The financial advice sector is experiencing a form of market failure. That is, market demand for the type of advice now favoured by the industry - comprehensive personal retirement planning advice - is severely limited by the cost of supplying it, often exceeding $5,000 for an initial engagement and $3,000 in annual service fees thereafter.
It is only in wealthy pre-retirees with complex retirement planning needs where the service that the financial advice sector offers currently intersects with a willingness and capacity to pay. If one were to assume this cohort represents 20% of those approaching retirement each month, this equates to only 4,000-odd prospective clients for the nation’s 16,000-odd advisers to engage with and compete for on a monthly basis.
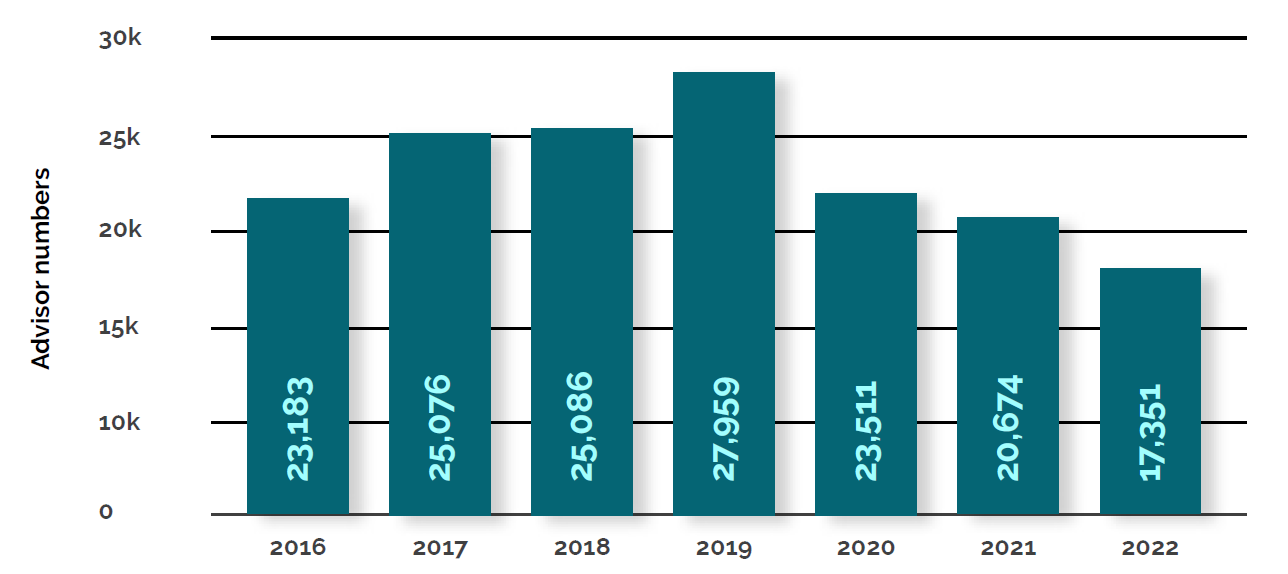
It should be apparent that the entire financial advice sector chasing this same, small addressable market is not a recipe for organic growth.
What might an alternative future for Australian wealth management look like? And what are the conditions to facilitate it? The following are suggestions that we believe will assist the financial advice sector to regain lost ground and, more importantly, create the foundations for sustained growth into the future.
Applying the Tinbergen Principle to financial advice
The Tinbergen Principle is named after Dutch economist Jan Tinbergen, the first economist to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Economics. In essence the principle states that in addressing complex economic dilemmas, sustainable solutions require as many instruments as there are policy objectives.
Which is a fancy way of saying “one size does not fit all”.
For financial advice, there is one dominant ‘instrument’ being bluntly applied to the varied advice needs of Australians of varying demographics, socioeconomic circumstances, financial literacy, engagement preferences and price point sensitivities.
This instrument is comprehensive pre-retirement personal advice, encapsulated in an unwieldy Statement of Advice (SOA), implemented via an adviser-directed investment/super solution, with ongoing fee arrangements still dominated by the percentage of ‘Funds Under Advice’ (FUA) model.
The advice sector could continue with this approach, and it would almost certainly perpetuate the issues currently constraining advice accessibility, as well as its own growth prospects. Or it can choose a different path.
Matching advice models to consumer needs
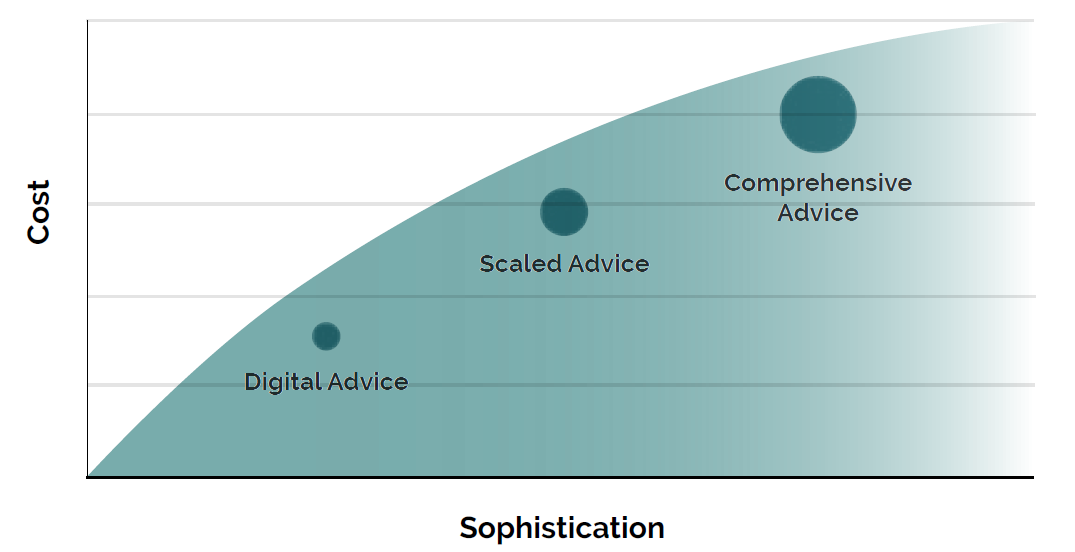
There needs to be a recognition that Australians engage with the financial services sector across multiple decades in ways that shift over that time span. Their needs differ according to their life-stage, and forward-thinking advice models ought to be able to cater for these life-stage cohort preferences.
In addition, research into engagement preferences suggests that consumers have varied preferences for how they choose to engage with their finances, and a ‘traditional’ financial advice relationship with a financial adviser is only one option.
The ASIC Financial Advice Report of 2019 found 31% of those surveyed said that they had received financial advice or guidance from family, friends, or colleagues, while 23% had done so from information found online.
Similarly, even when consumers become engaged with their finances, there are a range of preferences that extend beyond receiving financial advice and/or outsourcing complex financial decisions to an adviser.
At the High Net Worth end of the market, CBA research into SMSFs found that only 22% of survey respondents were ‘Coach Seekers’ and 13% ‘Outsourcers’, those more likely to engage with financial advice on an ongoing basis.
Quite remarkably, 30% described themselves as ‘Self-Directed Investors’ with a preference for a DIY approach toward financial decision making, while 35% were ‘Controllers’, eager to do things themselves, but open to some advice to support their decision-making. For these individuals, an online SMSF admin solution, coupled with a next-gen investment platform and some episodic advice from a Financial Adviser may be all that is required to meet their needs.
Right across the age and wealth spectrum, from Gen Z commencing their wealth journeys to wealthy Baby Boomers with sizable assets in their SMSF, the notion of ‘one-size-fits-all’ is no longer appropriate.
Technology to the fore
The rapid adoption of all things digital in daily life since the initial COVID lockdown of March 2020 points to the possibilities for advice productivity that is still untapped in the sector.
Workarounds to lockdown, such as online virtual advisor/client meetings, the rise of electronic signatures over ‘wet ink’ and the improvement of adviser/client interactivity within leading-edge investment platforms allow advisers to better leverage their time and resources.
These developments will not regress in a post-COVID world.
Rather, forward-thinking licensees and advice practices need to revisit the entirety of the FinTech and AdviceTech landscape to look for ongoing opportunities to increase prospect engagement and reduce the cost of advice provision.
One such example is the CRM, often considered the heart of any financial advice operation. Advice CRMs have been a slow work-in-progress since the 1990s, with the rise of server technology and the ubiquity of the internet leading to advances in CRM capabilities in the years since.
Yet the seamless integration of all the aspects of running an efficient financial advice practice, from prospect engagement to financial modelling to advice provision to the implementation of recommendations (possibly incorporating investment/platform account opening) to ongoing servicing and advice remains elusive.
Part of the reason is that advisers may not be using existing advice CRMs to their full capabilities. Also, the lack of integration between different advice technology systems means that data captured in one system may not flow freely into another to be leveraged for productivity gains.
The advancements in API usage, led by a host of FinTech start-ups over the past several years, represents a large and underappreciated opportunity for advisory groups to drive productivity upward while restraining, and possibly lowering, the cost of advice provision.
A host of novel FinTech applications, from robo-advice to next-gen investment platforms, have conclusively demonstrated that many aspects of traditional advice workflow can be automated to a large degree. AML/CTF client identification and compliance via API calls to relevant databases being only one such example. Automated account opening being another.
Legislative/policy interventions
While technology can help in increasing productivity, the opportunity to improve financial advice affordability and accessibility rests even more so with amendments to the legislative framework surrounding advice provision.
There is a reticence to sail outside the ‘safe harbour’ enshrined in the definition of best interest duty, with the ‘catch-all’ provision of Section 961B(2)(g) proving particularly problematic.
While this remains the case for personal financial product advice, risk averse compliance committees will continue to enforce advice workflows that preference costly comprehensive advice over less expensive, lighter touch scaled advice.
It is therefore hoped that the current inquiry by the Australian Law Reform Commission into Australia’s financial services legislation, including a review of key definitions such as ‘Financial Product Advice’ and ‘Retail’ v ‘Wholesale’ client definitions will yield recommendations for pragmatic changes to Chapter 7.7 of the Corporations Act 2001
Alternative models – Guidance and assistance
Finally, in respect of the Tinbergen Principle, there must be an acceptance that even with legislative relief, an abundant adaptation of AdviceTech and FinTech and all the goodwill the advice sector can muster, there will be a cohort of Australians who will still face barriers to accessing financial advice.
This may be due to a lack of financial literacy and proficiency in dealing with advisory professionals. It may be due to financial circumstances, with price inevitably being a barrier for some even were advice costs to fall over time. Or price may not be a barrier, it may simply be an individual preference to remain a ‘Controller’ or to continue with a ‘DIY’ strategy.
Whatever the reason, a well-rounded financial services sector would have a range of viable alternatives to attaining financial advice from a ‘traditional’ provider.
Robo-advice, while not anywhere near the penetration of the US or Asia, is one such example. Here consumers with more modest requirements can ‘self-serve’ within the confines of a regulated environment where choices are deliberately constrained to avoid consumer choice overload.
Next-generation investor-directed portfolio services (IDPS) where consumers can choose either a DIY experience or to have some guidance from a Financial Adviser are another such example.
These solutions point to a hybrid advice future, where the interaction between consumer and adviser might evolve along a spectrum over time, starting with a highly digital, near self-serve model and evolving toward a human-centric relationship as retirement approaches.
Beyond the constraints of the current legislative edifice, the concepts of ‘Guidance’ and ‘Assistance’ should be brought in from the cold to sit in between General/Personal Advice on the one hand and Factual Information on the other.
The recent Budget submission by Super Consumers Australia, in calling for a government-funded retirement guidance service in-line with the UK’s Money and Pension Service where consumers can gain access to impartial guidance on a range of retirement planning issues, points to a possibility.
The Melbourne University ‘FinFuture’ white paper of 2019 proceeded in much the same direction, calling for the establishment of a National Financial Wellbeing Agency that would be tasked with improving the financial wellbeing of the nation in aggregate.
These and other ideas need to sit alongside the push toward appropriate legislative relief and amendments spearheaded by the Levy Review and the ACLR Review, and the continued advancement of AdviceTech and FinTech into the fabric of the Australian financial advice sector.
Harry Chemay has more than two decades of experience across both wealth management and institutional asset consulting. An active participant within the wealth and superannuation space, Harry is a regular contributor to investment websites in Australia and overseas, writing on investing and financial planning. Brett Ebedes is a financial services industry consultant who specialises in working with and solving the business problems of financial services participants.
The full report "Australian Wealth Management at the Crossroads: Where to from here?", including detailed references and important disclaimer information, can be viewed here.