug McBirnie is a Consulting Actuary at Accurium. This information is factual and is not intended to be financial product advice or legal advice and should not be relied upon as such. You should seek appropriate professional advice before making any financial decisions.