Many Australians are concerned about the proposed additional tax on super balances over $3 million and are looking for strategies to keep their balance below this threshold.
For those with high balances, staying below the threshold would require taking money out of super. Typically, this can only be done after meeting a condition of release such as retiring or reaching the age of 65.
What about those who are yet to meet a condition of release? Are their options limited until they retire or attain age 65?
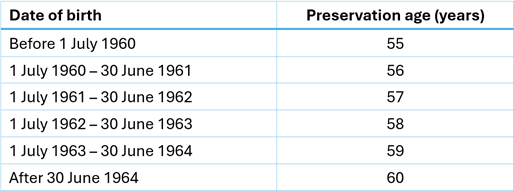
Not necessarily. After reaching preservation age, a Transition to Retirement Income Stream (TRIS), allows people to withdraw an income stream from their superannuation balance before they retire. Preservation age is the age at which you can access superannuation and depends on when you were born. It was age 55 for those born before 1 July 1960 and has gradually increased to age 60 for those born after 1 July 1964.
How a TRIS works
A TRIS allows super fund members to gradually move toward retirement by accessing a limited amount of their super balance before they stop work completely. They must satisfy their minimum annual pension requirement but cannot withdraw more than 10% of their TRIS balance in one financial year.
Drawing a TRIS becomes most tax effective after the age of 60, when the income stream payments become tax free.
There is no upper limit for a TRIS account, unlike the transfer balance cap which limits the amount people can have in a pension account to $1.9 million after meeting a condition of release. The TRIS does not count toward a member’s transfer balance cap until they enter retirement or attain age 65, whichever comes first.
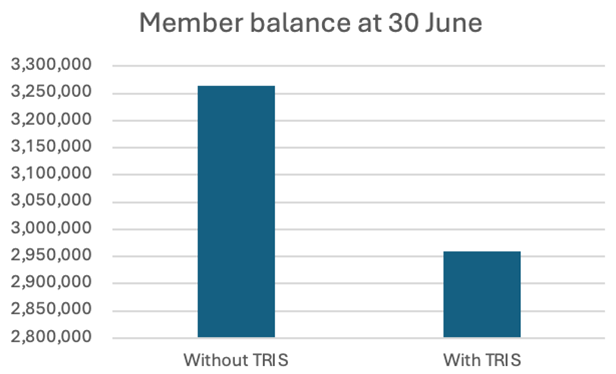
Take the example of John who is 62 and has a total super balance of $3.05 million. If John were to commence a TRIS with his full balance, he could withdraw up to $305,000 from his super balance in one financial year tax free.
Assuming his account produces investment returns of 7% for the year, his balance would reduce to $2.96 million after withdrawing the $305,000.
A drawback of the TRIS, and reason why this strategy is not as popular as it once was, is that earnings on the assets supporting the TRIS balance do not receive the same tax-free treatment as earnings on a pension balance. Instead, income is taxed at the standard rate of 15%, with capital gains taxed at 10% as is the case during accumulation phase.
Setting up a TRIS
First a member must decide how much of their total super balance they wish to convert to a TRIS. A TRIS account is distinct from the members accumulation balance and typically requires the establishment of a new account. Those in a retail super fund will need to open a new member account with their super provider. If they are still contributing to superannuation, they may have two member accounts, an accumulation account to contribute to and a TRIS account they are withdrawing from.
Setting up a TRIS within an SMSF may be simpler. Once the fund assets are valued to determine the members benefit a TRIS account can be set-up within the SMSF, alongside the accumulation account if the member is still contributing. Establishment paperwork would need to be completed by the member.
Key points about starting a TRIS:
- A TRIS can be started at any point during the financial year.
- A minimum pension must be withdrawn during the financial year. For those under the age of 65 the minimum percentage is currently 4%.
- The minimum pension may be pro-rated if the TRIS commenced after 1 July during the financial year.
- The member cannot withdraw more than 10 per cent of the TRIS balance in one financial year.
Super rules are complex, so it’s important to get advice before implementing any strategy.
Who should consider a TRIS strategy?
Those between the ages of 60 and 65, who are yet to retire and wish to access to their super balance, are most likely to see the benefits of a TRIS strategy.
It could also be a way for people to reduce their total super balance, giving them the opportunity to equalise super amounts between spouses or transition wealth above $3 million into other investment structures.
The proposed legislation to introduce the tax on super balances over $3 million is yet to be passed and there is growing doubt over whether it will pass in its current form due to opposition in the Senate.
If passed, the legislation would come into effect from 1 July 2025, meaning a member’s total super balance would only be assessed at 30 June 2026. So, there is no need to rush to implement any strategies. Members have time to seek advice and consider the available options before making changes to their superannuation strategy.
Lindzi Caputo is a Wealth Management Director at HLB Mann Judd. This article is for general information only. It should not be accepted as authoritative advice and any person wishing to act upon the material should obtain properly considered advice which will take into account their own specific circumstances.