After a few small wobbles earlier in the year, the chase for yield has resumed, pushing US equities to record peaks and taking credit indices close to their most expensive post-GFC levels. Fixed interest managers are reaching further along the credit rating menu in the search for higher returns. The credit market is sufficiently diverse to cater to different investor tastes in terms of risk and return, however, behind the lure of the high yield lies some not-so-hidden dangers which every investor should be wary of. We examine the case for spread decompression and the near-term catalysts that render high yield debt vulnerable.
High yield more vulnerable with falling inflation
One of these dangers is the evolving broader macroeconomic backdrop. For the first time in the post-GFC era, most of the world’s developed market central banks are on the path to policy normalisation. Critically, this is in the absence of a material pick-up in inflation and inflation expectations. In fact, both measures have actually fallen this calendar year as reflected in the chart below.
Inflation expectations have fallen recently
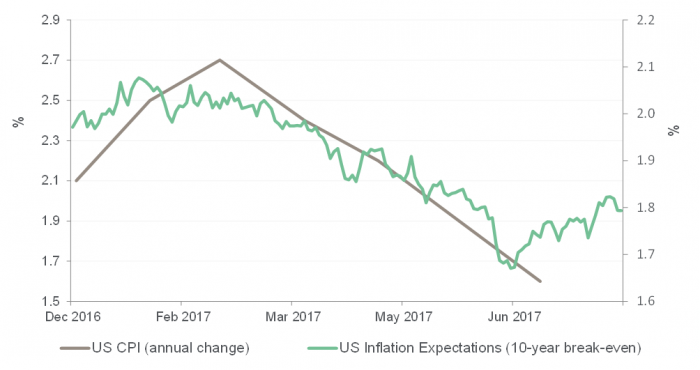
Source: Bloomberg
Historically, such declines in inflation expectations have been a negative for credit. Inflation expectations provide a gauge of sentiment towards future economic growth, which helps drive company revenues and debt servicing. It is important to make a distinction between debt in the investment grade camp (BBB or above) and junk bonds (BB or below), also known as high yield. It is the latter camp that is the most sensitive to a shift in the economic landscape. For example, the spread between the difference in yield on junk and investment grade typically widens when inflation expectations fall i.e. junk bonds underperform.
Contraction in high yield spreads versus inflation
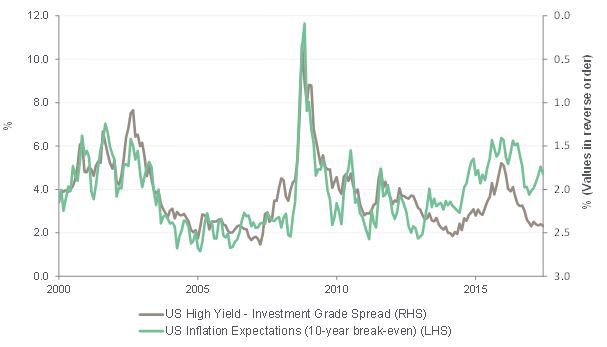
Source: Bloomberg
Risks vary considerably within each credit rung of the junk bond category. While many credit investors turn to this area in an attempt to boost yields, there are varying degrees of risks that do not necessarily compensate the investor with a higher return. For example, in the CCC rating category, the extra yield declines considerably as debt increases. On average, a company with three times leverage only offers an extra 10 basis points above a company with two times leverage. Further, the ability of CCC issuers to service their debt would be severely impeded if rates rose just 1%, to the extent that the interest payments would need to be funded by issuing further debt.
Structural change leads to risks at sector level
There are also varying vulnerabilities at the sector level due to ongoing structural industry changes. These shifts cannot be weathered as easily by the high yield space when compared with their investment grade counterparts, given the former lacks the same financial flexibility.
Delving deeper, while the energy sector faces challenges from weaker oil prices, the telecommunications and consumer spaces look increasingly concerning as they endure significant drops in the price of their services. The Wireless Services Price Index has fallen 11% in the six months to the end of June 2017. While the reaction has been relatively muted in high yield credit so far, the negative impact has clearly hit share prices.
High yield telecommunications vulnerabilities increase as service prices plunge
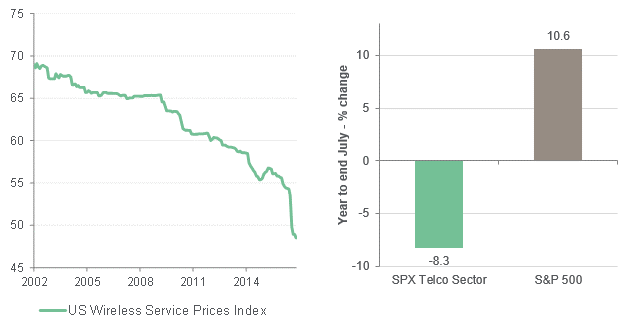
Source: Bloomberg
The consumer-orientated areas are also a worry as supermarkets and food have joined the longer-term weakness in broader retail on the back of the Amazon-Wholefoods announcement.
High yield (junk) bonds to underperform
With these factors in mind, we believe the high yield credit area is much more vulnerable than its investment grade counterpart. Benefitting from the underperformance of junk bonds is achieved through buying protection on high yield indices and selling protection on safer investment grade credit. By selling protection on investment grade, the cost of our high yield trade is reduced. In turn, the trade performs well if we see a widening of high yield spreads versus investment grade. This is a relatively defensive approach that aims to protect portfolios, as well as offering a more active alternative that can still deliver returns when more conservative credit outperforms.
Within yield-focused funds, we advocate for a more diversified approach to generating regular income by looking beyond credit markets by exposure to Australian shares that are generating consistent dividends. The Australian share market has established a reliable track record of delivering dividend yields of around 4% since 1982 and presents a suitable complement to a portfolio of high grade credit and corporate debt. With this approach investors can mitigate the exposure to risks that are gathering steam in parts of the credit spectrum.
Amy Xie Patrick is Portfolio Manager, Income & Fixed Interest at BT Investment Management. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.