We have all borrowed to fund large purchases, and, sometimes, not so large. We are told that debt is bad. We try and pay back our loans and credit cards as quickly as possible. But not all debt should be considered bad. With careful planning, debt has the potential to be ‘good’.
In Australia, investors who borrow to buy property benefit from a tax regime that allows them to reduce their taxable income by losses they incur from interest payments and other investment costs for the property they have borrowed to invest in. This tax benefit has been in the news recently, as it always seems to be following a change to tax laws or whenever there is an election.
Like these property investors, Australian equity investors can also borrow to invest. This gearing combines the investors’ funds with borrowed funds making the amount available for investing larger, so thereby magnifying returns (in both directions). Gearing is not suitable for everyone, and we recommend you speak with your financial adviser. Below we provide two potential benefits of gearing as well as introducing a simple and convenient way to gear Australian equities.
But first let’s understand gearing and its impact on an Australian equity portfolio.
The modelled table below illustrates how gearing can affect investment gains and losses in comparison to a fund that is not geared.
Table 1: Modelled performance of a geared and ungeared fund
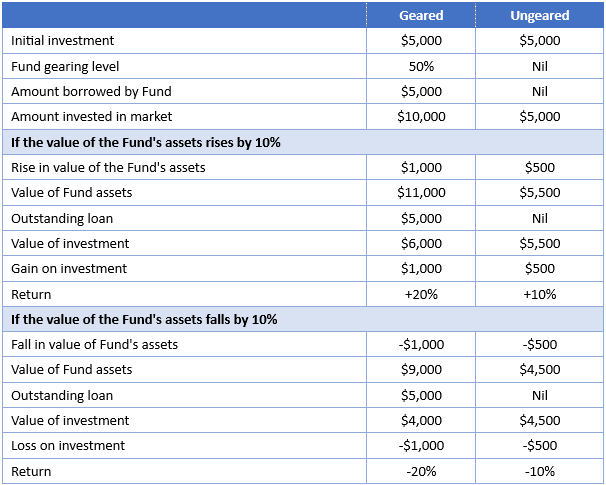
The table above considers gains and losses in the value of the underlying assets. It does not consider income or associated franking credits. The table assumes that the loan is not increased or decreased as the asset values change.
If you also consider income, you can see another potential benefit of gearing Australian equities. Because you have increased the amount invested, you also increase the amount of dividends you receive, thereby increasing your franking credits.
Table 2: Modelled dividends of a geared and ungeared fund
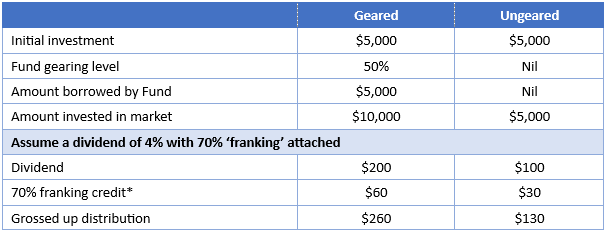
Now, if we consider the costs of borrowing, which the simple examples above do not, when gearing the dividends are used for interest payments associated with the costs of borrowing. It is important to note that for tax purposes these costs are deducted from the dividends received and do not impact the associated franking credits. The franking credits associated with the dividends received remain. In the example above, irrespective of the borrowing costs, the franking credit would still be $60. In the example above, if the borrowing costs were $150. The taxable dividend would be reduced to $50, but the franking credit would still be $60, making the grossed-up dividend $110.
These are simple examples. Gearing is complex, but you can see the potential benefits it can provide, albeit with additional costs and an increased risk of losing money.
We think there are two ways investors can use gearing and fund managers are helping all types of investors including SMSFs increase their exposure to Australian equities.
Potential benefit 1 – Wealth accumulation strategy
You can see above in Table 1 that gearing provides greater exposure to the share market and thus potential increased gains or losses compared to an ungeared portfolio. Additionally, geared Australian equity investors receive more associated franking credits than if they were not geared. There is no doubt gearing is riskier and has additional costs, so it is not for everyone, but with careful planning, it can be used as a part of an overall portfolio solution.
Potential benefit 2 - As a portfolio diversification tool
By gearing your Australian equities exposure, capital may be freed up to invest in other asset classes.
Think about an investor with $10,000. Putting all your eggs in one ‘asset’ basket may not be prudent risk management. Gearing allows investors to put a portion of their funds in one asset class, enhancing that exposure to the asset class, meaning they can use the leftover funds to invest in other asset classes.
In the table below, investor A retains their $10,000 allocation to Australian equities, but because they have geared, they have spare capital to allocate elsewhere.
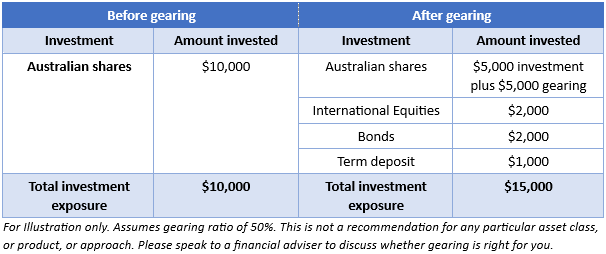
Gearing can be difficult, but some fund managers do the work for you, creating ‘geared’ versions of their Australian equity funds. These funds combine investors' funds and borrow funds to invest in an underlying Australian equities strategy.
Gearing Australian equities may not be suitable for all investors. While it can have benefits, including the tax benefits associated with franking credits, undertaking a gearing and the potential associated benefits will also depend upon your attitude to risks and your personal situation.
Recently, VanEck launched the VanEck Geared Australian Equal Weight Fund (Hedge Fund) (ASX: GMVW) on the ASX.
Russel Chesler is Head of Investments and Capital Markets at VanEck, a sponsor of Firstlinks. Russel is responsible for managing VanEck's Australian ETFs. This is general information only and does not take into account any person’s financial objectives, situation or needs. Any views expressed are opinions of the author at the time of writing and is not a recommendation to act.
For more articles and papers from VanEck, please click here.