When do we know for certain that we are on a path toward recession and that what we are experiencing is not simply a reversion to trend? How can investors prepare? Those questions captured the minds and emotions of investors and pundits alike through the first quarter of 2019.
While some of the global economic data released in Q1 was disappointing, we are not put off. The theme of Vanguard’s 2019 outlook was ‘down, but not out’ as we anticipated some deterioration in economic growth indicators. Holding that view is easier said than done when consumption, income, housing, and manufacturing indicators in several nations signal weakness. Almost in spite of the uncertainty, however, share markets in Australia and overseas returned over 10% for the first quarter.
The yield curve and central banks
It was hard – even for the most steadfast of investors – to ignore the debate around the economic cycle once the US Treasury yield curve briefly inverted in the final weeks of March 2019. When short-term interest rates are higher than long term rates, investors become pessimistic about what could happen in the next year, yet optimistic when looking five to ten years into the future. Traditionally, this pattern has preceded every major US recession in recent memory, so quite understandably, investors are taking these warning signs seriously.
Central banks only added to the feeling that economic storm clouds are gathering. Ironically, their actions might have been intended to instill confidence in their respective economies, but markets, especially bond markets, had none of it. The US Federal Reserve revised its vaunted ‘dot plot’ to suggest that interest rates would be on hold for the rest of the year; they had previously signalled two more hikes. Locally, the Reserve Bank of Australia became more tentative in its official policy communications. Even the Reserve Bank of New Zealand changed its tune and openly discussed the possibility of a rate cut.
Investors are now asking; “What do the banks know that we don’t?”
Economic and market outlook
This questioning comes at a precarious time for the global economy, as we recently passed the 10-year mark from the onset of the Global Financial Crisis. Those who say the US economic expansion must end soon, simply because the expansion has been remarkably long, overlook Australia’s record-setting recession-free expansion in their review of the global economy. Investors feel that we are close to crossing a line, albeit a blurry one, between economic growth reverting to trend (2% in the US, 2–3% in Australia) and an outright global slowdown.
Part of this concern is driven from a tightening of financial conditions. According to our analysis, financial conditions and heightened anxiety over economic policy probably contributed to some of the decline in US GDP growth for the last quarter of 2018. In a recent research note, Known unknowns: Uncertainty, volatility, and the odds of recession, we estimated that these shocks could have subtracted as much as 0.4% from 2019 GDP growth.
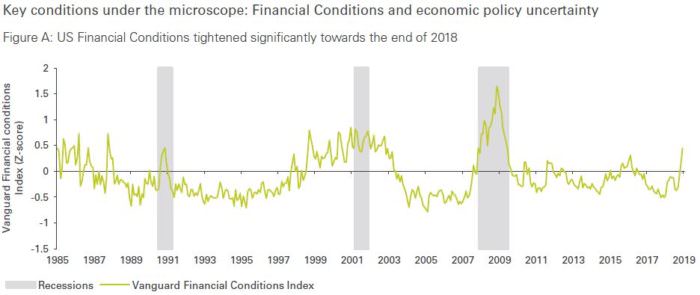
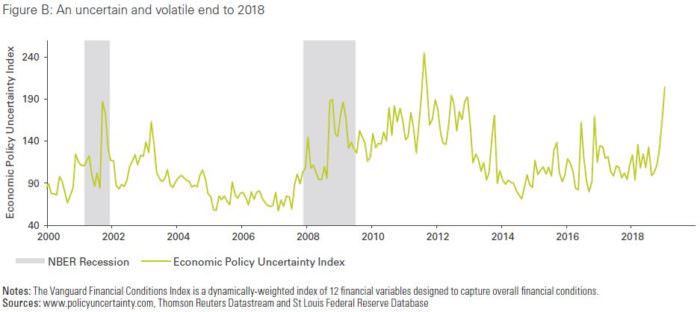
Inevitably, with each new development in this cycle, we are asked by investors what they can do to prepare. Regular readers of Vanguard’s commentary will not be surprised by our answer: revisit asset allocation, diversify, and review active risks in your portfolio.
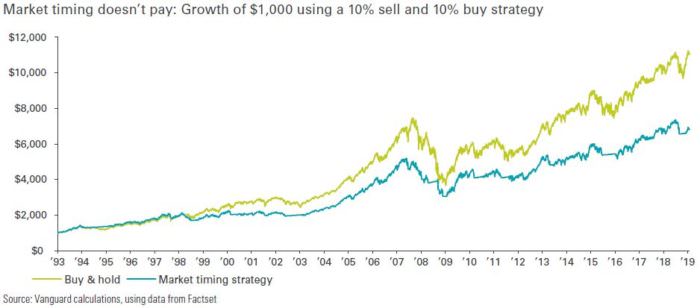
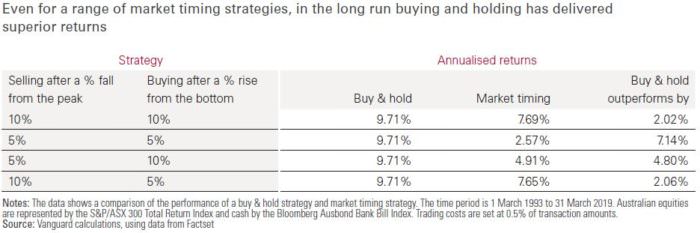
Market timing does not pay
Attempting to time markets can backfire and lead to long term underperformance, as our analysis shows in the figure and table below. The questions investors ought to be asking are: ‘If a recession occurs, how should I respond?’, ‘Am I adequately prepared?’ and, ‘Does my financial plan reflect my comfort with uncertainty?’ rather than ‘When will the next recession occur?’
Adequate preparation, whether increased savings, a new asset allocation, or even a conversation between an adviser and their client, is the best way to prepare. The market will take us for a ride as it tries to guess (with limited success) what will happen in 2019. If we stay calm and adhere to a long-term approach, we limit the effect of the market’s fits and tantrums on our journey toward investment success.
Matthew Tufano is an Economist at Vanguard Australia, a sponsor of Cuffelinks. This article is for general information purposes only and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.
For more articles and papers from Vanguard Investments Australia, please click here.