[Editor's introduction. In The Sydney Morning Herald on 29 June 2018, columnist and advertising executive Howard Mitchell described how he first met "the brilliant Phil Ruthven" when their businesses were both starting out. "Forty-two years later, his company, Ibis World, has a staff of 450 providing astute forecasts to business and government. Phil’s forecasts about our rapidly changing world have been a key part of my business planning for decades."
The recent taxation bills in Federal Parliament generated the usual heated arguments from the benches. The legislation was in no way ‘reform’ as some claimed, since it only dealt with personal and business income tax, and the GST was left untouched. Many other indirect taxes, such as payroll tax and stamp duties, were also unchanged recently at the state level.
Income taxes versus spending taxes
The broad principle of wealth creation by going easier on taxing incomes and going harder on taxing spending has been ignored yet again. The current ratio of income taxes to spending taxes (such as GST, customs, excise and stamp duties) is over 2.5:1 in favour of income taxes on wealth creation. Hardly a recipe for higher savings and investment as a share of GDP.
So-called class warfare has become the order of the day. Is there substance to the claim that the rich are getting richer and the poor, poorer? Not quite, allowing for the changes in household structures and age groups. More on this shortly.
Wealth and income inequality in Australia
The first chart shows the latest ABS data (FY16) on income and wealth distribution as it applies to quintiles (each one fifth of all households).
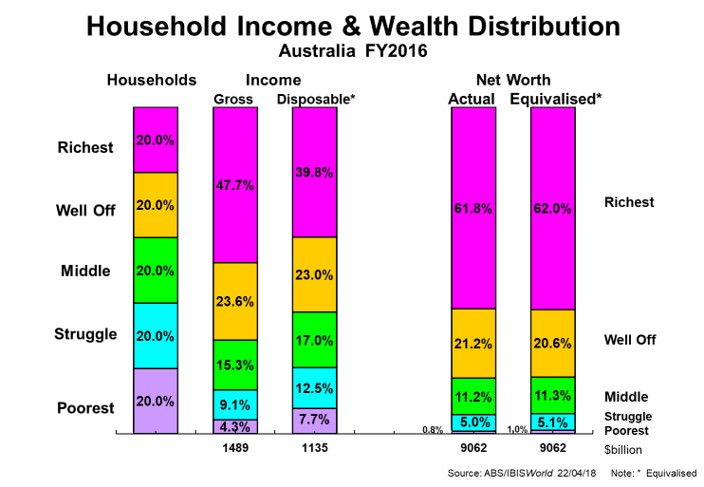
Click to enlarge
Yes, the richest and well-off 40% of all households enjoyed 71% of gross incomes and had 83% of the wealth (net worth). But they paid 87% of all income taxes, and the remaining 60% of all households paid 13% of all income taxes. This diluted the disposable income shares of the affluent 40% from 71% to 63%, and lifted the struggle and poorest 40% of households from 13.4% of gross incomes to over 20%.
So, are the poor getting poorer?
Interestingly, no. The next chart shows the changing distribution of gross incomes over the past 20 years. The Struggle and Poorest sectors have kept the same share, virtually unchanged. In disposable income terms, their higher share has also remained constant. If anything, there has been a slight dilution of the middle-income sector, but hardly anything to write home about.
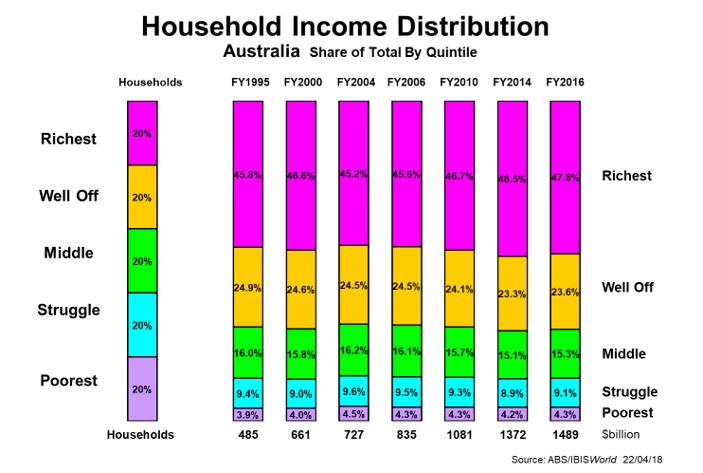
Click to enlarge
Then again, we need to be careful with terms such as ‘struggle’ and ‘poor’. Lest we think of strugglers as being big families with one income, or the poor as elderly pensioners, it isn’t that simple. Among the so-called poor in both income and wealth measures, there are many students at universities with minimal incomes who have not yet had the time to accumulate assets.
Holding up the ‘middle’ quintile’s share are growing numbers of retired baby-boomers, who have had much more opportunity in salaries and wealth accumulation than older generations that experienced the Great Depression of the 1930s and World War II. This is giving them a better lifestyle via their investments. The eventual retirement of the Gen Xers (37-52 years-of-age today) will amplify this trend even more so, given their near-entire working lifetime with superannuation savings. They are more financially savvy too.
The recent tax changes have been about addressing bracket-creep and lowering corporate taxes, in line with overseas trends. The bracket creep issue has not been as great as in the past because of very low inflation and slow-growing incomes, the result of an under-performing economy over the past 10 years.
Are our corporates doing well by global standards?
Some argue that the corporate tax case was not strong considering how poorly our top corporations perform compared with our US cousins, as the final chart shows. Our profitability is half theirs.
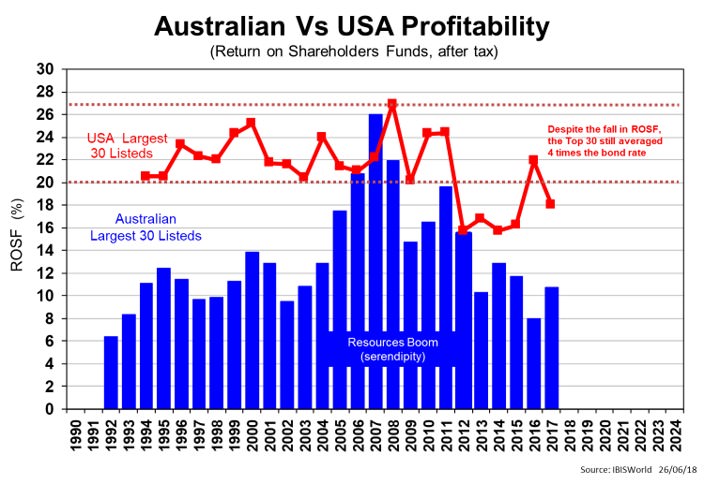
Click to enlarge
If our big end of town wanted to make better net profits, then becoming more profitable by global standards would be better than just paying slightly less income taxes.
It seems genuine taxation reform is on the too-hard list along with other overdue reforms to the labour market, energy market, parliament (lack of the democratic-election principle with the unrepresentative Senate and its obstructionist power), and the Budget (balancing the books).
But compared with other western nations, we are still doing better, and we can preserve the moniker of the lucky country. Phew.
Phil Ruthven is Founder of IBISWorld and is recognised as one of Australia’s foremost business strategists and futurists.