When looking to purchase an investment property, most buyers consider location, purchase price and tenanting ability, while depreciation is often overlooked. Depreciation can unlock the cash flow potential within an investment property, often resulting in thousands of additional dollars for the investor each financial year.
Announcements made in the 2017 Federal Budget may change some of the eligibility for depreciation, but investors should not overlook where it remains available.
What is depreciation?
As a building gets older, items wear out – they depreciate. The Australian Taxation Office (ATO) allows property owners to claim this depreciation as a tax deduction by any property owner who obtains income from their property.
Capital works deductions are based on the historical cost of the building excluding the cost of all ‘plant’ and non-eligible items. As a general rule, residential buildings which commenced construction after 15 September 1987 and commercial properties after 20 July 1982 are eligible for the capital works allowance.
Although these time restrictions apply, older properties have often undergone renovations. Renovations completed within the legislated dates can also entitle the owner of the investment property to deductions, even if the renovations were completed by a previous owner.
Common depreciable items in an investment property
Plant and equipment items, commonly known as removable assets, are also eligible for depreciation deductions (but see comment on 2017 Budget later). Each plant and equipment item has an effective life set by the ATO which determines the deduction.
Some plant and equipment depreciable items commonly found within a property include hot water systems, dishwashers, carpets, blinds and curtains, light shades, ovens, furniture, range hoods, smoke alarms and cook tops.
Case study
An investor has purchased a property for $420,000 and is receiving $490 per week in rent for a total income of $25,480 per annum. The estimated expenses for the property include interest, rates and management fees, which total $32,000 per annum. The following scenario shows the investor’s cash flow with and without depreciation. A typical $420,000 unit will show a total deduction of $11,500 in the first full financial year.
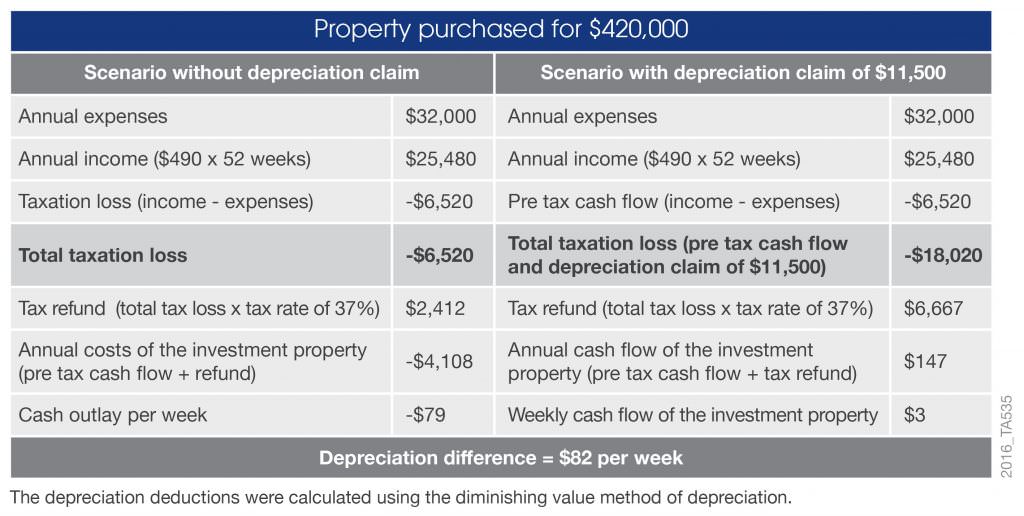
In this example, the investor uses property depreciation to go from a negative cash flow, paying out $79 per week, to a positive cash flow scenario, earning $3 per week, saving $4,255 for the year.
Claiming depreciation during renovation
When old assets like carpet or hot water systems are replaced during a renovation, the owners may be entitled to claim any residual depreciation as a tax deduction. Property owners should consider a pre-renovation depreciation schedule and update an existing tax depreciation schedule after work is completed to ensure they capture deductions for any new items added during the renovation.
Changes in the 2017 Federal Budget
Under proposed changes, investors who exchange contracts on a second hand residential property after 7:30pm on 9 May 2017 will no longer be able to claim depreciation on plant and equipment assets. Investors who purchase a new property will be able to continue to claim these items as previously.
We are currently speaking with government to further understand the intricacies relating to the proposed changes.
Claim property depreciation this financial year
To maximise cash flow, investors should engage a specialised Quantity Surveyor to complete a tax depreciation schedule. The fee for a tax depreciation schedule is 100% tax deductible. The schedule will show deductions for the life of the property (40 years) and will ensure the property owner improves the return on their investment.
Bradley Beer is the Chief Executive Officer of BMT Tax Depreciation, a leading provider of tax depreciation schedules for investors. This article is general information and individuals should seek their own tax advice.