It is no secret that Federal Reserve Chair Janet Yellen is preparing the market for higher interest rates, but how many investors and their advisers know how exposed their portfolios are to meaningfully higher interest rates?
We have been doing the client rounds lately and have been taken aback by how intimidated some clients seem to be by the world of fixed income, and particularly the notion of interest rate duration. Eyebrows rise when we walk them through the potential impact of higher interest rates.
The effect of a general rise in interest rates is straightforward. A bond’s interest rate duration is a measure of its price sensitivity to changes in interest rates. The greater the time to maturity, the longer it takes to receive all the coupons and principal back, and hence generally the more exposed to a change in market interest rates.
A simple way to think about duration
If a bond has a duration of five years, for example, for every 1% move in the nominal level of market interest rates, its price will move by about 5%. In other words, if market interest rates were to rise by approximately 3%, the capital value of the bond would fall by around 15%.
To take the issue of interest rate duration to the next level, and indeed to start to apply some magnitude, it is important to understand how low interest rates are around the world:
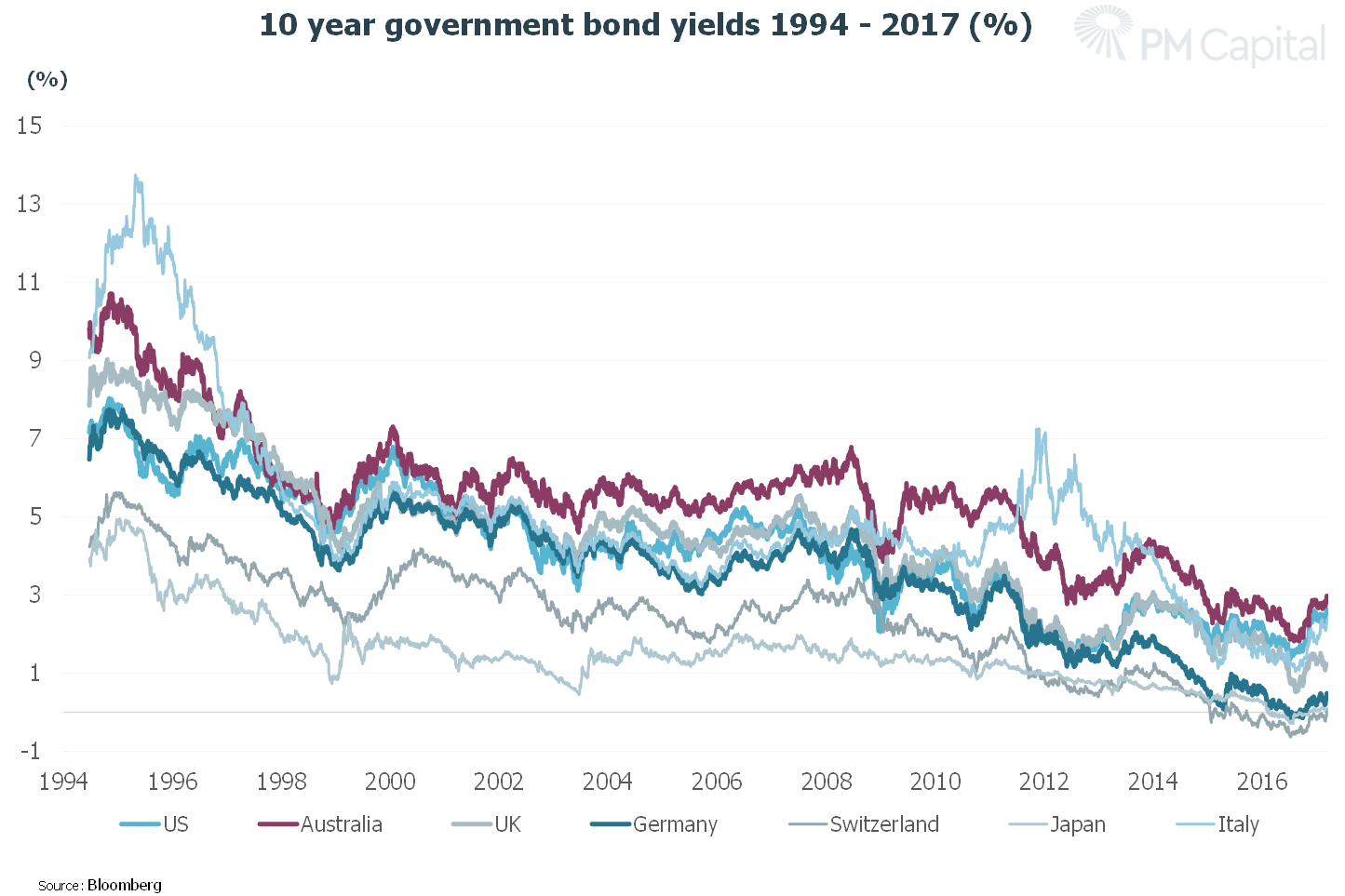
There have been some shorter-term peaks and troughs, but the long-term trend has been going down for decades. Market interest rates went negative in Japan and Germany, and some parts of their interest rate curves still are. However, we now think that we have seen the inflection point in this long-term trend.
The US is a good example. For the better part of a decade, official US rates have been at or below 1%. For a considerable part of this period, the Federal Reserve was injecting huge amounts of liquidity into the system via their quantitative easing program. So, will a more normalised level for US rates longer term be at a lower peak than previous as most of the market is expecting today? Or with the enormous amount of stimulus that has been injected into the US economy over the past eight years, could the peak in the next cycle be notably higher than the market is currently expecting?
Note that prior to the GFC, official US rates peaked at 5.25%, over 4% above where they are today. Additionally, in the 20 years prior to the 5.25% peak, official US rates still averaged just under 5%.
On-the-ground concern about inflation
When we talk to US companies, for the first time in a while we are hearing management report that they are competing for staff and this is pushing up wages. Unemployment in general is low and we are well into the recovery in the US housing market.
Additionally, for years now many US companies have been borrowing at very low rates, in some cases less than 3%, and sometimes with time horizons as long as 10 to 15 years. They are investing that capital back into their businesses, often with the objective of earning around 10-20% type returns or higher.
All of these points will likely feed into growth and inflation over time, suggesting that interest rates should move materially higher in the US in the medium to longer term. This potentially has significant implications for interest rate securities, especially those with meaningful duration.
At PM Capital, we have in effect removed all interest rate duration from our portfolios. This should avoid material negative capital falls due to higher rates, but also, as rates rise over time, the floating rate yields on the securities we own will ratchet up.
Investors should find out the interest rate duration of their fixed income portfolio. Only then can they make a proper assessment as to whether, in a rising interest rate environment, their investments are positioned to deliver the outcomes they are expecting.
Jarod Dawson is Director and Portfolio Manager at PM Capital. This article is general information that does not consider the circumstances of any individual.