Some of us worry more than we should: what if this happens, what if that happens?
That said, truly awful events and disasters do make us at least wiser and cautionary. Bushfire losses, floods, typhoons, economic depressions, nasty car accidents, burglary, serious assault and other traumatic episodes in our lives or the lives of others can be traumatic.
But there are usually more good things, progress and happiness in our lives than bad things.
We live longer than any generation since the days of Methuselah. We have cures or preventions for all manner of ills and pains. We are safer at work, at leisure, in sport and on the roads. We live in dwellings with far greater comfort than mansions and castles of old.
Our standard of living is rising exponentially with only some setbacks from time to time as the first exhibit shows convincingly. We have had four depressions and 22 recessions over the past 225 years from 1788, but they are well and truly outweighed by growth years. Our standard of living today is 4½ times higher than 1913, and over 9 times that of 1813, 200 years ago.
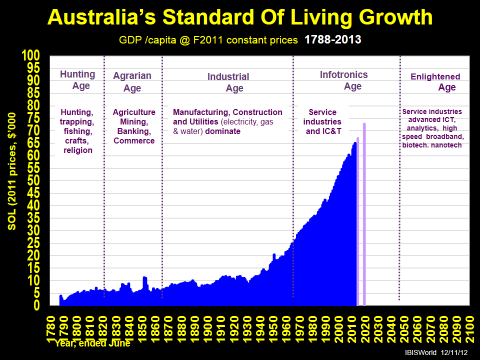
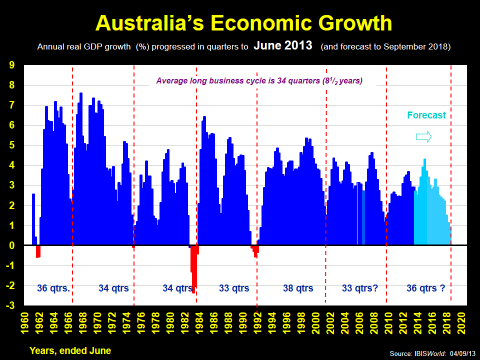
Even if we take a much shorter time frame - the last half century - the news is still good, as the second exhibit reveals: only three recessions, and none in over 20 years since 1992.
These days we measure confidence as well as talk about it. Before 1970, talk is all we could do as there was only opinion, anecdotal evidence and scuttlebutt.
The Consumer Sentiment Index (CSI), created monthly by the Westpac/Melbourne Institute tells us about the propensity to spend money at the household level. It’s important given that household expenditure accounts for 54% of the economy directly, and over three-quarters of the economy indirectly via our taxes and housing capital expenditure. It shows quite volatile changes at times, as we will see shortly, but is a good bell-weather indicator of the economy for 3-6 months in advance.
But businesses need to be careful to avoid long term decisions based on consumer confidence, as they are based on short term perceptions by individuals. Most people do not think much further out than 9-12 months on most things except perhaps schooling, holidays and a change of residence. Business decisions, especially about strategy and capital expenditure, require time frames of 3-5 years and often longer. That is where business confidence indicators are more relevant.
So, where does consumer confidence fit in all of this? Firstly, it should be said that growth in consumption expenditure - over 70% of the economy - has never been negative in any year since the end of World War II. It may be taking a step too far to suggest we can thank female steadiness for this, unlike criticising males for the opposite with investment. Boards of directors are over 85% males and the volatility in capital expenditure range is enormous (+12% growth to 10% falls!) compared with consumption expenditure with a range of 1-5%, and all positive.
Of course, consumer sentiment can turn negative even if spending doesn’t. The third chart shows the 12 month progressive average of the CSI over the past 40 years. At 100 points there is a 50:50 split between positive or negative opinions for the year ahead. Anything below 100 points could be a worry, except history shows that the index has to fall below 83 points for a recession to eventuate. That has occurred only twice over this period, in 1982-83 and 1991-92.
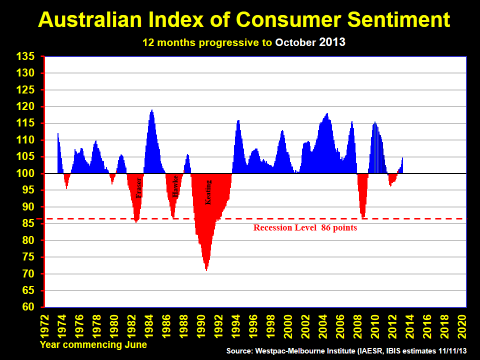
So there is a dichotomy between this volatility (± 15 or more points), and much narrower 1-5% spread (all positive) in actual consumption spending, as said before.
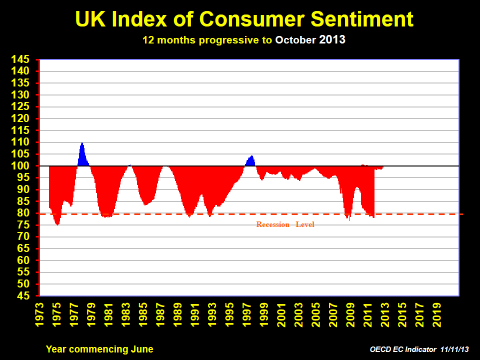
And should anyone still think we aren’t all that confident, a look at the history of the CSI in the UK, the fourth chart below, should render them silent if not speechless at the near-perpetual misery in the Old Dart. How do you make a Pom happy for more than four or five years in a century?
The irony is that up until the GFC in late 2008, the UK economy had been growing at a somewhat similar rate of growth as Australia. Perceptions, national psyches and inherent cultures are often at odds with reality.
Confidence is important but can be misleading in terms of what is actually going on. Our emotions, which make us human, need to be balanced by facts from time to time to remind us that things are rarely as grim as they seem, are not grim for long, and we should celebrate the immense progress in longevity, health, living conditions, leisure and happiness.
Often.
Phil Ruthven is chairman of IBISWorld, Australia’s best-known business information corporation, and he is also a director of other companies, advisory boards and charitable organisations.