Investing in markets means accepting volatility, but investors are paid to take risk. Why do sharp drops in the market have such a visceral impact on us? This article explores why we feel and react the way we do, and how to develop a sound strategy to deal with volatile markets.
The most recent fall that attracted media headlines, in February 2018, was far from unusual. Since 1979, there have been 182 five-day periods worse than the February decline. It happens, on average, every three months. It’s about as frequent as a 29-degree day in Sydney. Warm, yes, but barely worth a comment.
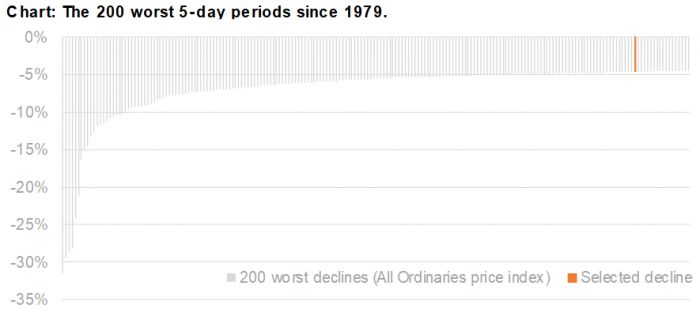
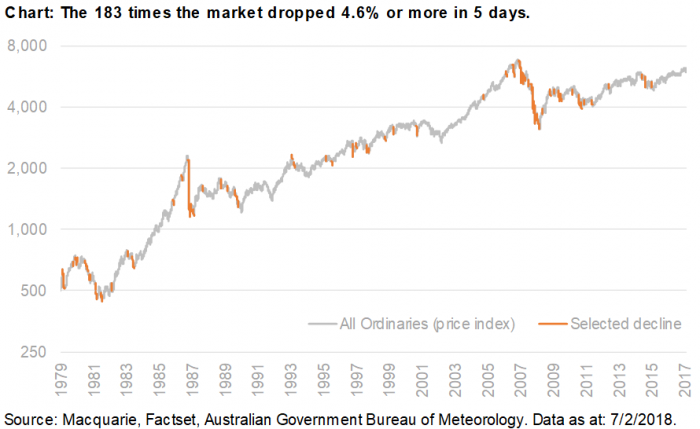
With central banks commencing or stepping up their interest rate hiking cycles and unwinding quantitative easing (QE) stimulus, together with a divergence in monetary and fiscal policies, the result should be greater volatility, and more movements such as the above.
Preparing for the inevitable
So the market fell, and you’re reading headlines claiming billions of dollars of value have been wiped off the stock market in a matter of hours or days. You check into your account and see that your investments have also been affected. What will you do?
What most people do is act. They sell in fear. This is natural, however, it is likely to be the wrong strategy. What should you do? To paraphrase a recent Wall Street Journal headline, ‘The Share Market Isn’t Being Tested, You Are’.
We need to feel in control
Nothing undermines a sense of control over your investments like a sharp and unexpected stock market fall. The immediate priority for many is to re-establish that sense of control. One of the most tempting actions is to do something, anything. This is linked to a deep-seated part of human nature and manifests in a desire to maintain the illusion of control.
In our daily lives, in order to act, we need to be confident in our ability to make an impact. In most cases this confidence can be classified as overconfidence, but without it we might not act at all. Being paralysed by indecision can be as bad as acting with overconfidence.
The tendency for people to overestimate their ability to control outcomes that they demonstrably do not influence has been academically studied and replicated in many different contexts. In the investing context, a study by Barber and Odean found a correlation between overconfidence and active trading and that the active traders in the study underperformed the market.
You will probably have a strong need to know why the market movement happened. It is more than mere interest. Needing to know is linked to the desire to act. Because jumping blind into a strategy feels wrong, we need an insight to give us enough confidence to act. Hence, the pressing need to find out why.
Actions have consequences
Adjusting your market exposure to suit evolving risk and return opportunities can be valuable. However, selling in fear is a powerful behavioural bias that costs investors dearly. Looking at Australian equities since 1983, if you were to sell in fear once a bear market starts (20% down from its peak) and return to the market 12 months later, or when a recovery was underway (rolling 1 year returns reached 10% pa), then instead of a compound annual growth rate of 10% pa, you’d have achieved only 8% pa. This is a costly bias.
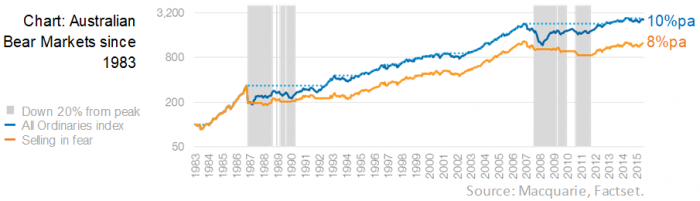
One of many costly biases
There is a panoply of behavioural biases which help us get through the day. They are valuable mental shortcuts that help us act fast, handle information overload and find meaning. Occasionally these mental shortcuts do not serve us well. If everyone is running out of a building, our instinct is to join them, no questions asked. This is a good example of the ‘herding’ bias, and the building could be on fire. However, this same bias in the investing context can be costly. Many studies have measured the costs of these ‘behaviour gap’ biases and estimates range from 1% pa to as much as 6% pa.
What to do
- Recognise that markets are complex. For example, it took the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission five months to report their findings on the cause of the 2010 flash crash.
- Seek advice and consider the impact. Ask why you are making this decision? Is this investment part of an overall plan? What might go wrong? What does the evidence say?
- Record your decision and why you made it. By tracking your decisions, you can reflect on the evidence and adjust or confirm your approach.
Keep your eyes on the prize, whether that prize is growth, income, capital preservation or a mix. Bouts of short term volatility don’t mean allocations have to change. Remember, this has happened before and will happen again. Selling in fear costs real returns in the long term. Financial advice is the best insulation from these and other biases waiting to erode our returns.
James Freeman is an Associate Director at Macquarie Wealth Management, a sponsor of Cuffelinks. This information is general in nature and does not take into account your objectives, financial situation or needs.