Calendar 2020 ended well for shares. Although the coronavirus crisis entered second and third waves in Australia and around the world, there was optimism from:
- the development of vaccines by three different companies
- the US elections that resulted in a Democrat clean sweep, and
- a belief that the worst of the economic contractions are behind us, thanks to huge deficit spending programmes by governments everywhere.
Following are the total returns for the ASX200 index by sector for each of the four quarters, and the full year:
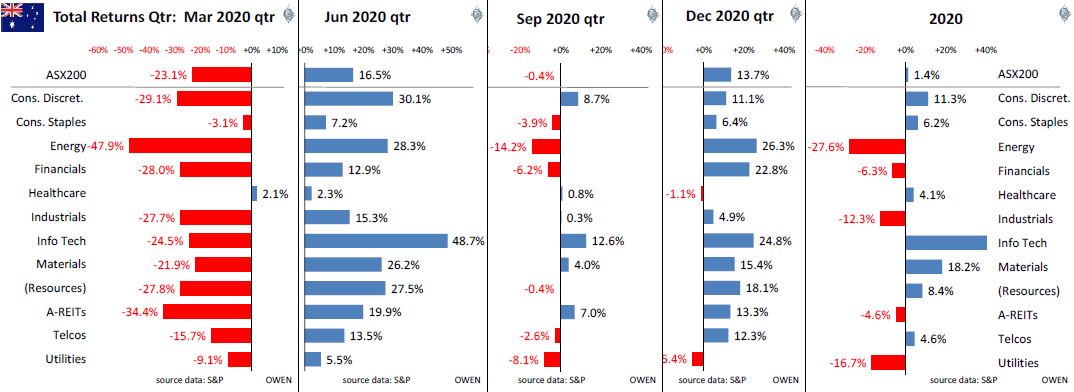
The overall market was back to square in 2020. The best returns for the December quarter were from ‘cyclicals’ in anticipation of easing of restrictions and economic recoveries:
- the big bank (also boosted by the ending of the dividend cap)
- oil/gas stocks (with oil prices recovering 20% on improved global demand outlooks)
- iron ore miners (on a 25% jump in iron ore prices with strong China demand and more export problems in Brazil)
- other cyclicals including gambling dens (Tabcorp, Star Casino), travel stocks (Flight Centre, Qantas), share registries (Computershare, Link), retail property trusts (Scentre, Mirvac), builders (LendLease, Cimic/Leighton), building materials (Boral, James Hardie, Bluescope), and other cyclicals like Seek (employment), REA (housing)
- tech stocks also continued their boom run (mainly Afterpay, Xero, Wisetech).
The main winners for the year included:
- Businesses that benefited from the lockdowns and welfare handouts, including Wesfarmers (Bunnings, Officeworks) and JB Hi-Fi (benefiting from the home office boom), Domino's Pizza (home delivery), supermarkets (Coles and Woolworths), Carsales.com (people buying cars instead of travel), Goodman (warehouses for the online retailing boom in lockdowns), and healthcare stocks (ResMed, Sonic, Ansell, Fisher & Paykel Healthcare).
- Businesses largely unaffected by the lockdowns, mainly in the tech sector: Afterpay (buy-now-pay-later lender), NextDC (data centers), Xero (accounting software), WiseTech (software).
- Iron ore miners Fortescue, RIO, BHP, benefiting from China's stimulus boom and Brazil mine closures and lock downs.
Worst for the year included:
- Oil/gas stocks – Oil Search, Origin Energy, AGL, Woodside, Santos, Worley (oil/gas engineering) – all of the global oil/gas majors around the world posting big losses after the collapse in oil prices in 2020.
- Insurers such as IAG, QBE, Suncorp – hit by a variety of disasters and crises – including some of their own making.
- Banks – hit by bad debt provisions, margin squeeze from rate cuts, lending demand, and regulatory penalties.
- Retail property trusts – most except Goodman (which owns distribution centers for Amazon and other online retailers) and Charter Hall.
- Construction – LendLease, Cimic (Leighton)
- Miners other than iron ore – most were lower due to the collapse in global demand, production, trade, prices.
- Transport stocks hit directly by the lockdowns – Qantas, Sydney Airport, Transurban, Atlas Arteria Brambles, Aurizon
- Some hit by retaliatory China trade actions – Treasury Wines. A2 Milk, Blackmores.
Global share markets
The leading sharemarkets in 2020 were those that had large weightings of companies in sectors that did well in the lockdowns and welfare hand-outs – mainly online retailing, streaming, gaming, social media, hardware, and essential household supplies.
Conversely, countries with weaker share market outcomes (including Australia) had larger weightings of companies in sectors worst affected by the lockdowns – banks, oil/gas, and retail/commercial property.
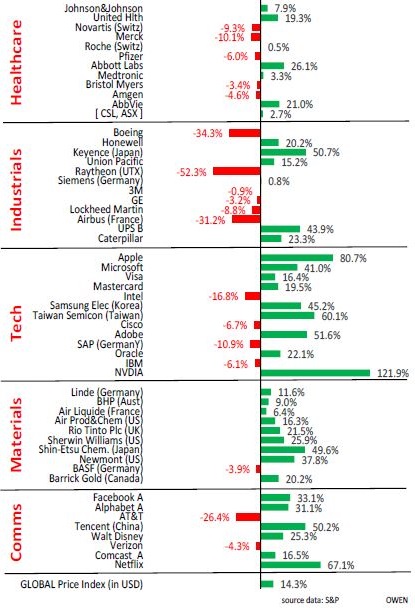
This can be illustrated by showing 100 of the largest global listed companies, organised into industry sector groups. Most of these are household names, and most are US companies, as the US makes up more than half of the global share market value.
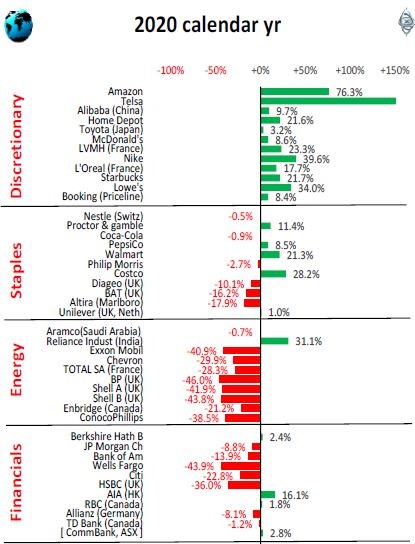
The US tech giants led the world in 2020, but this is obscured by the fact that they are categorised into three difference industry sectors – ‘consumer discretionary’, ‘technology’ and ‘communications’.
The ‘consumer discretionary’ sector was led by Amazon +76% for the year. We now also have Tesla +743% for the year (Tesla was added to global indexes only in December, so its impact on indexes in 2020 was limited) US hardware chains Home Depot (the model for Bunnings) and Lowe’s also benefited from the home office/renovation boom in the lockdowns.
The ‘tech’ sector also did well in the lockdowns and welfare sprees, led by Apple, Microsoft, Adobe, Oracle, Nvidia for the US. Visa and MasterCard (classified as ‘tech’ stocks for some reason) also did well in the online sales boom. Samsung lifted South Korea, and Taiwan Semiconductor lifted Taiwan.
The ‘communications’ sector has the social media giants Facebook, Alphabet/Google, plus streamers Netflix and Disney for the US, and Tencent for China. However, this sector also contains the old style telcos that dragged the sector down (AT&T, Verizon in the US, as did Telstra in Australia).
The healthcare sector had another good year with most shares up, although the coronavirus crisis partially deprived many firms of their normal revenues. (Australia’s CSL doesn't make the global list but is included in the table for reference).
The other winning market was ‘Materials’. In most countries, this refers to industrial materials like chemicals and gases, but also miners like BHP and RIO, which were lifted by the windfall spike in iron ore prices and volumes.
‘Consumer staples’ were mixed – but the winners were Walmart and Costco for the US (likewise, Coles and Woolworths did well in Australia).
‘Industrials’ were also mixed – airplane makers Boeing (US), and Airbus (France) were down heavily, but UPS (parcel delivery) soared in the online retail boom.
Weighing down the market were ‘energy’ (oil/gas and coal) –this is where the US market was less affected by the negative oil price shock; and ‘financials’ (mainly banks) – hit by bad debt provisions, margin squeeze from the rate cuts, and regulatory fines and penalties. (Australia’s CBA doesn't make the global list but is included for reference).
The remaining sectors (real estate and utilities) are smaller, with negligible impact on global markets. Australia has the largest real estate sector, and this was also a factor in Australia's below-average outcome in 2020.
Ashley Owen is Chief Investment Officer at advisory firm Stanford Brown and The Lunar Group. He is also a Director of Third Link Investment Managers, a fund that supports Australian charities. This article is for general information purposes only and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.