Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) can add material shareholder value to companies that get it right. Conversely, failure to deliver anticipated M&A benefits will either result in destroying shareholder value, or in extreme cases, put the entire company at risk.
Acquisitions require detailed execution and integration plans that identify key issues and focus on the early delivery of synergies. M&A inevitably increases staff workloads and management will need to ensure the existing core business is not overlooked or compromised. Success rates are dramatically improved if a company has a good management team, robust systems and processes and a board with M&A capability and experience. The most successful acquisitions will typically increase earnings per share (EPS), increase the net present value (NPV) per share and provide a short payback period.
Current conditions for M&A
The current environment is generally favourable for M&A as interest rates are low and the economy is expanding slowly, so companies are attracted to opportunities that supplement low organic growth. The main negative is that valuations are comparatively high. In FY16, the value of M&A exceeded $30 billion. Larger deals included:
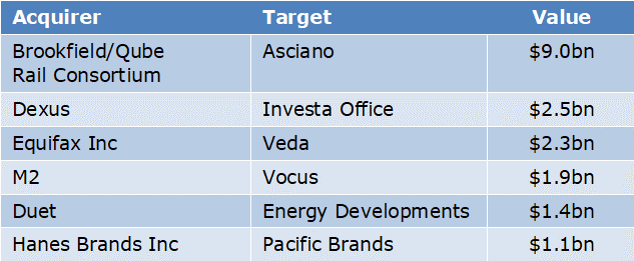
Over 40% of acquirers were overseas companies with private equity accounting for nearly 20% of overall activity.
Friendly takeovers traditionally result in a completion rate of ~80% compared to hostile bids with a lower success rate of ~50%. Premiums in friendly deals tend to be lower, averaging between 20-30% compared to 50% in hostile bids. Hostile acquisitions are considered higher risk due to the additional price premium and limited due diligence that is typically undertaken.
Case studies show value creation or destruction
1. Justifying the premium paid
Most companies obtain cost or revenue synergies when making acquisitions which allows them to pay a premium. The most common example is the elimination of a target’s financial, legal and other head office functions, which reduce unit overhead costs as they are typically spread over a larger revenue base. This has been a reason given for acquisitions by several companies including G8 Education, although synergies may also be gained from integrating existing systems or operating the additional centres in a cluster managed by an existing staff manager.
2. Cost synergies are more convincing
Significant cost synergy savings are generally available in the financial sector. For example, Westpac’s acquisition of St. George Bank and CBA’s acquisition of Bankwest resulted in significant head office and systems cost reductions as back offices were integrated and branch networks rationalised.
3. Boosting future organic growth
Acquisitions that contribute to future organic growth include Motorcycle Holdings, the top motor-bike seller in Australia, acquiring dealerships as part of its growth strategy. It is the only player of scale with funding in the industry, and it is able to acquire dealerships at low prices. As several dealerships only sell new bikes, it increases acquired dealership profitability by adding second hand bike sales along with accessories, finance and insurance to supplement new bike sales.
National Veterinary Care has made several vet clinic acquisitions since listing. After an acquisition, it typically introduces its ‘Best for Pet’ loyalty program, which generates increased revenue and profitability. It also identifies additional revenue streams such as dentistry and trains vets if they are not already performing this work.
4. Organic growth for both acquirer and target
Telco and software company, MNF, recently acquired Conference Call International (CCI), which provides audio conferencing to 5,000 customers. MNF will obtain organic growth by offering these services to its own customer base as well as offering its own existing products and services to CCI’s customers. MNF will also obtain cost savings by moving CCI’s customers onto its global voice network. MNF has a history of organic and acquisition growth, having delivered double EPS growth over several years and astute acquisitions provide it with a significant future growth runway.
5. Knowing what you’re getting in friendly acquisitions
Steadfast is the largest Australian insurance broker and has been a serial acquirer. A key growth strategy is to acquire interests in insurance brokers, which join its network. Steadfast’s subsequent knowledge of their profitability reduces its acquisition risk as it often consolidates ownership of these brokers.
6. Knowing what’s in the box in hostile acquisitions
Downer made a hostile bid for Spotless after a significant drop in Spotless’ share price. Although Spotless has highlighted new long-term contract wins and renewals, formal due diligence was not permitted. Acquisition risk therefore remains despite Spotless claiming the bid is opportunistic and should be rejected.
CIMIC recently acquired Sedgman and United Group opportunistically at the bottom of the cycle. Although these were similar, hostile acquisitions, the acquisition risk was again partly mitigated as relatively low prices were paid. Unfortunately, this can’t be said for Rio after it heavily overpaid for a coal asset in Mozambique and ALS, which bought an oil company at top of the cycle. Both not only destroyed significant shareholder value but also put the companies under pressure due to elevated debt levels. The assets were subsequently divested at much lower prices.
7. ‘Di-worsifying’ by making a large overseas acquisition with a broken business model
Arguably, the worst type of acquisition is ‘di-worsification’, that is, acquiring a new, different, large-scale business, potentially in a new geographic area. Slater & Gordon’s acquisition of Quindell’s Professional Services Division in the UK is an example that went ahead despite questionable management practices, poor profitability and poor cash flow. It paid a high price for the operation which also required a large equity raising. The disastrous result is well known.
Conclusion
M&A done well can be highly shareholder accretive, but healthy scepticism can save investor dollars. Investors should be particularly sceptical of M&A that simply increases earnings that trigger management rewards but does nothing to increase earnings per share or NPV/share.
Matthew Ward is Investment Manager at Katana Asset Management. This article is general information only.