The market has been anticipating a US recession for quite some time. Since July 2022, the US yield curve has been inverted, which has often been a precursor to recessionary periods. So far, a recession hasn’t materialised. Economic growth has remained strong, with generally positive corporate earnings reports and unemployment still close to historic lows.
But even if an economic slowdown isn’t imminent, there will be one eventually. The economy moves in cycles, with periods of economic strength followed by contractions and vice versa. Historically, recessions (generally defined as at least two consecutive quarters of declining growth in gross domestic product) have occurred about once every five to 10 years, although the length of time between recessionary periods varies.
It’s impossible to predict the timing or severity, but it’s often only clear that a recession has happened after the fact, or after the market has already started reacting to slower economic growth.
Looking at which types of investments have historically fared best during economic downturns can help limit some of the damage. In this article, I’ll look at investing during a recession from multiple angles, including asset classes, factors, and sectors. Though it's focused on the US, much of it is applicable to Australia too.
Asset classes
From an asset-class perspective, stocks are usually one of the worst places to invest during a recession. Recessions happen when there’s a decline in economic activity, which is usually accompanied by weaker trends in revenue and earnings growth.
Stocks had negative returns in most (but not all) previous recessions dating back to the Great Depression. Some of the worst recent results were during the GFC, when stocks lost an annualised 24% between late 2007 and mid-2009.
Total returns (%) by asset class
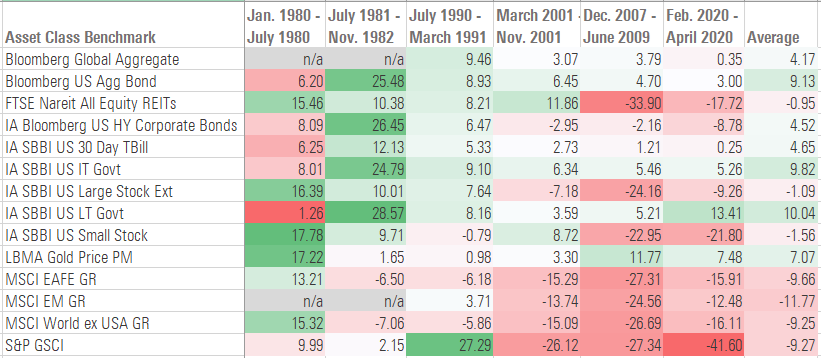
On the flip side, bonds have been the best place in most previous recessions. The Federal Reserve often cuts interest rates in an attempt to stimulate economic growth, also resulting in higher bond prices, with long-term bonds historically faring best during recessions, although intermediate-term bonds and cash have also been pretty resilient.
Gold has also been a winning asset class during recessionary periods, with positive returns during the eight most recent recessions since 1993. But the yellow metal had a relatively anaemic showing during recessions in the early 1980s and early 1990s, with returns were negative after inflation.
Investment style
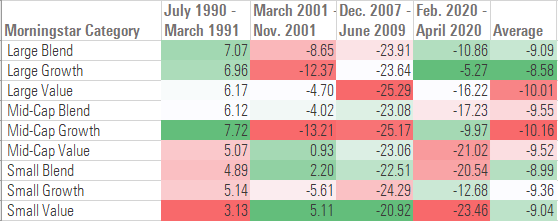
I used Morningstar’s U.S. equity fund categories as a proxy for measuring investment style. As shown in the table below, growth stocks have typically held up better during recessionary periods. Companies that have growth-oriented stocks typically have higher earnings growth, cleaner balance sheets, and better profitability, all traits that often help them hold up better than companies with cheaper stock prices during recessionary periods. But growth stocks haven’t fared well during every recessionary period. Growth stocks were hit hard in the tech-stock correction in the early 2000s, which coincided with a brief recessionary period in 2001.
From a style perspective, large has generally been better than small during periods of economic weakness. Larger companies tend to have more stable earnings, diversified business operations, and the financial wherewithal to sustain their operations even during recessions. Smaller companies, on the other hand, may depend heavily on a single line of business and often have fewer financial reserves to sustain them during recessions.
Total returns (%) by investment style
Equity factors
Equity factors are another way of examining the drivers of equity market returns. Factors describe additional characteristics (beyond traditional metrics such as sector, market cap, and value/growth) that help to explain investment management styles and resulting performance differences.
Because equity market returns are generally negative during a recessionary period, no investment factor consistently generated positive returns. In relative terms, the quality factor has historically fared best during periods of economic weakness. Definitions for quality vary, but the MSCI index that I used for this study focuses on stocks that score well on three main metrics: high return on equity, stable year-over-year earnings growth, and low financial leverage.
Total Returns (%) by Investment Factor
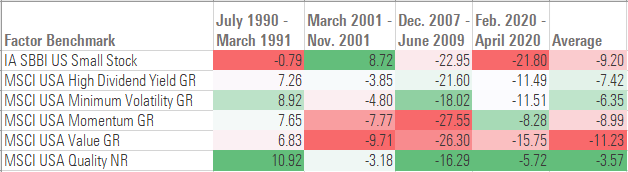
The minimum volatility factor, which is designed to capture stocks with lower betas, volatility, and idiosyncratic risk, has fared second-best, and dividend stocks have also held up relatively well.
On the negative side, the value factor has performed the worst during most recessionary periods by a fairly wide margin. (Note: This benchmark for this factor is similar to the value fund categories I discussed above, but it has more extreme performance traits because it has a more pronounced value bent than the typical value fund.) The value factor tends to be overweighted in economically sensitive sectors, such as basic materials, consumer cyclicals, and financials. This is usually a negative, but the early 1980s’ recession—a “stagflation” period that featured sluggish growth, high inflation, and high unemployment rates—was an exception. The value factor posted the best returns during that period.
Equity sectors
From a sector perspective, healthcare and consumer staples stocks have been the most resilient performers during periods of economic weakness. Consumers can’t easily cut back on prescription drugs, medical devices, or household basics like canned goods and paper towels even if they’re feeling the effects of a weaker economy.
On the negative side, energy and infrastructure stocks have been the hardest hit in recent recessions. Companies in these sectors are acutely sensitive to swings in demand. Financials stocks also can suffer during recessions because of a rising default rate and shrinking net interest margins.
Total returns (%) by sector
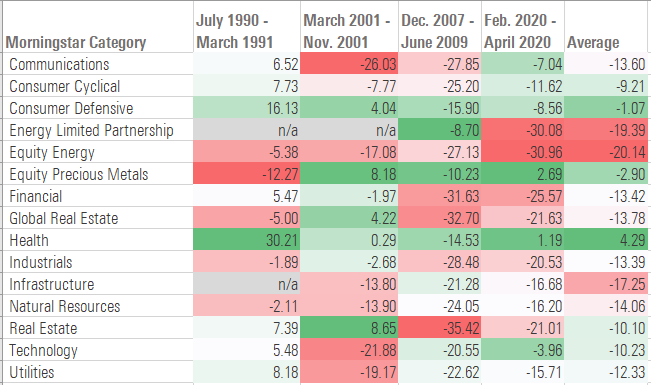
Technology and communications stocks have a mixed record. During the 1990-91 recession amid the Gulf War and oil supply issues, the communications and technology sectors held up relatively well, and tech leaders such as Microsoft MSFT, Apple AAPL, and International Business Machines IBM continued to generate double-digit returns. After surging during most of the 1990s, the tech bubble finally popped in 2000, followed by a brief recession in 2001. Because valuations were still inflated leading up to the recession, the communications and technology sectors suffered the deepest losses.
Does the prospect of a looming recession mean an overhaul of portfolios? No. In fact, making wholesale shifts in portfolio holdings is usually a bad idea. But studying how the market has historically performed can help you set expectations for how your holdings might react if and when the economy weakens.
Amy C. Arnott, CFA, is a portfolio strategist for Morningstar Research Services LLC, a wholly owned subsidiary of Morningstar, Inc. The author owns shares in one or more securities mentioned in this article. Find out about Morningstar’s editorial policies. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor. It has been edited somewhat from the original US version for an Australian audience.
Register for a free trial of Morningstar Premium on the link below, including the portfolio management service, Sharesight.
Try Morningstar Premium for free