The market share of ETFs and index trackers keeps rising and with it concerns about reduced market efficiency. In theory, if everyone would simply track an index, new information would no longer be reflected in share prices, and it would become highly profitable to be active and short stocks with negative news flow while buying stocks with positive news flow. This theoretical argument shows that there should be an equilibrium between index funds and active investors or that markets stop working. But where that equilibrium is, is anyone’s guess.
If we look at the latest figures from the Investment Company Institute about ETF market share in different countries (note this is across stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities, so the numbers are lower than equity markets alone) we can see that in Anglo-Saxon countries, ETFs and index trackers typically have a much higher share than in continental Europe. Japan and South Korea seem to follow more the US and UK example, which is why we should consider Germany, France, or Switzerland outliers (there is a future post in that statistic somewhere).
Market share of ETFs across all major asset classes
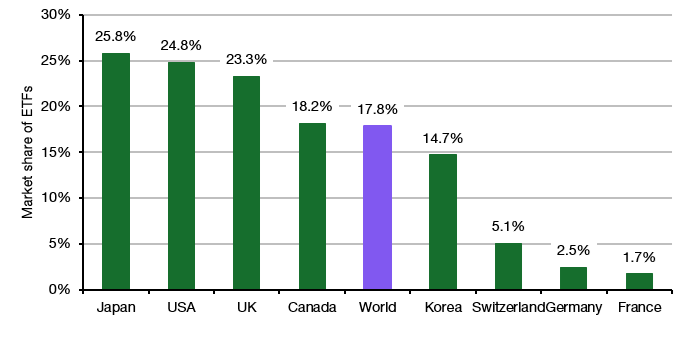
Source: ICI, The Investment Association
The question is whether the market share of 15-25% reached by index trackers today is the peak. I doubt it and I expect index trackers to continue to gain share for many years to come.
But there are also increasing signs that with the rising share of index trackers, markets are becoming less efficient, particularly in the large-cap space.
Theresa Hambacher reviewed the last 20 years of research on index funds to see if index funds really reduce market efficiency and if active managers can drive markets back toward efficiency if too many investors switch to index trackers.
Her literature review concludes that the majority of studies show that the rise of index investing creates an ‘index inclusion effect’. Historically, this index inclusion effect meant a price jump in stocks that are newly included in an index and a drop for stocks that are excluded. But this price impact has declined significantly and all but disappeared in the US.
Nowadays, the index inclusion effect is more related to other metrics, most notably an increase in liquidity in stocks in an index. With this increase in liquidity also comes an increase in investor attention and a somewhat higher valuation. The increase in investor attention leads to higher institutional ownership, higher analyst coverage, and increased media coverage. But it also has other, more material effects. Most notably, increased liquidity and higher valuations reduce the cost of capital for both debt and equity capital and thus give index constituents an advantage over smaller stocks that are not part of the index.
On the other hand, there is ample evidence that market efficiency and price discovery decline if index funds capture a larger share of the market. This should in principle give an opening for active managers, who on average increase price efficiency and take advantage of market mispricing.
The reality, however, is more complex. Market efficiency is driven by a whole lot of factors, not just the share of index funds. This means that if active funds capture market inefficiencies and make markets more efficient, this does not drive investors away from index funds. Instead, markets may adjust in such a way as to become more efficient without reducing the market share of index funds. Plus, market efficiency is not the only driver of index fund market share. Hence, active funds may outperform index funds and improve market efficiency but get no reward in the form of higher market share. Instead, index fund investors may simply free-ride on the work of active fund managers.
These two effects are not new. They have been known for some time. But taken together they imply that the market share for index trackers may well increase past the optimal level and stay there for many, many years. And there seems very little if anything that active managers can do to reverse that. Hence, we do not know where peak ETF is, and while active managers provide a valuable service in making markets more efficient, they are not necessarily rewarded for it by capturing a larger share of investor assets.
Joachim Klement is an investment strategist based in London. This article contains the opinion of the author. As such, it should not be construed as investment advice, nor do the opinions expressed necessarily reflect the views of the author’s employer. Republished with permission from Klement on Investing.