With the exception of the immediate post World War II period, history is not kind to equity markets when interest rates are low and not falling. Either interest rates remain low, in which case we have a Japan-type situation, or interest rates rise and we finish up with negative equity risk premiums (that is, the return that the equity market provides over the bond rate is negative). Either way the outcome is not good for equities.
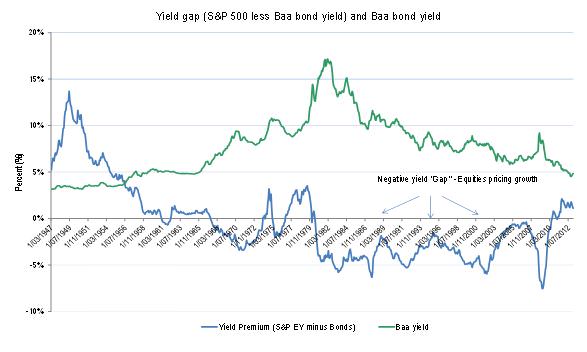
The chart below shows the yield gap or margin between the earnings yield on the S&P 500 and the Baa bond yield since 1947 (when equity yields exceed bond yields, the margin is negative). The chart also shows and the outright level of Baa bond yields. When the yield gap is positive, Price/Earnings are relatively low. When the yield gap is negative (line below the horizontal axis) investors are buying equities at lower yields (higher P/Es) than Baa bonds because they are anticipating economic and earnings growth. Note that earnings yield (E/P) is the inverse of the P/E ratio.
Two trends are apparent. Firstly, interest rates have been falling steadily for the past 30 years and secondly, over much of the same time frame the US has experienced a negative yield gap (i.e. investors are pricing in earnings growth).
Does the yield gap matter?
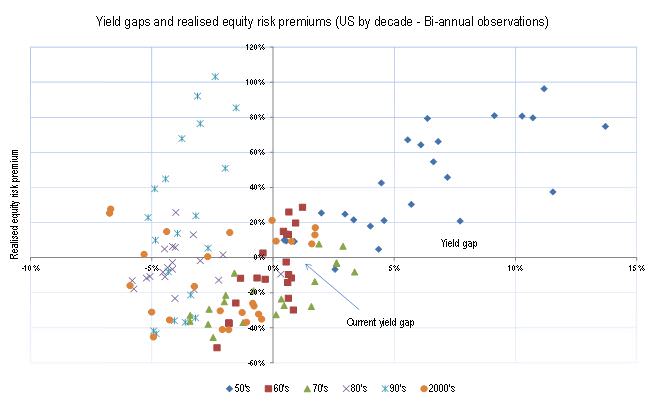
In the following chart, we have compared the yield gap on the horizontal axis and subsequent realised equity risk premiums on the horizontal axis. A positive yield gap results from either relatively low Baa bond yields or low P/E’s with the realised equity risk premium being the difference between the Baa bond yield at the time and the subsequent 5 year equity returns.
If equities outperform Baa bonds, a positive equity risk premium exists. A position in the top left hand quadrant indicates negative yield gaps (expensive P/E’s or high bond yields) and equity markets performing better than bonds, while the bottom right hand quadrant indicates positive yield gaps where bonds outperformed equities.
A bit of history
There were two decades where equities outperformed Baa bonds: the 1950’s and the early 1990’s. In the case of the 1950’s, it was after a 15 year period when there had been a global depression and a world war. Not surprisingly, there may have been some pent up investor pessimism, but despite this both GDP and earnings grew strongly contributing to the excellent equity outcomes.
The early 1990’s was another interesting case where a combination of good GDP growth, after the 1991 recession, produced explosive earnings growth and there was some P/E contraction. Interest rates fell strongly over the period which would have affected both the economy and P/E contraction. Sadly, most other decades haven’t been as rewarding.
What are the lessons?
If history repeats or even rhymes, it’s not looking particularly positive for equities despite the low absolute level of interest rates and undemanding P/E’s. This is because it is the direction of interest rates rather than the absolute level of interest rates that seems to be a substantive driver of equity returns. Prior to the 1970s, rising interest rates meant poor future equity market returns.
We have just experienced a 30 year bull interest rate market and have no more recent parallels. Within the last 30 years most periods when equities outperformed bonds have occurred when interest rates are ‘falling’ rather than when interest rates are ‘flat’. Interest rates are currently at emergency lows and are more likely to rise than fall from this point. Based on past evidence, equities are unlikely to outperform bonds in this case.
And if interest rates don’t rise? The only parallel we can find for a case of sustained low interest rates is Japan and that is not a pretty outcome for equity markets. Equity markets in Japan have underperformed bond markets in 12 of the 15 rolling 5 year return periods since 1993. This translated to a gross equity underperformance of the bond market by a staggering 70%.
Norman Derham is on the executive at Elstree Investment Management. Elstree is a boutique fixed income fund manager.