US economist Frank Knight was the first to draw a distinction between 'risk' and 'uncertainty' in his 1921 book, ‘Risk, Uncertainty, and Profit’.
Risk is what many investors in portfolio construction address, using statistics like expected mean returns, standard deviations and cross-asset correlations.
Uncertainty, according to Knight, is when you simply do not know what could happen, when even the basic parameters are unknown.
The impact of new technology in retailing, for example, is not just a risk for the retail property industry, but fundamental uncertainty. In the same way, the fact that global monetary policy is in unchartered waters means that the problem investors face is not just risk, but uncertainty.
Furthermore, risk models may not work if the environment in the future is fundamentally different to the recent past. Therefore, uncertainty and backward-looking risk models in a changing environment are both critical today.
Today’s main 'uncertainty' problem is extreme low rates
Our starting position is unusual and extreme. Balance sheet recessions in the Northern Hemisphere have resulted in the lowest rates in recorded history in the United States, Japan, the Euro zone, and the United Kingdom in this cycle. These extraordinary rates are the result of balance sheet recessions that followed debt-fuelled property booms.
Given that Australia’s residential prices peaked higher than those in the United States, Euro zone and United Kingdom and that Australia’s household debt is higher than household debt in those countries, Australia may also experience a balance sheet recession. Under that scenario, rates will move even lower than they are now, despite the cash rate reduction to 1.25% this week.
There is also the opposite (and recently forgotten) risk of inflation. All of these northern countries have engaged in non-standard monetary theory, such as quantitative easing. In the United States, there is also late-cycle fiscal stimulus and speculation about Modern Monetary Theory (MMT), a new acronym for an old idea: the government printing money to spend it.
The established theory in the 1970s, 1980s, and 1990s was that a combination of large government deficits and money printing was the best way to generate high inflation. Yet the example of Japan, where despite extraordinary fiscal and monetary stimulus, inflation has still not emerged, means that MMT is no longer viewed as the best theory of inflation.
In fact, today, we do not have one agreed theory of inflation, which is why some government officials advocate experiments like MMT. The risk is, of course, that there is no such thing as a free lunch, and that if you print money to spend it, inflation eventually arrives and presents the bill.
Portfolio implications and will bonds defend?
In a world of risk and uncertainty, where can investors go to generate adequate returns?
In recent years, bonds have proved to be a successful hedge to falling equity markets, but this is not always the case.
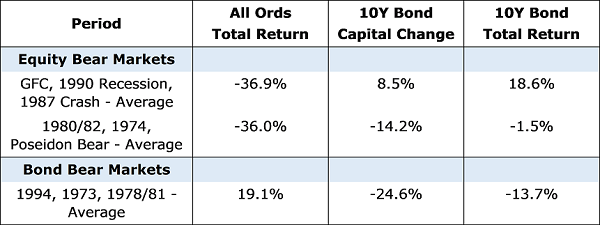
During the GFC, the 1990 recession and the 1987 stock market crash, bonds provided decent off-setting diversification. When the equity market lost a third its value, the bond market, as represented by the 10-year Australian bond delivered about 19%.
But before the great bond bull market that started in 1983, things were different. In the late 1960s, in 1974 and in the 1980 market downturns, equity markets lost about a third of their value, but bonds lost around 14% of capital value and also recorded a negative total return (see table). Given the starting point, the last 35 years may not be the best guide to the future.
The second concern is that from the current starting point of the Australian 10-year bond yield of 1.53%, (as at 29 May 2019), the gains from bonds will be mathematically limited, considering the yield is already near historic lows.
Today’s problem: bonds do not always play defense
investment returns
Source: FactSet, MSCI, Standard & Poors.
Today, the experiences of the last 35 years may not be relevant, with economic models calibrated with decades of past experience perhaps falling into the same trap that caught those valuing mortgage backed securities in 2007.
Think outside the box
If the outlook for bonds is uncertain, asset allocators may have a major problem. Modern asset allocation frameworks are often built on the premise that bonds will act as the defensive part of the portfolio.
Indeed, certain asset allocators may need to re-think their entire portfolio. Equities will have to play a role for the equity yield and the long-term growth. They offer income and inflation protection. However, the benefits come with risks, and some investors may need to think more about their equity exposure and their defensive properties if trouble strikes.
The lesson is that even the growth portion of a portfolio may need to offer defensive properties.
Uncertainty not risk
Risk is often measured on backward looking statistical measures, but this may not offer a guide to the future. The behavior of an asset class at some time in the past, does not mean that it will always behave that way.
In our view, equities are needed for inflation protection and income, and the risk of capital loss from owning equities can be limited by focusing on valuation and more defensive (sustainable yield) equites, given that cash (and not bonds) is the only perfect defensive asset.
Philipp Hofflin is a Portfolio Manager and Analyst on the Australian Equity Team with Lazard Asset Management. His views may not represent those of other portfolio management teams at Lazard Asset Management. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.