Australia’s mix of industries in its economy is broadly similar to all advanced economies. It is dominated by the fast-growing information and financial sectors (quaternary) as well as health, hospitality, culture and other service themes (quinary), as we see below.
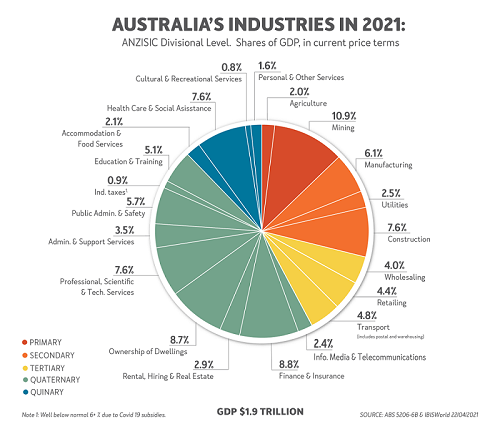
Indeed, these two sectors, mainly growing fast in the post-industrial age since the mid-1960s, now account for almost 60% of our GDP.
Agriculture is tiny but mining stands out
Agriculture is a fraction of the importance it had in the 1960s and is nearly as tiny a share as the USA’s 1% of their GDP, such has been the increasing capital-intensity of agriculture that has displaced its millenniums-long labour-intensity.
But our mining industry stands out with over 10% of our GDP compared with other developed economies where this industry is a quarter or less of that importance. And it is reflected in our exports where over half our half our $400+ billion are minerals. More if downstream manufactures are added.
Stock market weightings, Australia v US
Which leads to our industry shares in the stock market, which is skewed both by minerals and financial services. As shown in the exhibit below, these two industry divisions account for a whopping 55% of the ASX's total market capitalisation.
This mix stands in vivid contrast to that of the USA, where these two divisions account for around 17% (a sixth) compared with Australia’s well over a half.
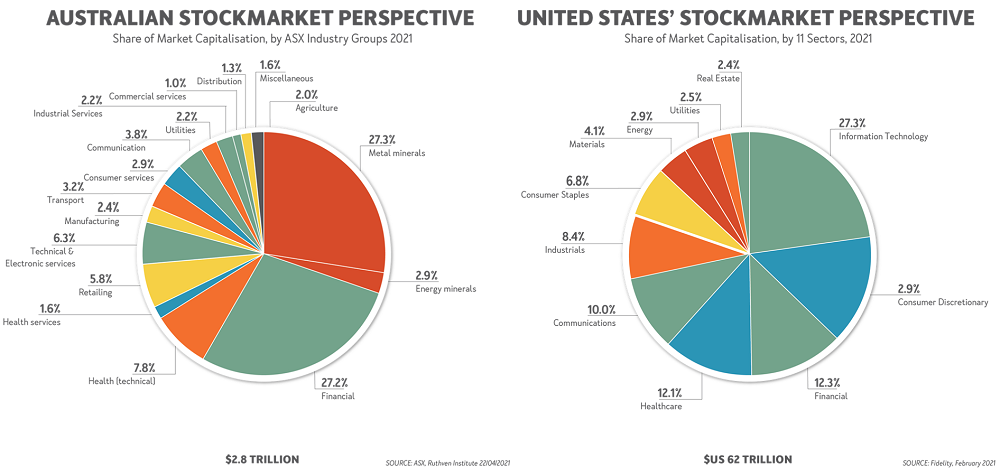
The USA has a stock market much more in tune with the new Infotronics Age of services, information and communication technologies (ICT) that displaced the goods industries and utilities of the Industrial Age up to the mid- 1960s. Their information technology sector (23% of the market capitalisation) rivals our mining industry for relative size. Then add the communications sector (10%) and ICT in total is a third of the market. It is bigger than either our minerals sector or financial services sector.
But does that explain our underperformance?
Does our skew to minerals and financial services explain why our All Ords has underperformed both the Dow Jones and NASDAQ for over 30 years and been left in their wake in the last 10 years?
No, that’s not the reason: profitability and wealth creation (dividends and share price growth) are independent of the industry. Any industry can have players with world best practice (WBL) performance. We have WBP performers in all our 19 industry divisions (as described in the first exhibit on our industry mix). As does the USA and most other advanced economies.
Other explanations often used are equally untrue, including: population size, fewer hi-tech companies, distance from markets, corporate tax regime and others.
Why are Australian companies not more profitable?
About one in 10 Australian companies achieve WBP profitability over 5-year periods while four in 10 companies do so in the USA.
The real reasons why we are lagging are more fundamental. We break too many of the keys to success rules and the most frequently breached are shown in the table below. We have to get smarter and understand strategic planning much better than we currently do.

Phil Ruthven AO is Founder of the Ruthven Institute and Founder of IBISWorld. The Ruthven Institute was created to help any business that wants to emulate world best performance and profitability using the Golden Rules of Success, based on over 45 years of corporate and industry analyses and strategy work. The Ruthven Institute is happy to provide a fuller explanation of these 12 Golden Rules.