Four months have passed since the country and the world were rocked by a pandemic not seen in the lifetime of almost everyone. The virus has caused a major shake-up in the way we work, play, shop and live. There will be huge ramifications for many years to come in almost every aspect of life in the developed economies.
We are all acutely aware of how the virus has affected us personally. In this article, I review the ramifications through the lens of one part of the research done back in 1979 by Michael Porter at Harvard Business School. Porter devised a way of analysing a business by looking at Five Forces which act on it:
- the threat of new entrants
- the power of buyers
- the power of suppliers
- the rivalry in the industry, and
- the threat posed by substitute products.
It’s this last one that I use most to make some predictions on the future of the economy.
Better, easier, cheaper
The threat of substitution comes from customers finding a different way of doing what a business previously did for them. In the case of the virus, various government regulations and lockdowns have compelled consumers to find new ways of running their lives.
Here are five industries that may be profoundly changed by the threat of substitutes.
1. Restaurants
Cafés, food shops and restaurants were effectively closed for months. Many people have learned a new skill: cooking for themselves. They have learned that it’s not that hard to create a tasty meal at home for a fraction of the cost of eating out. Home-cooked food is healthier, can have more variety, can bring families closer together and can save a lot of money. Sure, there are plenty of things that a home cook cannot do but with the lockdown pushing people into the kitchen, many local restaurants which will have to compete against substitute meals cooked at home. Why get a steak at a pub for $30 when you can make one at home for around $6?
Equally threatening, it will be a long time until the social distancing rule of four square metres is relaxed and many restaurants cannot survive devoting so much space to each person.
2. Pubs
Judging by the queues at Dan Murphy’s, people still like to have a drink. With local pubs closed there was nowhere else to venture for a drink but to the bottle shop. And people certainly did venture there. For the price of a pint of beer at the local hotel, people bought four cans of beer at an off-licence. That’s a huge cost differential just to be served a drink in a glass.
And yes, there’s a large social element to meeting at the local pub but for the cost-conscious, the saving from staying home is material. And a big bonus is that you don’t have to travel home afterwards. Pubs will have some hard work and maybe some margin shedding to do in order to bring back customers in the same numbers as before, socially-distanced apart.
3. Gymnasiums
It’s possible that all the home cooking and backyard drinking has put people off gyms completely. Thirteen weeks away from exercise could be the end of a fitness regime for many. But those who maintained their exercise routine while the gyms were closed might have found that their monthly subscription fee was better spent on their own equipment that could be used around the home or in the local park. There are plenty of media stories about people setting up home gyms.
Others may have learned that the treadmill, while it does have a TV and iPod connection, isn’t as much fun as pounding the pavement in your local area. Outside exercise was one of the few excuses allowed for escaping the lockups. My gym has halved fees during the reintroduction period but they’re going to have to do more than that to regain the level of attendance they once enjoyed. The convenience of your own backyard or local park, compared with making the trip to the gym, may be hard to overcome, especially as JobKeeper and JobSeeker benefits are wound back and the purse strings tighten.
4. CBD office space
Early in the pandemic the sales teams at Officeworks and JB Hi Fi could barely keep up with demand as the home office fit outs began in earnest. Office workers now do everything they used to do from the comfort of their home and, if some recent surveys are any indication, many are not keen to revert to the daily commute to the city any time soon.
Consider the Google Mobility Trends on how slowly Australians are returning to the office, with time spent in transit (the purpple line) still 50% less than normal.
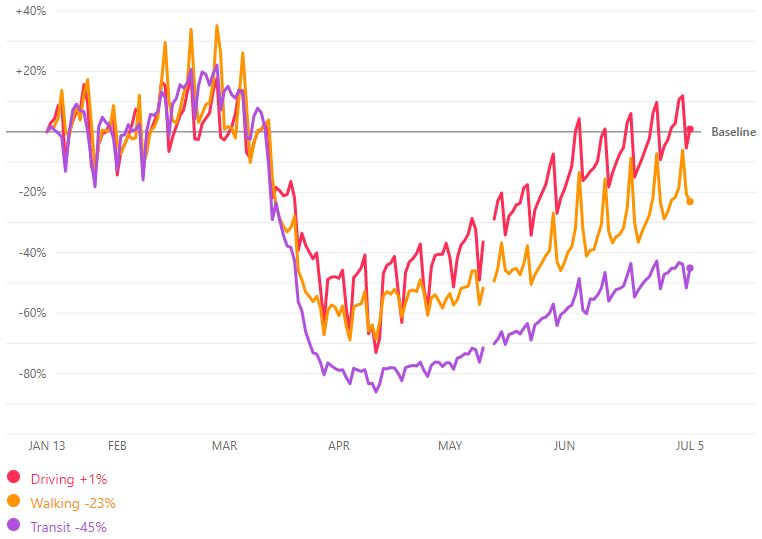
As the virus is recurring in some places, with Metropolitan Melbourne returning to lockdown, life as we knew it seems a long way off. So what is in store for city office space? The cube farm has been replaced by the home office, delighting many workers but doubtless worrying a few commercial property executives who may be wondering how much space will be required by firms when their leases come up for renewal.
5. Air travel
There was a time when the Melbourne-Sydney route was among the busiest in the world with over 54,000 take-offs (and landings!) a year. Now Virgin is struggling and Qantas is slashing staff. The majority of travel was there-and-back business travel. Coronavirus has put a stop to that, and the face-to-face meeting has been replaced by the videoconference. The savings to firms have been massive with one organisation I know slashing their travel bill by over 90%, saving nearly $17,000,000 per year. How can the airlines compete with that?
The productivity increases for firms from not having staff away from the office for a day to attend a two-hour meeting, on top of the flight costs, are unbelievably large. After sustaining the revenue attack from the virus, airlines will be hard-pressed to lower costs enough to entice business travel back to anywhere near the level it was before COVID.
History as a guide
Back in the 1930s the Dupont company was the first to successfully create and sell fully man-made fibre and the market for nylon was born. Very quickly demand for natural silk was decimated and by the late 1940s the market for silk hosiery was almost entirely replaced by nylon. This is one example of the power of substitutes on a company’s fortunes.
Will we see a similar game of substitution play out in the wake of the coronavirus pandemic of 2020? While the use of the alternatives I’ve mentioned was driven by necessity, one of the prime motivators that will help to maintain their use is the considerable cost savings to be had by not reverting to the original product.
Just as nylon cut the cost of silk and vinyl cut the cost of leather, the substitutes for restaurants, pubs, gyms, offices and air travel have put more money back in consumers’ pockets. And with the economy in its current state, it might be impossible to get that money out again.
Angus McLeod writes for The Money Question blog, he is also a lecturer in the Master of Finance course at RMIT University and a former fund manager.