Australians living on modest budgets, that is, those living close to or at pension level, are suffering the greatest additional cost imposts in retirement, according to new figures released by the Association of Superannuation Funds (ASFA). The calculations distinguish between 'modest' and 'comfortable' living, with the comfortable standard budget affording a much more dignified existence for Australian retirees.
ASFA Retirement Standard (RS) June 2017 quarter figures show couples aged around 65 living a comfortable retirement need to spend $60,063 per year and singles $43,695, up 0.2% on the previous quarter. The modest retirement budget has much to be modest about and is at near pension level subsistence, with singles needing to spend $24,270 and couples $34,911.
Modest retirement level suffers higher increase in costs
The annual increase in living costs at the modest level was in each case higher than at the comfortable level, reflecting the greater relative importance of electricity, health care and council and water rates in the modest budgets. The annual increase was 1.5% for comfortable and 2.1% for modest. These compare to 1.9% for the general Consumer Price Index (CPI).
The cost of retirement over the most recent quarter only increased by a relatively small amount, but many retirees are still finding it difficult to achieve a comfortable standard of living. Too many people are living without enough super, especially women. Australian retirees living at the basic level are doing it tough meeting costs of living. Financial support and literacy are part of the solution and super funds across the country can help members sort out their retirement living planning.
People need to be retirement-ready by saving for the sort of life they want to live. The magic of compound interest and tax savings in super can help lift living experiences in later life. Retirees now and in the future need super to increase and be safeguarded.
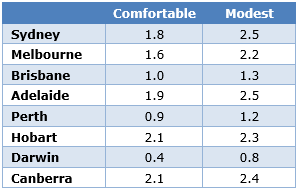
Living costs for retirees by capital city
Cost increases for retirees were highest in Sydney, Adelaide, Hobart and Canberra, while Darwin, Perth and Brisbane had the lowest average overall price increases.
In Sydney, a 3.8% increase in food costs, a 12.5% increase in electricity costs and a 5.1% increase in health costs were higher than average increases in the retirement budgets.
Annual increase in retiree living costs by capital city
Updated retirement standard costs
While seasonal fruit and domestic holidays were more affordable, critical costs of power, health care and rates and water bills continue to be a big cost issue for many retirees.
The most significant price increases in the June 2017 quarter contributing to increases in annual budgets for retirees were for medical and hospital services (4.1%) reflecting the annual increase in private health insurance premiums on 1 April. The most significant offsetting price falls were for domestic holiday travel and accommodation (-3.2%), automotive fuel (-2.5%) and fruit (-4.4%).
Fluctuations in world oil prices continue to influence domestic fuel prices. During the June quarter, automotive fuel prices fell in April (-0.8%), rose in May (+0.2%) and fell in June (-0.6%). Overall, food prices fell 0.2% in the March quarter. Clothing and footwear prices fell 0.3% as a result of sustained periods of specials.
Budgets for various households and living standards for those aged around 65
(June quarter 2017, national)
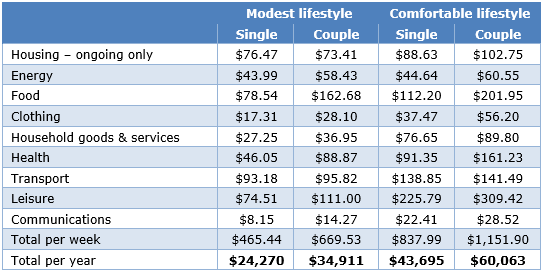
The figures in each case assume that the retiree/s own their own home and relate to expenditure by the household. This can be greater than household income after income tax where there is a drawdown on capital over the period of retirement. Single calculations are based on female figures. All calculations are weekly, unless otherwise stated.
The difference in enjoyment of retirement years is stark between modest and comfortable (and both sets of numbers assume the retirees own their own home). The most striking difference is the amount available for leisure activities and health. Superannuation should be taken more seriously by those who seek a comfortable retirement. Inflation may seem to have stabilised, but costs are increasing for retirees on smaller budgets especially as the essentials become more expensive.
Dr Martin Fahy is Chief Executive Officer at the Australian Superannuation Funds Association. Costs and summary figures can be accessed via the ASFA website. The ASFA Retirement Standard Calculator can be used to obtain a breakdown of the Retirement Standard budgets for each state. Australians can find out more about superannuation on the Super Guru website.